Marketing91

E-Business: Definition, Meaning, Types and Components
July 20, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Business
E-business (short for electronic business) is the conduct of business processes on the internet. These e-business processes include buying and selling products, servicing customers, and collaborating with business partners. An E-business can be a company that sells products and services online, or it can be a more traditional brick-and-mortar business that uses the internet to enhance its offline activities.
For example, a brick-and-mortar business might use the internet for e-commerce (selling products online), e-marketing (promoting its products and services online), or for e-service (providing customer service or support online).
Table of Contents
What is E-Business?
Definition: E-Business is any form of commercial or business activity that takes place over the Internet It refers to the administration of any type of business that is done over the Internet, web, extranet, or intranet.
Online commercial transactions, such as buying and selling products or services via online commercial transactions, as well as providing customer or technical support utilizing the internet, are examples of eCommerce.
Meaning of E-Business
E-business (electronic business) can be defined as the conduct of business transactions via electronic means. E-business activities include buying and selling goods and services, conducting business operations, and managing enterprise resources. E-business transactions are conducted over the Internet, through email, online chat, or other electronic means.
The process of supply chain management is an important part of e-business. E-business enables businesses to manage their supply chains more effectively and efficiently. E-business also allows businesses to conduct business transactions more securely and with greater transparency.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are another important element of e-business. ERP systems help businesses to manage their resources more effectively and to automate different business processes. E-business also enables businesses to sell their services online. Online sales provide businesses with a wider reach and a larger customer base.
E-business Model Origins and Evolution

The development of the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) was one of the first building blocks in the evolution of online business. This method replaced physical document delivery with a digital transfer of information from one computer to another, requiring no human intervention.
Michael Aldrich is considered the developer of the predecessor to online shopping. In 1979, the entrepreneur connected a television set to a transaction processing computer with a telephone line and called it “teleshopping”, meaning shopping at distance. From the mid-nineties, major advancements were made in the commercial use of the Internet.
The concept of purchasing goods over the internet was first developed by Michael Aldrich, who is known as the “father of online shopping.” In 1979, Mr. Aldrich connected a television set to a transaction processing computer with a telephone line and called it “teleshopping,” which means shopping at a distance. Then the mid-nineties onwards period, significant advances took place in commercial Internet usage.
Amazon was founded in 1995 and is now the world’s largest online retailer, specializing in food, toys, apparel, electronics, and other items. Some of the other popular e-commerce marketplaces were eBay and Etsy.
In 1994, IBM launched an advertising campaign to promote itself as a leader in Internet-based company through the phrase “e-business.” This new brand was planned to cost $1 billion to market. Louis V. Gerstner, Jr., CEO at the time, was willing to spend $1 billion on marketing this new brand.
In October 1997, IBM began with an eight-page essay in The Wall Street Journal to promote the idea of “e-business” and advertise IBM’s competence in the new domain.
According to one source, IBM chose not to register the phrase “e-business” as a trademark in the hopes that other businesses would use it and create a new industry. This, however, proved to be too successful, and in 2000, IBM launched a $300 million campaign about its “e-business infrastructure” capabilities in order to set itself apart.
Since then, the words “e-business” and “e-commerce” have been used interchangeably in common parlance, having become a part of the vernacular. The US Department of Commerce claims that projected retail e-commerce sales in Q1 2020 are expected to account for almost 12% of total US retail sales, up from 4% in Q1 2010.
Market participants in Electronic Business
The key market participants in e-business can be broadly classified into the following categories:
- Online retailers
- Online service providers
- Online content providers
- Online financial service providers
Some of the major online retailers include Amazon, Flipkart, and Myntra. Major online service providers are Google, Microsoft, and Apple. Some of the online content providers are Netflix, Hotstar, and Amazon Prime Video. Lastly, some of the online financial service providers are PayPal, ICICI Bank, and HDFC Bank.
Different types of e-business models
1. business-to-consumer (b2c) model.
In this type of e-business model, businesses sell their products and services to consumers directly through an online channel. A few examples of businesses that use this model are Amazon, Walmart, and Target.
2. Business-to-business (B2B) model
In this type of e-business model, businesses sell their products and services to other businesses. A few examples of businesses in the USA that use this model are Alibaba, Global Sources, and eWorldTrade.
3. Consumer-to-business (C2B) model
In this type of e-business model, consumers sell their products and services to businesses. A few examples of businesses that use this model are eLance and oDesk.
4. Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) model
In this type of e-business model, consumers sell their products and services to other consumers. A few examples of businesses that use this model are eBay and Etsy.
Components of E-Business

