Write Better Essays: 7 Mistakes to Avoid

By Cari Bennette

Academic essays are an unavoidable part of the educational journey. Learning to write well may be one of the greatest skills you gain during your college years. Most students, however, will commit many errors before learning the art of academic essay writing.
While you can't avoid writing essays, you can avoid making some of these common mistakes:

Writing a Synopsis, Not An Analytical Essay
Not having a strong thesis statement, using too many quotes in an essay, making grammar, spelling and pronoun mistakes, not having a good bibliography, using resources that aren't credible, want to improve your essay writing skills.
The point of an essay is to create an argument and defend a thesis. If you're writing about a work of literature, some background to clarify the topic can be helpful. But the majority of your essay should involve your analysis based on credible research. Don't simply restate what happened in the book.
Coming up with a strong thesis statement is essential to writing a good essay. The thesis statement is the hook on which the rest of your essay hangs. It should state an opinion and be as specific as possible. Example weak thesis statement: The Great Gatsby is a great example of American Literature. Example strong thesis statement: The Great Gatsby captures the essence of America's Jazz Age in its decadence, materialism and ultimately, its tragic emptiness.
The essay is supposed to reflect your understanding of the topic and the research you've done to back up your argument. Overuse of quotes either from the work you're analyzing or from the research you've done undermines your authority on the topic. Quotes should be used sparingly and only when they drive home a point with an eloquence you can't match with your own words.
Defined as “the practice of taking someone else's work or ideas and passing them off as one's own,” plagiarism is a serious offense. Colleges and universities have strict policies against plagiarism and use various tools to check your work for plagiarised content. You won't get away with it, and sometimes it can even get you suspended. Professors can recognize if something sounds like a student wrote it or if it came from another source, so don't try to fool them.
There are two kinds of plagiarism:
- The first kind is directly taking the words from a source and using them in your paper without quoting or giving credit.
- The second kind is trickier and you should take special care to make sure you're not committing this kind of plagiarism. It consists of rewording an entire article or section of an article. In this case, instead of coming up with your own original ideas and analysis, you're just rewording someone else's ideas including the order in which they present those ideas.
Your essay should contain your own original thesis, analysis and ideas backed up by credible research from academic authorities.
Worried about plagiarism? ProWritingAid's plagiarism checker checks your work against over a billion web-pages, published works, and academic papers so you can be sure of its originality. Did you know that many of the free plagiarism checkers online sell your writing to other sources? With ProWritingAid, you can be certain that your original work is secure. Paying for this kind of service might feel like a lot, but trust me, it's worth it.
Okay, let's break these down:
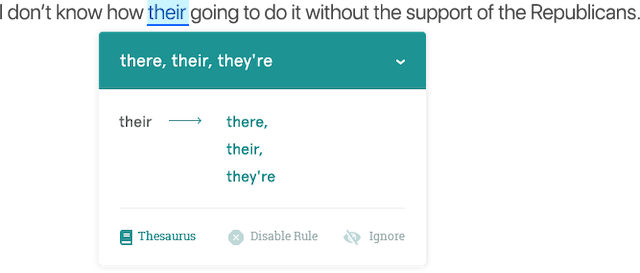
- Get your contractions right. You're = you are. Your = second person possessive. It's = it is. Its = third person possessive. They're = they are. Their =third person plural possessive.
- Make sure your subjects and verbs agree.
- Beware of incomplete sentences (there must be both a subject and a verb to be complete).
- Use your spell check.
- Essays should be written in the third person (he/she/it/they). Don't use the first or second person (I, you or we) in an essay.
- Follow proper formatting ( MLA formatting is a common example.
You can check for all of these errors using ProWritingAid. The Homonym report will highlight all of the words in your essay that sound the same as others but are spelled differently. This will help you avoid any 'its/it's or 'their/they're/there' mistakes.
The bibliography format for academic essays is usually the MLA style unless your professor specifically requests a different format. For a complete list of how to cite resources in MLA style, check out this site . Don't lose points over your bibliography. The hard part of your essay should be coming up with an original analysis of your topic. The bibliography is formulaic and easy to get right if you give it a little effort.
In the age of the Internet, it's easy to type in a keyword and find dozens of articles on it. But that doesn't mean all of those articles are credible. Make sure that the resources you use come from academic experts. For tips on how to find credible academic resources online, check out this site .
Avoiding these mistakes will improve your essay writing, so you can achieve higher quality and confidence in your academic writing. And it will make your professors happy, too.
Use ProWritingAid!
Are your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe your sentences are too long and your meaning is getting lost or you're using the same sentence starter over and over again.
ProWritingAid helps you catch these issues in your essay before you submit it.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Cari Bennette
Cari Bennette is an avid blogger and writer. She covers different aspects of writing and blogging in her articles and plans to try her hand in fiction writing.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Visit our Help Center or let's stay in touch via:
How to Write the Perfect Essay
06 Feb, 2024 | Blog Articles , English Language Articles , Get the Edge , Humanities Articles , Writing Articles

