- How it works

"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

Glossary in a Dissertation – A Comprehensive Guide
Published by Owen Ingram at August 26th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
A list of glossary contains all those terms used in your dissertation, but the meanings of which may not be evident to the readers. Here is all you need to know about the glossary in a dissertation.
Basically, any term you use in your dissertation that you know, without a doubt, is not going to be common knowledge to readers outside of your field, is included in a list called glossary. And since every field has its unique, technical jargon, a glossary list can contain many terms some readers might not have even heard of before.
A typical glossary in a dissertation may look something like this:

Do you Even Need Glossary in your Dissertation to Begin with?
You may or may not be required to have a separate list of glossaries in your dissertation . The decision whether to have a list of glossaries in a dissertation depends on whether it will improve the readability of your paper.
For example , if you are writing a dissertation for an engineering degree and have used several technical terms that readers—especially laymen—may not be familiar with, \ it is advised to add a glossary in a dissertation.
Listing Terms in a Glossary
A recommended practice of adding a glossary in a dissertation is to sort the terms alphabetically and provide a definition or explanations for each of those terms. Having the terms listed in alphabetical order will help the readers to easily locate the information they are interested in.
Location of a Glossary List in a Dissertation
The glossary list is generally placed at the beginning of the dissertation paper, just after the list of tables and figures or the list of abbreviations. However, if your paper does not have a list of abbreviations or a list of tables and figures, you can place the glossary right after the table of contents .
This gives readers the opportunity to understand the meanings of key terms they are not familiar with even before they start to read the main content of the paper.
However, if you haven’t used a lot of technical terms in your dissertation, you can choose to provide an explanation and meanings of the few terms that you have used in the form of footnotes .
Difference Between Abbreviations and Glossary
It is important not to confuse the glossary in the dissertation with the abbreviations, which are put in the list of abbreviations.
A list of abbreviations contains all the terms that have abbreviations. For instance, if you have used terms like NASA , UNICEF , UNESCO , UN , NIH , etc., such terms along with what they stand for will come under the list of abbreviations.
Note, however, that only their full forms, and not their meanings, are mentioned in that list. That is what’s mentioned in a glossary list, though: meanings. Definitions of terms, terms that were used in the dissertation. The terms themselves aren’t abbreviation.
For instance, in a linguistics’ dissertation, you might end up creating a glossary list containing terms like phenomenology, code-switching, diglossia, etc. Notice how these are complete terms , not abbreviations.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across various disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Example of a Glossary in Dissertation
If you haven’t created a list of glossaries before then you will find the below example of a glossary in a dissertation particularly useful:
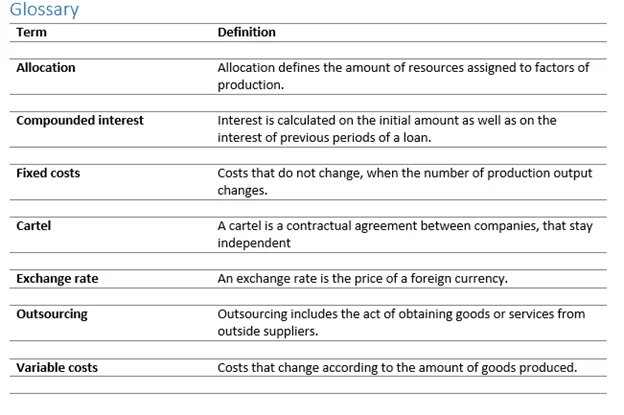
Other Lists you can have in your Dissertation
You might also want to have a list of tables and figures as well as a list of abbreviations in your dissertation particularly if you are writing a master’s or PhD dissertation. However, make sure to keep the following order:
- Table of contents
- Lists of figures and tables
- List of abbreviations
How Does ResearchProspect can Help
ResearchProspect is UK’s leading dissertation writing service. Our UK-qualified writers are hired following a strict recruitment process which helps us make sure that each of our writers is capable of delivering the quality guarantees we promise to our clients. Whether you need help with the whole dissertation or just a part of it , ResearchProspect can help.
Learn More About Our Dissertation Services
Place Your Order For Dissertation or Individual Chapters Now
FAQs About Glossary in a Dissertation
What is a glossary.
It’s a list of special terms—single words, phrases, etc.—that are not commonly known to the ‘average’ reader or to a reader who isn’t an expert in that field.
What is included in a glossary?
Ideally, words are included in a glossary. However, in some cases—depending on the topic— abbreviations , phrases etc. might also be mentioned within the list of glossary in a dissertation. Sometimes, it might also include a brief definition of how to pronounce a certain word/phrase.
What is the best way to create a glossary?
Keep in mind two things while creating a glossary list: keep the language of the definition simple so that every kind of reader can understand it. That’s why a glossary is given, to begin with, to simplify technical jargon and inform laymen. Secondly, arrange the terms inside it alphabetically.
How many times can I include the same term in a glossary list?
No matter how many times a word or a phrase appears in your dissertation , include it and define it only once in your glossary. There should be no duplicate entries in a glossary list.
You May Also Like
Wish that you had more time to write your dissertation paper? Here are some practical tips for you to learn “How to get dissertation deadline extension”.
Learn how to write a good declaration page for your thesis with the help of our step-by-step comprehensive guide. Read now.
Dissertation conclusion is perhaps the most underrated part of a dissertation or thesis paper. Learn how to write a dissertation conclusion.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
Glossary in Dissertation
Discover how to create an effective glossary in your dissertation. Learn tips & examples to help you define key terms clearly and concisely.
Creating a glossary in a dissertation is an essential step to ensure clarity and comprehensibility for readers who may not be familiar with specialized terminology. Glossary entries and definitions are considered part of shared common knowledge and may not necessarily have to be cited, but it is still important to cite sources to avoid accidental plagiarism. A well-crafted glossary provides concise definitions of key terms and concepts, aiding in the reader’s understanding and enhancing the overall coherence of the document. In this guide, we will delve into the importance of including a glossary in a dissertation, how to structure it effectively, and best practices for curating entries that are both informative and accessible. Let’s explore how to make your dissertation more reader-friendly with a comprehensive glossary.
Importance of a Glossary
Clarifying technical terms.
A glossary in a dissertation plays a pivotal role in clarifying key terms that may be unfamiliar to the reader. Academic writing often involves the usage of specialized language and jargon that can be daunting for those not well-versed in the subject matter. Citing the definition in-text can provide a more explicit elaboration of a given point within the document. By providing clear and concise definitions, a glossary ensures that readers can grasp the nuances of your discussion without confusion. This not only aids in better comprehension but also makes your research more accessible to a broader audience. Moreover, it demonstrates your meticulousness and attention to detail, reinforcing the credibility of your work. Including a glossary is particularly important in interdisciplinary research, where terms may have different meanings across fields. Thus, a well-structured glossary is essential in enhancing the readability and overall coherence of your dissertation.