1. E-Procurement
E-procurement is the use of electronic means to purchase goods and services. It generally involves the use of an online marketplace where suppliers can bid for contracts to supply goods or services. Online procurement platforms such as SAP Ariba and Coupa are used by businesses to streamline their procurement process.
2. Online Stores
An online store is a website that sells goods and services to consumers over the internet. Online stores can be either brick-and-mortar stores that have an online presence, or they can be e-commerce businesses that operate exclusively online. Some examples of online stores in the USA are Amazon, Walmart, and Target.
3. Online Marketplace
An online marketplace is a platform that allows buyers and sellers to trade goods and services online. Online marketplaces are similar to online stores, but they typically offer a wider range of goods and services. Some examples of online marketplaces in the USA are eBay and Etsy.
4. Online Communities
An online community is a platform where people with common interests can interact and connect. Online communities can be used for a variety of purposes, such as networking, marketing, and e-learning. Some examples of online communities in the USA are Facebook and LinkedIn.
5. Online Companies
An online company is a business that operates primarily or exclusively online. Online companies can be brick-and-mortar businesses that have an online presence, plus they can further be e-commerce businesses that operate exclusively online. Some examples of online companies in the USA are Amazon, Google, and Microsoft.
Advantages of e-business
There are several advantages of e-business, which include
1. Increased Reach
E-business allows businesses to reach a wider audience more easily and at a lower cost than traditional marketing methods.
2. Improved Customer Service
E-business provides customers with 24/7 access to information about products and services, which can improve customer service.
3. Increased Efficiency
E-business can help businesses to automate processes and reduce the need for paper documents. This can lead to increased efficiency and cost savings.
4. Improved Communication
E-business provides a variety of communication tools that can improve communication between businesses and their customers.
5. Increased Sales
E-business can lead to increased sales as businesses can reach a wider audience more easily.
Disadvantages of e-business
Despite the many advantages of e-business, there are also some disadvantages, which include:
1. Security concerns
One of the main concerns with e-business is security. businesses need to ensure that their website and payment system are secure to avoid data breaches and fraud.
2. Dependence on technology
E-businesses can be disrupted by technical problems such as power outages, internet downtime, and server issues. This can lead to lost sales and decreased customer satisfaction.
3. Competitive pressure
E-businesses can create competitive pressure for businesses as they attempt to keep up with the latest technology trends.
4. High cost of entry
The high cost of setting up and maintaining an e-business can be a barrier for small businesses.
5. Limited customer interaction
E-business can limit customer interaction as customers may not be able to see or touch products before they purchase them. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
Order Fulfillment Process
A customer sees your ad and has questions about a product.
1. Sales Quote
The sales team provides the customer with a quote for the product.
2. Order Configuration
The customer configures their order on your website or in-store.
3. Order Booking
The customer places their order and pays for the product.
4. Order Confirmation
The customer receives an email or other type of notification confirming their order.
The customer’s credit card is charged for the product.
6. Order Planning
The order is planned and production begins.
7. Order Processing
The order is processed and ready for shipment.
8. Shipment
The product is shipped to the customer.
9. Delivery
The product is delivered to the customer.
10. Settlement
The order is settled and the customer is charged for any additional fees.
11. Returns
The customer returns the product if they are not satisfied.
Revenue Model