You can keep adding to this plan, crossing bits out and linking the different bubbles when you spot connections between them. Even though you won’t have time to make a detailed plan under exam conditions, it can be helpful to draft a brief one, including a few key words, so that you don’t panic and go off topic when writing your essay.
If you don’t like the mind map format, there are plenty of others to choose from: you could make a table, a flowchart, or simply a list of bullet points.
Discover More
Thanks for signing up, step 2: have a clear structure.
Think about this while you’re planning: your essay is like an argument or a speech. It needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question.
Start with the basics! It’s best to choose a few major points which will become your main paragraphs. Three main paragraphs is a good number for an exam essay, since you’ll be under time pressure.
If you agree with the question overall, it can be helpful to organise your points in the following pattern:
- YES (agreement with the question)
- AND (another YES point)
- BUT (disagreement or complication)
If you disagree with the question overall, try:
- AND (another BUT point)
For example, you could structure the Of Mice and Men sample question, “To what extent is Curley’s wife portrayed as a victim in Of Mice and Men ?”, as follows:
- YES (descriptions of her appearance)
- AND (other people’s attitudes towards her)
- BUT (her position as the only woman on the ranch gives her power as she uses her femininity to her advantage)
If you wanted to write a longer essay, you could include additional paragraphs under the YES/AND categories, perhaps discussing the ways in which Curley’s wife reveals her vulnerability and insecurities, and shares her dreams with the other characters. Alternatively, you could also lengthen your essay by including another BUT paragraph about her cruel and manipulative streak.
Of course, this is not necessarily the only right way to answer this essay question – as long as you back up your points with evidence from the text, you can take any standpoint that makes sense.

Step 3: Back up your points with well-analysed quotations
You wouldn’t write a scientific report without including evidence to support your findings, so why should it be any different with an essay? Even though you aren’t strictly required to substantiate every single point you make with a quotation, there’s no harm in trying.
A close reading of your quotations can enrich your appreciation of the question and will be sure to impress examiners. When selecting the best quotations to use in your essay, keep an eye out for specific literary techniques. For example, you could highlight Curley’s wife’s use of a rhetorical question when she says, a”n’ what am I doin’? Standin’ here talking to a bunch of bindle stiffs.” This might look like:
The rhetorical question “an’ what am I doin’?” signifies that Curley’s wife is very insecure; she seems to be questioning her own life choices. Moreover, she does not expect anyone to respond to her question, highlighting her loneliness and isolation on the ranch.
Other literary techniques to look out for include:
- Tricolon – a group of three words or phrases placed close together for emphasis
- Tautology – using different words that mean the same thing: e.g. “frightening” and “terrifying”
- Parallelism – ABAB structure, often signifying movement from one concept to another
- Chiasmus – ABBA structure, drawing attention to a phrase
- Polysyndeton – many conjunctions in a sentence
- Asyndeton – lack of conjunctions, which can speed up the pace of a sentence
- Polyptoton – using the same word in different forms for emphasis: e.g. “done” and “doing”
- Alliteration – repetition of the same sound, including assonance (similar vowel sounds), plosive alliteration (“b”, “d” and “p” sounds) and sibilance (“s” sounds)
- Anaphora – repetition of words, often used to emphasise a particular point
Don’t worry if you can’t locate all of these literary devices in the work you’re analysing. You can also discuss more obvious techniques, like metaphor, simile and onomatopoeia. It’s not a problem if you can’t remember all the long names; it’s far more important to be able to confidently explain the effects of each technique and highlight its relevance to the question.