Enhancing Readability
A glossary in a dissertation significantly enhances the readability of your document. A glossary list plays a crucial role in providing explanations and meanings of technical terms used in the paper. When readers encounter unfamiliar terms, they can quickly refer to the glossary for precise definitions, avoiding the need to search for explanations elsewhere. This uninterrupted flow of reading helps maintain their focus and engagement with your content. Additionally, a glossary can prevent misinterpretations by providing authoritative definitions of complex terms. By offering these clarifications, you ensure that your arguments and findings are accurately understood, thereby strengthening your overall narrative. Moreover, a glossary serves as a valuable reference tool, particularly in lengthy dissertations, where readers might forget the meanings of earlier introduced terms. In essence, a well-crafted glossary enhances the user experience by making your dissertation more approachable and easier to navigate, thereby broadening its appeal and impact.
Supporting Non-Experts
A glossary in a dissertation is especially beneficial for non-experts who may not be familiar with the specialized terminology of your field. Academic dissertations often attract a diverse readership, including peers from other disciplines, policymakers, and even the general public. If the dissertation does not contain a lot of technical terms, the glossary can be replaced by footnotes to provide explanations and meanings of the few terms used. Providing a glossary ensures that these readers can fully engage with your work without being hindered by unfamiliar terms. By translating complex jargon into accessible language, you make your research more inclusive and widely understood. This not only broadens the impact of your findings but also fosters interdisciplinary dialogue. Moreover, supporting non-experts through a glossary demonstrates a commitment to clear and effective communication, which is a hallmark of good scholarship. In summary, a well-curated glossary makes your dissertation approachable to a wider audience, enhancing its relevance and reach.
Creating Your Glossary
Selecting relevant terms.
When creating a glossary in your dissertation, selecting relevant terms is a crucial step. Begin by identifying the specialized terminology and jargon that are central to your research. An in-depth exploration or analysis of specific components or aspects of your dissertation can help in selecting the most relevant terms for the glossary. These could be technical terms, acronyms, or concepts that are specific to your field of study. It is important to consider the perspective of your readers—both experts and non-experts—when deciding which terms to include. Ask yourself whether a term is likely to be unfamiliar or ambiguous to someone outside your immediate research community. Additionally, review your dissertation to spot any terms that recur frequently and are integral to understanding your arguments. By focusing on the most pertinent terms, you ensure that your glossary is both comprehensive and useful. Keep in mind that the goal is to enhance clarity and accessibility, so avoid including overly basic terms that your audience is likely to know.
Defining with Precision
Defining terms with precision is a key aspect of creating an effective glossary in your dissertation. Adding page numbers to the terms in a glossary allows readers to easily find where the terms are used in the text. Each definition should be clear, concise, and accurate, providing the reader with a quick yet thorough understanding of the term. Avoid using overly complex language or technical jargon within the definitions themselves. Instead, aim for simplicity and clarity, ensuring that even readers with limited background knowledge can grasp the meaning. It is also important to be consistent in your definitions. If a term has multiple meanings, specify which one is being used in the context of your research. Additionally, providing examples or context can further clarify the term’s application and relevance. Remember, the purpose of a glossary is to aid comprehension and enhance the reader’s experience. Therefore, precision in your definitions is paramount, as it eliminates ambiguity and ensures that your findings and arguments are correctly interpreted.