A revenue model is a plan for generating revenue. It is a structure that a business uses to generate income by selling products or services. There are several different types of revenue models, which include:
1. Advertising
The advertising model involves selling advertising space on a website or other online platform. This can be done through banner ads, text ads, or video ads.
2. Subscription
The subscription model involves charging customers a recurring fee for access to content or services. This can be done on a monthly or yearly basis.
3. Pay-per-click
The pay-per-click model involves charging businesses for each click on their ad. This is a common model used by search engines such as Google and Bing.
4. Pay-per-sale
The pay-per-sale model involves charging businesses a commission for each sale that is generated from their ad. This is a common model used by affiliate marketing programs.
5. Freemium
The freemium model offers a basic level of service for free, with additional features available for a fee. This model is common among online services such as email and cloud storage.
Customer Relationship Management in e-Business
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is a process that businesses use to manage their relationships with customers. It helps businesses to understand their customers better and to provide them with the best possible service. CRM can be used in e-business to help businesses:
1. Build customer loyalty
CRM enables businesses to build customer loyalty by providing them with the ability to track customer behavior and preferences. This information can be used to tailor services and offers to each individual customer.
2. Increase sales
CRM can help businesses to increase sales by providing them with the ability to upsell and cross-sell products and services.

3. Improve customer service
CRM lets businesses to improve customer service by providing them with the ability to track and resolve customer issues more effectively.
4. Reduce costs
CRM empowers businesses to reduce costs by automating tasks such as marketing and customer service.
5. Increase efficiency
CRM lets businesses to increase their efficiency by providing them with the ability to track and manage all their customer data in one place.
Critical Factors of E-Business Development
Several critical factors must be considered when developing an e-business. These include
1. Website design
The website must be designed in a way that is user-friendly and easy to navigate. It should also be optimized for search engines so that potential customers can easily find it.
2. Payment processing
The e-business must have a secure payment processing system in place so that customers can safely and easily make payments.
3. Shipping and fulfillment
The e-business must have a shipping and fulfillment system in place so that products can be delivered to customers in a timely and efficient manner.
4. Customer service
The e-business must have a customer service system in place so that customers can easily get help and support when they need it.
5. Marketing
The e-business must have a marketing plan in place so that potential customers can be made aware of the products and services offered.
6. Business model
The e-business must have a sustainable business model that will generate revenue and profit.
7. Competitive analysis
The e-business must understand its competitors and what they are offering so that it can position itself in the market accordingly.
8. Regulatory compliance
The e-business must comply with all relevant laws and regulations.
9. Scalability
The e-business must be able to scale up or down as needed so that it can accommodate changes in demand.
10. Security
The e-business must have a security system in place to protect customer data and transactions.
Product Inquiry Fulfillment Process
E-commerce product inquiry fulfillment process eCommerce product involves the interactions between a customer and an organization during which the customer inquires about a product. There are four main steps in this process:
- The customer initiates an inquiry by visiting the organization’s website or contacting them through another channel such as phone or email.
- The organization receives the inquiry and gathers the necessary information to fulfill the request.
The organization responds to the customer with the requested information.
The customer receives the information and decides whether or not to purchase the product.
This process can be further broken down into specific tasks that need to be completed at each stage. These tasks are
1. Customer initiates inquiry
The customer visits the organization’s website or contacts them through another channel.
2. The organization receives inquiry
The organization’s CRM system captures the inquiry and creates a case for it.
3. The organization gathers information
The relevant staff gathers the necessary information to fulfill the inquiry.
4. The organization responds to a customer
5. the customer receives information, 6. customer purchases product.
If the customer decides to purchase the product, they complete the purchase through the organization’s e-commerce system.
7. Organization ships product
The organization ships the product to the customer.
8. The customer receives product
The customer receives the product and is satisfied with the purchase.
The E-Business Supply Chain
The e-business supply chain is the process that e-businesses use to source, produce, and deliver their products and services to customers. There are four main steps in this process:
1. Planning
It creates a plan for sourcing, producing, and delivering its products and services.
2. Sourcing
It sources the materials and components needed to produce its products and services.
3. Production
It produces its products and services.
4. Delivery
It delivers its products and services to customers.
E-business vs. E-commerce
E-business and electronic commerce are often used interchangeably, but there is a difference between the two concepts. E-business refers to the use of technology to enable businesses to operate more efficiently and effectively. E-commerce, on the other hand, refers to the use of technology to enable businesses to conduct transactions with customers.
E-business includes all aspects of a business, such as marketing, sales, customer service, and operations. E-commerce is limited to the transactions that take place between a business and its customers.
E-businesses use e-commerce to conduct transactions with their customers, but they also use e-business technologies to run their businesses more efficiently. For example, an e-business might use e-commerce to sell products online, but they might also use e-business technologies to automate their manufacturing process.
The term “e-business” is broader than the term “e-commerce” and includes all aspects of a business that are enabled by technology. E-commerce is a subset of e-business and refers specifically to the transactions that take place between a business and its customers.
Conclusion!
E-business has transformed the way businesses operate and conduct their selling activities.
E-business provides businesses with a number of advantages, such as increased efficiency, transparency, and security. E-business is here to stay and will continue to grow in popularity in the years to come.
What are your thoughts about the growth of e-business processes in comparison to traditional business processes? Share with us in the comments below.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Business
Related posts:
- Business Model: Meaning, Key Components and Types
- Cost Efficiency – Meaning, Components, Analysis and Steps
- Business Model Of Ikea and its Key Components
- Social Audit: Definition, Example, Importance, Objectives & Components
- Business Tax – Definition, Meaning, Types and Calculation
- Demand Management – Importance, Components and Benefits
- Cost Management: Important Components, Techniques, and the Steps
- Commerce – Definition, Meaning, Elements and Business Models
- Deep Pockets in Business: Definition and Meaning
- Doing Business As (DBA) – Definition, Meaning and Filing Process
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON:
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