Step 4: Be creative and original throughout
Anyone can write an essay using the tips above, but the thing that really makes it “perfect” is your own unique take on the topic. If you’ve noticed something intriguing or unusual in your reading, point it out – if you find it interesting, chances are the examiner will too!
Creative writing and essay writing are more closely linked than you might imagine. Keep the idea that you’re writing a speech or argument in mind, and you’re guaranteed to grab your reader’s attention.
It’s important to set out your line of argument in your introduction, introducing your main points and the general direction your essay will take, but don’t forget to keep something back for the conclusion, too. Yes, you need to summarise your main points, but if you’re just repeating the things you said in your introduction, the body of the essay is rendered pointless.
Think of your conclusion as the climax of your speech, the bit everything else has been leading up to, rather than the boring plenary at the end of the interesting stuff.
To return to Of Mice and Men once more, here’s an example of the ideal difference between an introduction and a conclusion:
Introduction
In John Steinbeck’s Of Mice and Men , Curley’s wife is portrayed as an ambiguous character. She could be viewed either as a cruel, seductive temptress or a lonely woman who is a victim of her society’s attitudes. Though she does seem to wield a form of sexual power, it is clear that Curley’s wife is largely a victim. This interpretation is supported by Steinbeck’s description of her appearance, other people’s attitudes, her dreams, and her evident loneliness and insecurity.
Overall, it is clear that Curley’s wife is a victim and is portrayed as such throughout the novel in the descriptions of her appearance, her dreams, other people’s judgemental attitudes, and her loneliness and insecurities. However, a character who was a victim and nothing else would be one-dimensional and Curley’s wife is not. Although she suffers in many ways, she is shown to assert herself through the manipulation of her femininity – a small rebellion against the victimisation she experiences.
Both refer back consistently to the question and summarise the essay’s main points. However, the conclusion adds something new which has been established in the main body of the essay and complicates the simple summary which is found in the introduction.

Hannah is an undergraduate English student at Somerville College, University of Oxford, and has a particular interest in postcolonial literature and the Gothic. She thinks literature is a crucial way of developing empathy and learning about the wider world. When she isn’t writing about 17th-century court masques, she enjoys acting, travelling and creative writing.
Recommended articles
Best Universities to Study Medicine in the World
A degree in Medicine spans many years, so it’s important to make a good choice when committing yourself to your studies. This guide is designed to help you figure out where you'd like to study and practise medicine. For those interested in getting a head start, the...

What Is A Year Abroad?
One of the great opportunities offered to UK university students is taking a year abroad. But what does this involve? Who can do it? What are some of the pros and cons? In our year abroad guide, we’ll explain some of the things to bear in mind when considering this...