Organizing in Alphabetical Order
Organizing your glossary alphabetically is the most straightforward and user-friendly method. An alphabetical arrangement allows readers to quickly locate specific terms without having to sift through the entire list. Additionally, organizing abbreviations in a glossary as a separate list from the main definitions makes it easier for the reader to navigate and understand the content. This structure mirrors that of dictionaries, making it intuitive for users who are accustomed to this format. Begin by listing all the terms you plan to include and then sort them alphabetically. Ensure that each entry is clearly distinguished, possibly using bold or italics for the terms themselves. Consistency in formatting is key to maintaining a clean and professional appearance. Additionally, if you have a large number of terms, consider breaking them into sections based on the initial letter for easier navigation. An alphabetically organized glossary not only enhances usability but also reflects a methodical and organized approach, further reinforcing the credibility and thoroughness of your dissertation.

Placement in Dissertation Paper
Introduction section.
Placing your glossary in the introduction section of your dissertation can be highly effective. By situating it early in your document, you provide readers with the necessary tools to understand specialized terms right from the start. This preemptive approach ensures that readers are not confused by unfamiliar terminology as they delve into your research. It also sets the stage for a smoother reading experience, allowing them to focus on the content without frequent interruptions to seek definitions. Including the glossary in the introduction serves as a helpful guide, particularly for non-experts or those new to your field. Additionally, it demonstrates your consideration for the reader’s experience, showcasing your commitment to clear and accessible communication. Overall, positioning the glossary in the introduction is a strategic choice that enhances the readability and comprehensibility of your dissertation.
Including your glossary in the appendices is another common and effective placement option in a dissertation. This approach keeps the main text of your dissertation uncluttered, allowing readers to focus on your core arguments and findings without frequent breaks to consult definitions. By placing the glossary in the appendices, you provide a comprehensive reference section that readers can easily access as needed. This is particularly useful for lengthy dissertations with extensive specialized terminology. It also allows for a more detailed and expansive glossary, as space constraints are less of an issue in the appendices. However, it is important to clearly indicate the existence and location of the glossary early in your dissertation, such as in the table of contents or through a brief mention in the introduction. This ensures that readers are aware of this valuable resource and can utilize it effectively throughout their reading.
Footnotes and Endnotes
Using footnotes and endnotes for glossary terms is a flexible option for dissertations. This method allows you to provide definitions directly where the terms appear, offering immediate clarification without requiring the reader to navigate to a separate section. Footnotes are typically placed at the bottom of the page, making them easily accessible, while endnotes are compiled at the end of each chapter or the entire document. Both methods ensure that readers have instant access to definitions, enhancing the flow and comprehension of your text. However, this approach can become cumbersome if your dissertation contains a large number of specialized terms, potentially cluttering the pages with excessive notes. Therefore, it is best suited for dissertations with fewer glossary entries. Regardless of the method, the key is to maintain consistency and ensure that all terms are clearly and accurately defined, supporting the reader’s understanding of your work.
Best Practices
Consistency in definitions.
Maintaining consistency in your definitions is crucial for an effective glossary in your dissertation. Consistency ensures that each term is clearly understood in the same way throughout the document, preventing confusion and misinterpretation. When defining terms, use a standard format and structure to provide a uniform reading experience. For example, always include the term, followed by a concise definition and, if necessary, an example or context. Avoid using different definitions for the same term in various parts of your dissertation, as this can lead to ambiguity. Additionally, if you refer to external sources for definitions, ensure that these sources are credible and cited consistently. Consistent definitions not only enhance the readability of your dissertation but also reflect your attention to detail and scholarly rigor. In summary, a uniform and systematic approach to defining terms strengthens the clarity and coherence of your glossary, making your dissertation more accessible and understandable.
Avoiding Jargon
Avoiding jargon in your glossary is essential to ensure that it serves its intended purpose—clarifying terms for all readers. While your dissertation may require the use of specialized language, the glossary should translate this jargon into clear, straightforward definitions. Using jargon within definitions defeats the purpose of a glossary and can alienate readers who are not experts in your field. Aim for simplicity and clarity, employing plain language that can be easily understood by a broad audience. If a term is unavoidably complex, consider breaking down its definition into more digestible parts or providing a brief example to illustrate its meaning. Remember, the goal is to make your dissertation accessible and comprehensible to as many readers as possible. By avoiding jargon in your glossary, you enhance the overall readability of your document and ensure that your research can be appreciated and understood by a wider audience.
Keeping it Concise
Keeping your glossary entries concise is a best practice that enhances the usability and effectiveness of your dissertation. While it is important to provide clear and accurate definitions, overly lengthy explanations can overwhelm readers and defeat the purpose of a glossary. Aim to distill each term down to its essential meaning, using as few words as possible without sacrificing clarity. Concise definitions are easier for readers to quickly comprehend, allowing them to maintain their focus on the main content of your dissertation. If a term requires a more detailed explanation, consider providing a brief summary in the glossary and directing readers to a specific section of your dissertation for further information. This approach ensures that your glossary remains a handy reference tool rather than becoming another lengthy section of text. In summary, concise entries in your glossary contribute to a more efficient and reader-friendly dissertation.