What is an E-business model?
E- business models utilize advanced communication technologies and digital information to streamline various business processes online. These processes include customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management, payment processing, employee services and recruitment, and information sharing.
Table of Contents
Understanding E-business models
E- business models are used by companies to create value and become profitable online.
E- business models were developed in response to the increasing prevalence and technological capabilities of the internet.
Seemingly overnight, the internet removed geographical barriers and allowed businesses to operate wherever it was available.
Businesses can now enter new markets with ease and can be open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week for very little outlay.
This shift has resulted in four broad transformations:
- Domestic business to multinational business.
- An economy based on industrial manufacturing to one that characterized by knowledge-based services.
- Enterprise resource management to enterprise network management, and
- Manual, document-driven business processes to those that are electronic, automated, and paperless.
With e- business models developed to take advantage of these transformations, they have virtually rendered traditional models of organizational design obsolete.
The four components of E-business models
In general terms, E- business models should have four components:
Value proposition

Advances in IT and communications have enabled many E-businesses to create and deliver various forms of customer value.
For example, Dell uses the internet to sell customizable, direct-to-consumer PCs.
Other companies offer value in the form of reduced prices, fast delivery, or access to more diverse inventories.
Customer relationships
There is a limit to how much an offline business can interact with its customers.
For the e-business, however, customer relationships have benefitted from data collection, increased communication, order tracking, and personalized support.
Revenue streams