The Ultimate Guide To Summer Internships
Are you eager to make the most of your summer break and jumpstart your career? There are so many productive things students can do in the summer or with their school holidays, and an internship is one of the most valuable! A summer internship could be the perfect...
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don’t need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary. Or it may come in the form of a sentence that brings your readers back to your thesis or main idea and reminds your readers where you began and how far you have traveled.
So, for example, in a paper about the relationship between ADHD and rejection sensitivity, Vanessa Roser begins by introducing readers to the fact that researchers have studied the relationship between the two conditions and then provides her explanation of that relationship. Here’s her thesis: “While socialization may indeed be an important factor in RS, I argue that individuals with ADHD may also possess a neurological predisposition to RS that is exacerbated by the differing executive and emotional regulation characteristic of ADHD.”
In her final paragraph, Roser reminds us of where she started by echoing her thesis: “This literature demonstrates that, as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Highlight the “so what”
At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what’s at stake—why they should care about the argument you’re making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put those stakes into a new or broader context.
In the conclusion to her paper about ADHD and RS, Roser echoes the stakes she established in her introduction—that research into connections between ADHD and RS has led to contradictory results, raising questions about the “behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
She writes, “as with many other conditions, ADHD and RS share a delicately intertwined pattern of neurological similarities that is rooted in the innate biology of an individual’s mind, a connection that cannot be explained in full by the behavioral mediation hypothesis.”
Leave your readers with the “now what”
After the “what” and the “so what,” you should leave your reader with some final thoughts. If you have written a strong introduction, your readers will know why you have been arguing what you have been arguing—and why they should care. And if you’ve made a good case for your thesis, then your readers should be in a position to see things in a new way, understand new questions, or be ready for something that they weren’t ready for before they read your paper.
In her conclusion, Roser offers two “now what” statements. First, she explains that it is important to recognize that the flawed behavioral mediation hypothesis “seems to place a degree of fault on the individual. It implies that individuals with ADHD must have elicited such frequent or intense rejection by virtue of their inadequate social skills, erasing the possibility that they may simply possess a natural sensitivity to emotion.” She then highlights the broader implications for treatment of people with ADHD, noting that recognizing the actual connection between rejection sensitivity and ADHD “has profound implications for understanding how individuals with ADHD might best be treated in educational settings, by counselors, family, peers, or even society as a whole.”
To find your own “now what” for your essay’s conclusion, try asking yourself these questions:
- What can my readers now understand, see in a new light, or grapple with that they would not have understood in the same way before reading my paper? Are we a step closer to understanding a larger phenomenon or to understanding why what was at stake is so important?
- What questions can I now raise that would not have made sense at the beginning of my paper? Questions for further research? Other ways that this topic could be approached?
- Are there other applications for my research? Could my questions be asked about different data in a different context? Could I use my methods to answer a different question?
- What action should be taken in light of this argument? What action do I predict will be taken or could lead to a solution?
- What larger context might my argument be a part of?
What to avoid in your conclusion
- a complete restatement of all that you have said in your paper.
- a substantial counterargument that you do not have space to refute; you should introduce counterarguments before your conclusion.
- an apology for what you have not said. If you need to explain the scope of your paper, you should do this sooner—but don’t apologize for what you have not discussed in your paper.
- fake transitions like “in conclusion” that are followed by sentences that aren’t actually conclusions. (“In conclusion, I have now demonstrated that my thesis is correct.”)
- picture_as_pdf Conclusions

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Contents: Writing a Synopsis, Not An Analytical Essay. Not Having a Strong Thesis Statement. Using Too Many Quotes in An Essay. Plagiarism. Making Grammar, Spelling and Pronoun Mistakes. Not Having a Good Bibliography. Using Resources That Aren't Credible. Want to improve your essay writing skills? Writing a Synopsis, Not An Analytical Essay.
Crucially, a good essay doesn’t progress through plot summary—resist shadowing the novel, story, or poem’s chronology in your own essay. A fluid, logical structure. An essay should have an introductory section during which the essay's central idea or argument is hinted at.
But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and organize your text logically.
Published on February 9, 2015 by Shane Bryson. Revised on July 23, 2023 by Shona McCombes. This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction, focused paragraphs, clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why. The best thesis statements are: Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
Learn how to build a rock-solid essay with our tips on the main parts of an essay, how many paragraphs should be in an essay, and essay structure examples.
Basics. All essays should be typed, double-spaced; pages should be numbered. Essays should be properly and carefully proof-read. Essays must adhere to standard grammatical, lin-guistic, and syntactical usage. Citation and referencing.
• suggests an answer complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of discussion. If the question is too vague, it won't suggest a line of argument. The question should elicit reflection and argument rather than summary or description. • can be explored using the sources you have available for the assignment,
How do you write the perfect essay? We take you through the process of writing a compelling essay using Of Mice and Men as an example.
In a short paper—even a research paper—you don’t need to provide an exhaustive summary as part of your conclusion. But you do need to make some kind of transition between your final body paragraph and your concluding paragraph. This may come in the form of a few sentences of summary.