Common Mistakes
Overloading with terms.
One common mistake when creating a glossary in a dissertation is overloading it with too many terms. While it is important to provide definitions for specialized terminology, including every possible term can overwhelm readers and dilute the effectiveness of the glossary. Focus on terms that are essential for understanding your research and are likely to be unfamiliar to your audience. Including overly basic or tangentially related terms can clutter the glossary and make it harder for readers to find the information they truly need. Additionally, an excessively lengthy glossary can give the impression of a lack of focus or an attempt to pad the document. Aim for a balance between comprehensiveness and relevance, ensuring that each term included serves a clear purpose in aiding comprehension. By avoiding the overload of terms, you can create a more streamlined and useful glossary that enhances the readability and coherence of your dissertation.
Vague Definitions
Vague definitions are a common pitfall when creating a glossary for your dissertation. Definitions that lack specificity can lead to confusion and misinterpretation, defeating the purpose of the glossary. It is important to provide clear, precise, and unambiguous explanations for each term. Avoid using imprecise language or circular definitions that do not add clarity. Instead, aim to offer concrete and easily understandable explanations that leave no room for doubt. If a term is complex, break it down into simpler components and provide context or examples to aid understanding. Remember, the glossary should serve as a reliable reference for readers, ensuring they can accurately grasp the terminology used in your research. By avoiding vague definitions, you enhance the clarity and effectiveness of your glossary, thereby improving the overall readability and comprehensibility of your dissertation.
Inconsistent Formatting
Inconsistent formatting is a common mistake that can undermine the effectiveness of your glossary in a dissertation. Uniform formatting ensures that your glossary appears professional and is easy to navigate. Discrepancies in font size, style, or layout can distract readers and make it difficult to find and understand terms. To maintain consistency, establish a clear format for your entries from the outset. For example, you might choose to bold the terms and use regular text for the definitions. Additionally, decide on a uniform structure for definitions, such as starting with a brief explanation followed by an example if needed. Consistent formatting also extends to the organization of the glossary, such as maintaining alphabetical order and using the same punctuation style throughout. By adhering to a consistent format, you enhance the readability and professionalism of your glossary, making it a more effective tool for aiding comprehension in your dissertation.
Elevate Your Scientific Graphics with Mind the Graph
Mind the Graph is your go-to platform for creating high-quality, scientifically accurate illustrations. With its intuitive design and extensive library of templates, you can effortlessly transform complex research data into visually appealing graphics. Whether you’re preparing for a presentation, designing a research poster, or enhancing your paper, Mind the Graph ensures your visuals are clear, engaging, and professional. Take your scientific communication to the next level – sign up for free and start designing today!

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
About Fabricio Pamplona
Fabricio Pamplona is the founder of Mind the Graph - a tool used by over 400K users in 60 countries. He has a Ph.D. and solid scientific background in Psychopharmacology and experience as a Guest Researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry (Germany) and Researcher in D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR, Brazil). Fabricio holds over 2500 citations in Google Scholar. He has 10 years of experience in small innovative businesses, with relevant experience in product design and innovation management. Connect with him on LinkedIn - Fabricio Pamplona .
Content tags

Simplifying a thesis by defining the key terms of the research
Thesis research involves many complex elements. Every chapter in a thesis serves a different purpose which simplifies these elements. For instance, the introduction chapter of a thesis discusses key information about the topic, objectives, and problem statement. Another key element of the chapter is the definition of key terms, which considers the knowledge level of the reviewer. This article explains how to present the definition of key terms of a thesis.
The reviewer may not be always from the field on which the thesis is based. Thus, there are chances of non-familiarity with the technical words of that field. To address this issue of lack of clarity, the researcher should include the definition of key terms section to define important terminologies. This section simplifies the complexity of the thesis and also enables better engagement.
Key terms are the main terminologies that are present in your thesis. For instance, in a thesis on the influence of branding, loyalty, and satisfaction on consumer buying behaviour, the key terms can be branding, loyalty, satisfaction and consumer behaviour. A reviewer who is unfamiliar with these terms because they do not belong to the marketing field will want to know their meaning before reading any further.

While defining the key terms includes definitions by other scholars to establish credibility. It also acts as a foundation for the research problem and the literature reviews (USCLibraries, 2017b).
The key terms section should be concise
The introduction chapter accounts for 10% of the thesis. Therefore the definition of the key terms section should be critical, relevant and concise. However, it should be indicative and explanatory. This section should start with a brief one or two-line opening sentence to enable the reviewer to get in the flow of the topic. This should be followed by the terms and their corresponding meanings and definition in bullet points format.
- The section must be written with the help of the most common, popular, and widely used definitions. They must also be sourced from credible and published authors. Data and statistics should be avoided in the definition of key terms unless it is indispensable.
- Every term should end with a mention of the relevance of the term in the field as well as the topic.
- Avoid giving more than one definition per term.
An example of how to present it
- Branding: Branding refers to the act of creating brands that are differentiated from the competition, thereby reducing the number of perceived substitutes in the marketplace (Sammut-Bonnici, 2015, p.1).
- Consumer loyalty: A deeply held commitment to rebuy or patronize a preferred product/service consistently in the future, thereby causing repetitive same-brand or same brand-set purchasing despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching behaviour (Oliver, 1997, p. 392).
- Consumer satisfaction: Consumer satisfaction is defined as pleasurable fulfilment. That is the consumer senses that consumption fulfils some need, desire, goal, or so forth and that this fulfilment is pleasurable (Oliver, 1999, p. 34).
- Consumer buying behaviour: Consumer buying behaviour refers to the selection, purchase and consumption of goods and services for the satisfaction of their wants (Ramya and Ali, 2016, p. 76).
- Cedep. (2015). Unit One : Introduction to Research. Soas , 1–41.
- Halloran, G. M., & Collins, W. J. (1974). Strategic human resource management. Annals of Botany , 38 (5), 1039–1044. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a084894
- Oliver, Richard L. (1999), “Whence Customer Loyalty”, Journal of Marketing , 63, Special Issue, 33-44
- Oliver, R. L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? The Journal of Marketing, 63, 33–44.
- Qassem, M. (2017). Thesis, Dissertation and Article Writing Preparing Research Paper, Dissertation and Thesis. February 2014, 1–20.
- Ramya, N. and Ali, SA (2016). Factors affecting consumer buying behavior. International Journal of Applied Research , 2 (10). 76-80.
- Salaman, G., Storey, J., & Billsberry, J. (2005). Strategic Human Resource Management: Defining the Field. SHRM-Intro , January , 1–12.
- Sammut-Bonnici, T. (2015). Wiley Encyclopedia of Management. New Jersey: Wiley & Sons.
- USCLibraries. (2017a). Glossary of Research Terms This . Usc.Edu. https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/background
- USCLibraries. (2017b). Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper . Usc.Edu. https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/background
- Priya Chetty
I am a management graduate with specialisation in Marketing and Finance. I have over 12 years' experience in research and analysis. This includes fundamental and applied research in the domains of management and social sciences. I am well versed with academic research principles. Over the years i have developed a mastery in different types of data analysis on different applications like SPSS, Amos, and NVIVO. My expertise lies in inferring the findings and creating actionable strategies based on them.
Over the past decade I have also built a profile as a researcher on Project Guru's Knowledge Tank division. I have penned over 200 articles that have earned me 400+ citations so far. My Google Scholar profile can be accessed here .
I now consult university faculty through Faculty Development Programs (FDPs) on the latest developments in the field of research. I also guide individual researchers on how they can commercialise their inventions or research findings. Other developments im actively involved in at Project Guru include strengthening the "Publish" division as a bridge between industry and academia by bringing together experienced research persons, learners, and practitioners to collaboratively work on a common goal.
My name is Neha and I have an experience of above 5 years in freelance content writing that includes academic writing, training and development module designing, questionnaire making, HR journal papers and other non-technical writing works. I am extremely professional in terms of my deadlines and quality assurance when it comes to project submission and approval. I have done Master of personnel management and PGDM(FIN) from pune university and I have a proficiency over english writing skills. My forte is in academic writing majorly in business management, human resource management, marketing and other non-technical assignments. Looking forward to convert my competence into performance.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
proofreading
blog @ precision
Definition of terms for every dissertation.
If you don’t know it already, you will very soon–the Definition of Terms section in the introductory chapter of your dissertation, that is. As your chair, peers, or friendly dissertation consultants have probably shared with you, this section serves to introduce your readers to key terminology that you’ll use throughout your dissertation or thesis writing in discussing your study’s specific contribution to your academic discipline.
You’ve also probably come across a few Definition of Terms sections in your own research (and especially in preparing for the literature review ) and found that they can include everything from specific populations, to key variables (for studies undertaking statistical analysis) or concepts (for qualitative research and analysis), to specific legislation or medical procedures–and beyond.
The best way to think about what to include in your study’s Definition of Terms section is by thinking of it almost as a short glossary or checklist of what your readers absolutely need to know to orient themselves to the specific ideas and language of your topic and field of research. By way of illustration, and since examples in context are often the best form of dissertation assistance, we thought we’d offer up our own Definition of Terms–basically, a short (or not-so-short) list of the main terms and concepts our dissertation consulting clients encounter, and often for the first time, during the research process.
For this and many other terms on the list, alignment has a specific meaning within the context of academic research and, especially, dissertation and thesis writing . However! Alignment, in its perhaps most common real-word usage–wheel alignment for automobiles–actually serves as a helpful analogy here. When your wheel alignment is off, your car might pull off to one side, shake, and often your steering wheel won’t actually correspond to how straight your car drives on the road. To fix wheel alignment, you don’t adjust the wheels themselves, but rather the suspension, the system that connects the wheels to the car.

Similarly, with dissertation research, alignment refers to how well you’ve clearly connected the foundational elements of your study. Does your purpose statement, in fact, address the specific issue identified in your problem statement–or does it pull away from the problem to focus on something perhaps only tangentially related? Does your methodology correspond to the problem as you’ve described it? If you’re planning on a quantitative study with statistical analysis , for example, do your variables tie back to the problem and purpose, as well?
The vast majority of doctoral candidates who reach out to us for dissertation consulting often need support with exactly this issue in their studies, and we’ve found that if you think about the dissertation as a system that needs to properly connect all of its key parts, then it often becomes easier to look at the foundations of your study with a fresh perspective.
Research problem
If there’s a word you’re likely to get sick of hearing first from your chair, committee, and yes, even your dissertation coach, we’re betting that word is problem, in all its variations–research problem, problem statement, general and/or local problem, business problem… You get the idea. That being said, as with the rest of the terms on this list, while problem gets used and abused during the dissertation process, it’s because it’s a very important (you might say the most important) element of your overall study.
The research problem is the specific issue in your field that you plan to explore or examine in your dissertation or thesis writing. It’s a “problem” in the sense that you’ve identified an unanswered question (or series of questions!) and other scholars have pointed out that the lack of research on this topic needs to be addressed.

As this might indicate, you can’t figure out your research problem, of course, until you determine the gap in the research that your study will address! So while you might find, first, that there’s a gap in the research on successful strategies for food delivery apps, you might then decide to further focus this gap to look at specific strategies or barriers for success for areas with more urban or suburban sprawl (after confirming this is part of the existing gap). Finding that initial gap is key–so that you can narrow it down to the specific problem that you can address.
Hook and anchor
While this phrase is most directly relevant for DBA candidates studying at Walden University (one of our primary universities for dissertation assistance), the concept of “hook and anchor” is one that offers some important insight when it comes to breaking down your problem statement into a clear and compelling justification for your topic. In fact, those of you with some background in business or management, regardless of your current doctoral program or research focus, may already be familiar with the idea of a “hook” and an “anchor” in a professional setting.

The purpose of a hook and anchor in your problem statement is to establish the larger significance of your proposed research (sometimes also called the general problem or the global problem) before outlining the specific aspect of this issue that you’ll focus on for your dissertation research. The hook, specifically, should introduce the issue and include support from very recent scholarship, to clearly indicate that this issue is current and unaddressed–in other words, it should “hook” your reader and get their attention! At Walden, the hook is specifically talked about in terms of a “WOW statement” , a well-known sales term for getting to the point fast (and making sure your point’s a good one).
Once you’ve established your hook, the purpose of the anchor, then (also well-named) is to ground this initial statement in concrete evidence (if you’re thinking “statistics,” here, you’re right!). It’s important to understand this difference between the hook and anchor, and we can absolutely help you review your progress so far if you’re currently seeking preliminary dissertation help as you finalize your topic and problem statement.
If approached properly, the hook and anchor help you to establish, immediately and clearly, the importance of continued research in your field. However, if you’ve found an appropriate research gap (see above), then this broader introduction is far too much to tackle for one dissertation–so the hook and anchor also set the stage for a more focused discussion of the specific research problem you’ll address through your original quantitative and/or qualitative research .
Social change
Again, this term is particularly critical for doctoral candidates attending Walden University [https://www.waldenu.edu/about/social-change], but even if you’re attending another online or brick and mortar university for your doctoral studies, the concept of social change is useful when you’re thinking and writing about the overall significance of your proposed dissertation research. This is especially true since, more and more, academic research is evaluated on the merits of its contribution to society at large.

Put simply, “social change refers to the transformation of culture, behavior, social institutions, and social structure over time” . In the context of dissertation or thesis writing, then, understanding your study’s contribution to social change involves asking yourself, “why does this matter?” The next step is looking to the literature in your field to see why the research gap you plan to address is an important one in a broader societal context (as we discussed above, just because there’s a gap in the research, doesn’t mean that gap needs to be filled).
Don’t be daunted by this idea if your study focuses on a very specialized (or not traditionally “academic”) topic! After all, even food can be a tool for social change, according to “social gastronomist” David Hertz (and we’d love to help you with your dissertation as you determine your study’s contribution):
We can use food to create a more inclusive society. Food touches on every aspect of human life: the environment, agriculture, our economy, health, even our social lives. Social gastronomy “uses food to turn social inequalities — such as hunger, poor nutrition, unemployment, inequality — into dignity, opportunities and well-being,” says Hertz.
Anthropomorphism
Even seasoned academic writers often find themselves taken to task for anthropomorphism, so if you’re finding comments pointing this out as an issue to address in your dissertation editing , you’re in good company! And as with many of the terms on this list, it’s important to keep in mind the dissertation as your specific context for anthropomorphism. After all, in other contexts, this concept–the tendency of humans to attribute human qualities to animals or inanimate objects–is actually helping us learn exciting new things about the world around us.
Take Inky the Octopus , for example, whose escape from a New Zealand aquarium into the Pacific Ocean highlighted the ways in which animals’ complex intelligence and abilities are often minimized in order to emphasize their difference from people. Viewing animal and human intelligence on a continuum could, in fact, ultimately allow us to understand more about both.

However, in the context of editing your dissertation, anthropomorphism is a bit more cut-and-dry. In less formal (or more literary speech), you can easily find instances in which speakers refer to the ways in which a study “suggests” or “claims” or even “finds” some important knowledge that you, as a researcher, are excited to incorporate into your own discussion. However, technically, research itself cannot suggest or claim anything–those are human qualities.
That being said, if you’re desperate to change up your sentences (so it’s not just X and Y found that Z, over and over), you can (following APA editing guidelines for anthropomorphism) write that studies “show” or “indicate.” But that’s it! So use sparingly.
Reliability
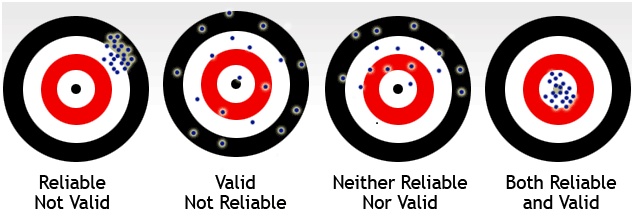
For those who are considering developing their own quantitative instrument, however, there are a number of options for determining that an instrument accomplishes the purpose of your study (pilot testing, again, is critical here). These range from evaluating the content development of the instrument (using experts to develop survey questions, for example) to a cross-comparison with existing instruments that should provide similar results. Again–additional literature searches, outreach to experts, and statistical analysis are often required here, so especially for those already planning to employ statistical> [link to quant methods page] or other dissertation assistance for your study, try to find an existing instrument first! (And if you still have questions or need further statistics consulting, [link url="contact.shtml"]we’re happy to help )!
Belmont Report
You’re bound to come across the Belmont Report at some stage in your doctoral journey–for most doctoral candidates, this report becomes important while drafting the methodology chapter and preparing for Institutional Review Board (IRB) review and approval . Published in 1979, the Belmont Report is an exhaustive discussion of ethical guidelines to follow when conducting research using human subjects. Most relevant to doctoral researchers are the report’s guidelines for assessing and minimizing risk to participants, identifying and recruiting research participants, and ensuring informed consent.
While the necessary steps to ensure adherence to the guidelines and principles of the Belmont Report can often feel like just another task to complete before beginning the most exciting part of your study–the actual research!–it’s very important to ensure that you clearly and carefully plan your process for selecting participants, recruitment, and informed consent. In fact, as many doctoral candidates who reach out for help with their dissertations while completing their IRB applications find, there is a direct benefit for you (beyond ensuring the safe and voluntary participation of your study subjects). The better you plan your recruitment and data collection process, the easier it will be to carry out when the time comes!
Luckily, you can access the entire Belmont Report in its entirety online, so this information is readily available to you as you finalize your research design and begin to think about carrying out your proposed quantitative or qualitative research and analysis. And if you’re wondering at all where to begin, be sure to check out our data collection checklist or contact us for more information about our specialized approach to this phase of dissertation assistance!
Peer-reviewed articles
For many novice researchers, the literature review is often the most daunting part of the dissertation or thesis writing process. In fact, it’s one of the main areas that doctoral candidates reach out to us about when they ask about dissertation consulting or dissertation coach services. Over the past 12 years, we’ve found that the primary stumbling block for many graduate-level researchers is finding appropriately scholarly (i.e., peer-reviewed) research to include in the literature review. (We’ve actually devoted a separate blog post to this topic – so if this is an issue for you, and you’re currently considering dissertation assistance, definitely check that out.)
What does “peer reviewed” mean in this context? Luckily, there’s nothing complex about the name. Peer-reviewed research is research that, once completed, is then subjected to an extensive critique by scholars in the field. Journals that follow a peer review process are generally viewed as more credible and trustworthy, because the methods and findings of the researchers they publish have held up under scrutiny by established experts in the field. Perhaps you’ve already begun thinking about how to turn your completed dissertation research into a published article in your “dream journal”–it’s an exciting next step once you’ve completed your doctoral degree, and one we can assist with as a next or final step for many of our dissertation consulting clients.
In terms of determining whether a journal article is peer-reviewed , most major databases (like ProQuest) offer you the option of searching only for this type of publication. Of course the next step is to ensure that the article (not an opinion piece or letter to the editor) is in fact peer-reviewed, and a quick way to verify this is to check out the journal’s homepage. If the editors submit their articles to peer review, they won’t be shy about letting you know!
Of course, once you’ve mastered the search process to include only peer-reviewed and scholarly sources, you then need to refine your newly honed skills further–to ensure that you’re reviewing and including only the most recent, relevant sources (to support the need for your study right now, today). This can definitely be tricky, particularly if you’re further along in drafting your literature review, but we can absolutely help you with your dissertation so that you keep moving forward!
Did we miss anything? Let us know the essential terminology you’ve learned during your dissertation or thesis writing process in comments!
- California Polytechnic State University. (2017). Find peer-reviewed articles. Retrieved from https://lib.calpoly.edu/support/how-to/find-articles
- D’Arcy, Patrick. (2018, July 12). How food–yes, food–can be a tool for social change. TED Talks: IDEAS.TED.COM. Retrieved from https://ideas.ted.com/how-food-yes-food-can-be-a-tool-for-social-change/
- Kaufmann Entrepreneurs. (2016, July 28). Powerful presentations: Crafting your WOW statement. Retrieved from https://www.entrepreneurship.org/videos/powerful-presentations/crafting-your-wow-statement
- Lazzaroni, M., Peretto, P., Rinaldi, P., & Catelani, M. (2011). The Concept of “Statistical” Reliability. In Reliability Engineering (chapter 2). Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-20983-3_2
- National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- Phelan, C., & Wren, J. (2006). Exploring reliability in academic assessment. Retrieved from https://chfasoa.uni.edu/reliabilityandvalidity.htm
- Riederer, R. (2016, April 26). Inky the Octopus and the upsides of anthropomorphism. The New Yorker. Retrieved from https://www.newyorker.com/culture/culture-desk/inky-the-octopus-and-the-upsides-of-anthropomorphism
- University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing. (2010). Understanding social change. In Sociology: Understanding and Changing the Social World (chapter 20.1). Retrieved from http://open.lib.umn.edu/sociology/chapter/20-1-understanding-social-change/
- Walden University. (2018). Social change. Retrieved from https://www.waldenu.edu/about/social-change

COMMENTS
• Define terms that are fundamental for your dissertation; those that you will frequently use in most sections of your study. • Keep in mind, there is absolutely no need to incorporate common knowledge terms. What do we mean by this? Here is an example: Let us pretend we are doing research on nurturing international business research
Revised on July 18, 2023. A glossary is a collection of words pertaining to a specific topic. In your thesis or dissertation, it's a list of all terms you used that may not immediately be obvious to your reader. Your glossary only needs to include terms that your reader may not be familiar with, and it's intended to enhance their ...
dissertation—that is,precursor of what is to come, with each element being more fully developed and explained fu. ther along in the book.For each key element, explain reason for inclusion, quality markers, and fr. OVERVIEWFRONT MATTERFollowing is a road map that briefly outlines the contents of. an enti.
Glossary in a Dissertation - A Comprehensive Guide. Published by Owen Ingram at August 26th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023. A list of glossary contains all those terms used in your dissertation, but the meanings of which may not be evident to the readers. Here is all you need to know about the glossary in a dissertation.
Defining terms with precision is a key aspect of creating an effective glossary in your dissertation. Adding page numbers to the terms in a glossary allows readers to easily find where the terms are used in the text. Each definition should be clear, concise, and accurate, providing the reader with a quick yet thorough understanding of the term.
You will then explicate the definition of each term that you have identified to best represent your understanding and application of each term in your dissertation. Generally, a component of Definitions and Terms is to ground the definitions using the literature. Specifically, a component of Definitions and Terms is to establish how the key ...
1-H. Definition of Terms: Briefly define key terms in the research that might not be well understood by the readers. Cite a source for each definition derived from the literature. It is acceptable for this section as well as sections 1-E and 1-G to appear in other chapters of the dissertation. CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
Figure 1: The purpose of defining the key terms of a thesis. While defining the key terms includes definitions by other scholars to establish credibility. It also acts as a foundation for the research problem and the literature reviews (USCLibraries, 2017b). Identify key formative works in 20 days with a comprehensive research paper order.
The best way to think about what to include in your study's Definition of Terms section is by thinking of it almost as a short glossary or checklist of what your readers absolutely need to know to orient themselves to the specific ideas and language of your topic and field of research. By way of illustration, and since examples in context are ...
GLOSSARY OF KEY TERMS IN EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH by ABDULLAH NOORI Assistant Professor Department of English, Kabul University ORCID: 0000-0003-2141-3675 Email: [email protected] Final Copy: Date of Completion: February 3, 2021 . Glossary of Key Terms in Educational Research