When clarifying revenue streams, it’s important to look beyond obvious sources of income such as eCommerce.
Other sources include advertising, licensing, sales commissions, syndication, subscription, and sponsorship.
Activities, capabilities, and resources
Like traditional business models, e- business models must define how the mission or vision of the company will be carried out and how much it will cost.
Some of these methods may be patented – such as Amazon’s 1-click checkout process – while others can be utilized for free.
E- business models also place more of an emphasis on less tangible resources such as intellectual property, software, customer data, and other IT infrastructure.
E-business model types
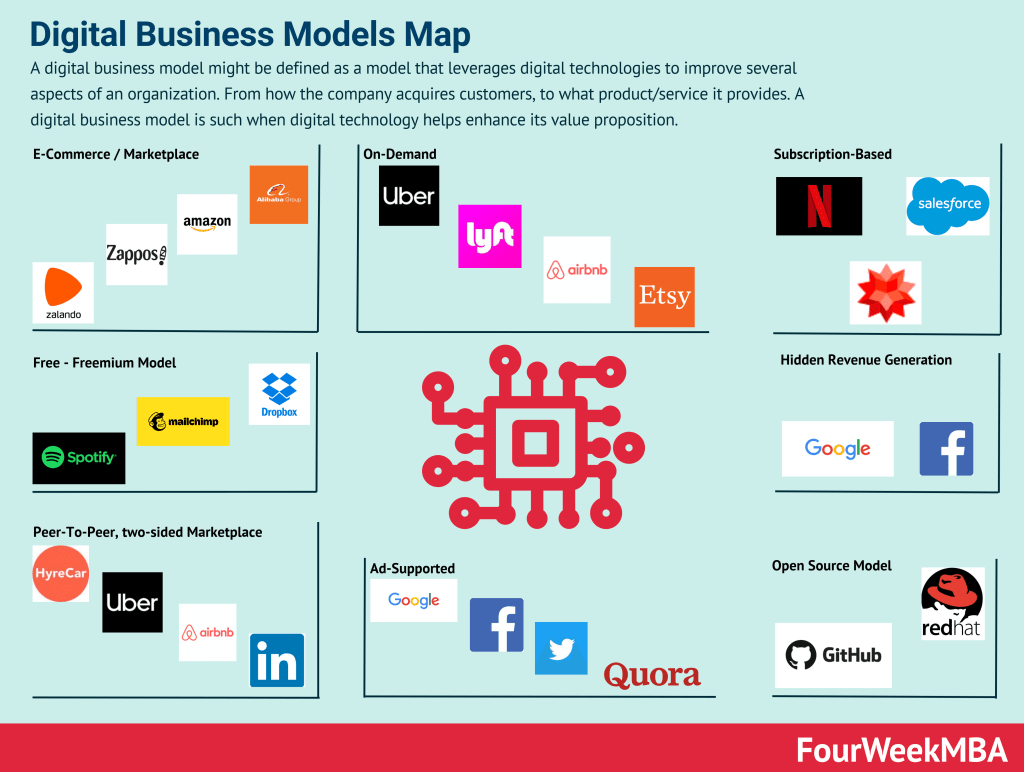
Let’s conclude by taking a look at some common e- business model types categorized according to functionality and transaction type.
Functionality
- Community model – a model used by Facebook, Wikipedia, and Flickr where communities share information, photos, or opinions. Revenue is earned via donations, advertising, and subscriptions.
- Advertising model – where businesses such as newspapers and journals provide content to readers and serve ads to generate revenue.
- Brokerage model – companies such as eBay and Amazon make money by bringing buyers and sellers together.
Transaction type
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) – where merchants sell products and services to buyers who then purchase them online.
- Business-to-business (B2B) – electronic transactions that occur between two businesses. Many SaaS companies follow this model.
- Consumer-to-business (C2B) – the reverse of B2C where consumers sell to businesses. A freelance graphic designer may sell a logo to a company, for example.
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) – this model is prevalent on online auction sites and other marketplaces for consumers.
- Business-to-government (B2G) – where government procures products, services, or information from external contractors. For example, governments that require city and open space maintenance will solicit these services from private companies.
Case Studies
Functionality-Based E-business Models:
- Facebook : A social media platform where users share information, photos, and opinions. Revenue is earned through advertising.
- Wikipedia : An online encyclopedia where the community collaboratively creates and edits articles. It relies on donations for funding.
- Google : Provides search engine services and earns revenue through targeted advertising.
- YouTube : A video-sharing platform that generates income through advertising and premium subscriptions.
- eBay : Connects buyers and sellers for online auctions and sales, earning fees from successful transactions.
- Amazon : Facilitates online shopping by bringing together sellers and buyers while selling its own products.
Transaction-Based E-business Models:
- Amazon : Sells a wide range of products directly to online consumers.
- Netflix : Offers streaming services directly to individual subscribers.
- Alibaba : Connects businesses with suppliers and manufacturers, facilitating wholesale transactions.
- Salesforce : Provides cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) solutions to businesses.
- Upwork : A platform where freelancers offer their services to businesses or individuals looking to hire.
- Fiverr : Allows individuals to offer various digital services and products to businesses.
- eBay : Enables individuals to sell products to other individuals through online auctions and fixed-price listings.
- Airbnb : Lets individuals rent their properties or accommodations to other individuals for short-term stays.
- FedBid : Connects businesses with government agencies for procurement and contracting.
- Grants.gov : Facilitates the application process for government grants and funding opportunities.
Key takeaways:
- E- business models are used by companies to create value and become profitable online. These models have taken advantage of the proliferation and technological advancement of the internet, rendering offline models almost obsolete.
- Most e- business models will incorporate four components: value proposition, customer relationships, revenue streams, and activities, capabilities, and resources.
- Various e- business model types have been developed over the years. In terms of functionality, some examples include the community model, advertising model, and brokerage model. The ever-evolving and diverse transaction types include B2C, B2B, C2B, C2C, and C2G.
Key Highlights:
- E-business Models Overview : E- business models utilize digital technologies and the internet to optimize various business processes, including customer relationship management, supply chain management, payment processing, employee services, and information sharing.
- Evolving Due to the Internet : The development of e- business models is a response to the internet’s transformative capabilities, which have removed geographical barriers and allowed businesses to operate globally 24/7 with minimal overhead.
- Four Transformations : E- business models have brought about four significant transformations: from domestic to multinational business, from industrial manufacturing to knowledge-based services, from enterprise resource management to enterprise network management, and from manual, document-driven processes to electronic, automated, and paperless operations.
- Value Proposition : Focused on delivering customer value through various means such as customization, reduced prices, fast delivery, and more.
- Customer Relationships : Enhanced through data collection, increased communication, order tracking, and personalized support.
- Revenue Streams : Diverse revenue sources beyond e-commerce, including advertising, licensing, sales commissions, syndication, subscription, and sponsorship.
- Activities, Capabilities, and Resources : Define how the company’s mission or vision will be executed, emphasizing intellectual property, software, customer data, and IT infrastructure.
- Community Model : Examples include Facebook, Wikipedia, and Flickr, with revenue from donations, advertising, and subscriptions.
- Advertising Model : Used by newspapers and journals, providing content to readers while generating revenue from ads.
- Brokerage Model : Companies like eBay and Amazon profit by connecting buyers and sellers.
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C) : Merchants sell products and services directly to online buyers.
- Business-to-Business (B2B) : Electronic transactions occur between two businesses, commonly seen in SaaS companies.
- Consumer-to-Business (C2B) : Consumers sell to businesses, such as freelance graphic designers offering services to companies.
- Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) : Found on online auction sites and marketplaces where consumers engage in transactions.
- Business-to-Government (B2G) : Governments procure products, services, or information from external contractors, such as city maintenance services.
Connected Business Model Types And Frameworks
What’s A Business Model

Business Model Innovation

Level of Digitalization

Digital Business Model
Tech Business Model

Platform Business Model

AI Business Model

Blockchain Business Model

Asymmetric Business Models

Attention Merchant Business Model

Open-Core Business Model

Cloud Business Models

Open Source Business Model

Freemium Business Model

Freeterprise Business Model

Marketplace Business Models

B2B vs B2C Business Model

B2B2C Business Model

D2C Business Model

C2C Business Model

Retail Business Model

Wholesale Business Model

Crowdsourcing Business Model

Franchising Business Model

Brokerage Business Model

Dropshipping Business Model

Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO