General Studies
All Programmes
Study Material

Artificial Intelligence - Benefits, Applications, Types, and Concerns
Sub-Categories:
Science and Technology
Table of Contents
- What is Artificial Intelligence
Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Advantages and disadvantages of artificial intelligence.
- India amp Artificial Intelligence
Prelims: General Science
Mains: Science and Technology- Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, Robotics, Nano-technology, and Biotechnology.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging technology that enables computers and machines to simulate human intelligence and problem-solving capabilities. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence , such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence has become increasingly prevalent in various domains, including natural language processing , computer vision, robotics, and decision support systems. As AI technology advances, it holds the potential to revolutionise numerous industries and aspects of our daily lives, while also raising important ethical considerations regarding its responsible development and deployment.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to machines performing human-like tasks. Its main components are Machine Learning algorithms that train on data, Neural Networks that mimic the brain's structure, and Natural Language Processing that understands human language. AI systems work by taking inputs, processing them with algorithms, and providing intelligent outputs that mimic human cognition and reasoning abilities.
Brief History of Artificial Intelligence
- Alan Turing proposed " Turing Test " to evaluate machine intelligence
- John McCarthy coined the term "Artificial Intelligence"
- Examples: DENDRAL (chemical analysis), MYCIN (medical diagnosis)
- Algorithms like decision trees and neural networks
- Systems learn from data instead of hard-coded rules
- Inspired by human brain structure and function
- Excelled in computer vision and natural language processing
- Driven by large datasets (e.g., ImageNet), computing power (GPUs)
- Algorithmic advances like deep learning
- Major tech companies invested heavily in AI research
- Natural language processing (e.g., ChatGPT by OpenAI )
- Computer vision (e.g., object detection by DeepMind)
- Reinforcement learning (e.g., AlphaGo by DeepMind)
- Widespread adoption of AI technologies across industries
Elements of Artificial Intelligence

- Example : Spam filtering in email clients, which learns to identify spam emails based on patterns in the data.
- Example: Facial recognition systems used for tagging people in photos or unlocking smartphones.
- Example : Virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa that can understand and respond to voice commands.
- Example : Self-driving cars that can detect and recognize objects, pedestrians, and traffic signals.
- Example : Recommendation systems used by streaming platforms like Netflix to suggest movies and shows based on user preferences.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
- Narrow AI is designed for specific tasks and operates within predefined boundaries.
- Examples: Virtual assistants, chess-playing programs, speech recognition, spam filters
- General Artificial Intelligence aims to mimic human intelligence across various tasks.
- Unlike narrow AI, AGI can reason, learn, and adapt like a human.
- A future form of AI surpasses human intelligence significantly.
- These AI systems operate in the present moment, reacting to current data without memory or past experiences.
- Examples: IBM’s Deep Blue (chess-playing AI) and Google’s AlphaGo
- Artificial Intelligence with limited memory can use past data to make decisions but does not have a full history of interactions.
- Examples: Self-driving cars, language translation software
- This type aims to understand human emotions, beliefs, intentions and thought processes.
- This type of AI is still in its infancy.
- AI that has a sense of self-awareness and consciousness, similar to human consciousness.
- It is highly speculative and not yet achieved.
How does AI work?
- AI systems acquire data, preprocess it, and extract relevant features.
- Appropriate algorithms like machine learning, deep learning, or rules are selected and trained on the data to learn patterns.
- The trained models are evaluated, optimized, and deployed to make predictions or decisions based on new input data.
- Artificial Intelligence combines techniques like natural language processing, computer vision, and reasoning to mimic human-like intelligence.
- It continuously learns and improves through exposure to more data and feedback.

Artificial intelligence has numerous applications across various industries. Some of the most common applications include:
- E-commerce : Helps in personalised recommendations, fraud detection, and chatbots for customer support.
- Education : Used for adaptive learning, personalised learning plans, and intelligent tutoring systems.
- Robotics : Powers robots for automation, inspection, and assembly line tasks.
- Healthcare : Aids in medical diagnosis, drug discovery, and patient monitoring.
- Social Media : Used for content moderation, recommendation systems, and sentiment analysis.
- Agriculture : Helps in precision farming, crop monitoring, and yield prediction.
- Manufacturing : Used for quality control, predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, and robotics.
- Finance : Aids in fraud detection, risk assessment, and investment management.
- Transportation : Used for self-driving cars, traffic management, and route optimization.
- Environment : Helps in climate modelling, pollution monitoring, and renewable energy management.
Examples of AI in Daily Life
Artificial Intelligence is an integral part of our lives, enhancing convenience, efficiency, and decision-making across various domains.
- Chatbots : ChatGPT by OpenAI, Copilot by Microsoft Bing
- Smart assistants : Siri, Alexa, and Cortana
- Recommendation algorithms : Google’s search algorithm, Netflix’s personalised content recommendations
- Face Recognition : FaceID on iPhones, Security cameras
- Navigation apps : Google Maps, Waze
- Social Media algorithms : Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter’s curated feeds.
- Ridesharing apps : Uber, Ola
Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers immense potential for innovation and efficiency but comes with challenges such as ethical concerns, job displacement, and data privacy issues.
Significance of AI
- Example : Robotic process automation in finance for data entry and report generation.
- Example : Predictive analytics in retail for demand forecasting and inventory optimization.
- Example : Chatbots for customer service inquiries in various industries.
- Example : Credit risk assessment in banking using machine learning models.
- Example : AI-assisted drug discovery and personalized medicine.
Concerns Related to Artificial Intelligence
- Example : Self-checkout systems in retail reducing the need for cashiers.
- Ethical concerns: AI systems can perpetuate biases present in training data or algorithms.
- Example : Facial recognition systems showing bias against certain ethnicities.
- Example : DeepFakes for spreading misinformation and propaganda.
- Example : Inaccurate medical diagnoses due to incomplete or biased patient data.
- Example : Chatbots failing to provide emotional support in mental health applications.
- Example : Significant investment required for AI research and development.
- Example : Lack of transparency in AI-based loan approval systems.
India & Artificial Intelligence
The Indian government and various organisations have taken several initiatives to promote the development and adoption of AI in the country. Here are some key initiatives:
- National Strategy for AI (2018) : It outlines the vision, mission, and a comprehensive plan to leverage Artificial Intelligence for economic growth and social development.
- AI for All : To promote AI education and research.
- Responsible AI for Social Empowerment (RAISE) : To develop AI-based solutions for social good.
- AI for Agriculture : To improve agricultural productivity and farmer welfare.
- Responsible AI for Youth: To equip young people with the necessary skills and mindset for AI readiness.
- AI Centers of Excellence : The government has established AI Centers of Excellence in various institutes and universities, such as IITs, to promote research and development in AI.
- FutureSkills PRIME : It is, a joint initiative by NASSCOM and MeitY, a skill development program aimed at reskilling and upskilling IT professionals in emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence, to bridge the talent gap.
- INDIAai : It is the National AI Portal of India, and serves as a knowledge portal, a research organization, and an ecosystem-building initiative.
PYQs on Artificial Intelligence
Question 1 : Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does AI help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to the privacy of the individual in the use of AI in healthcare? ( UPSC Prelims 2023 )
Question 2 : With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below: ( UPSC Prelims 2020 )
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Answer: (b)
FAQs on Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an emerging technology that enables computers and machines to simulate human intelligence and problem-solving capabilities.
What is the difference between Artificial Intelligence, Machine learning and Deep Learning?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad field of creating intelligent systems. Machine Learning (ML) is an AI technique that allows systems to learn from data. Deep Learning (DL) is a specific ML technique inspired by the brain's neural networks.
How do we measure if Artificial Intelligence is acting like a human?
The Turing Test, proposed by Alan Turing, evaluates if an AI system can exhibit human-like responses that are indistinguishable from a real person's responses in a conversational setting.
© 2024 Vajiram & Ravi. All rights reserved

Essay on Artificial Intelligence UPSC
Why is an essay on Artificial Intelligence UPSC relevant?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an increasingly important part of the modern world. Artificial Intelligence is what we can call the stimulation of human intelligence onto machines. In this boom of technological revolution, we are left to wonder if natural intelligence matters anymore.
Quite often AI is misunderstood and misrepresented as something powerful and dangerous. As aware citizens who see the possibility of technology development and innovation through AI, it is essential that we understand what AI really is and isn’t.
Here we will look at artificial intelligence, including how it can be used, the components that makeup AI, and its impact on our daily lives. This article will help you design and write an essay on artificial intelligence UPSC style. The first step to writing an Artificial Intelligence essay UPSC level is to define what AI is.
Read on to familiarize yourself with the term AI.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): What Exactly Is It?
Ai vs machine learning, what characteristics does ai have, artificial intelligence developments around the world, why artificial intelligence is beneficial, artificial intelligence in india: challenges.
- Ways to Harness AI's Power
FAQs On Artificial Intelligence
What is the 4.0 industrial revolution, is ai the beginning of the industrial revolution 4.0, state 2 examples of ai., what is the future of artificial intelligence, what are the potential risks and concerns with artificial intelligence.
John McCarthy coined the term “artificial intelligence” in 1956 at the Dartmouth conference, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
The most prevalent misconception about artificial intelligence (AI) is that it refers to robots that perform monotonous repetitive tasks and behave like humans.
However, this isn’t quite accurate. The ability of machines (computers) to accomplish cognitive functions usually related to the human brain is referred to as artificial intelligence (AI), like learning, planning, and problem-solving (in other words, many human intelligence processes)all without any explicit programming from humans or any kind of human interaction!
Now that we have defined and understood what AI is, let us explore what AI does, how it is of use today along with what the future holds in store. We can also show the difference between two technologies in the same domain in our Artificial Intelligence UPSC essay.
Both AI and machine learning go hand in hand. However, their difference is significant. The scope of these two technologies is the fundamental difference between these two advancements of technology.
- Artificial Intelligence(AI) refers to computer systems that can do activities that would ordinarily need human intelligence.
- Machine learning refers to systems that are not explicitly intended for a certain activity but do include some amount of learning.
People frequently confuse which of these two technologies is superior when using them. While deep learning and machine learning are both powerful technologies, the former comprises neural networks that require human intervention to optimize results.
Human specialists determine the hierarchy of features and distinguishing qualities of data in traditional machine learning. To streamline the learning process, humans create labels for the data. Deep learning also relies on labeled data. This way, the system learns to differentiate objects based on their characteristics via a Machine Learning algorithm.
Now we know what AI is and isn’t. This basic knowledge will not suffice for a UPSC-level essay on Artificial Intelligence. To make the examiner understand more about our extent of knowledge in the subject matter, we can also list out features in our Artificial Intelligence UPSC essay.
Also Read: How To Write An Essay In UPSC Mains
Computer programs have a natural tendency to look for patterns and predict the outcome of future situations. As these patterns emerge, computer programs can be categorized as “intelligent.”
An AI-based system is also capable of learning, which means that it can adapt to new conditions. In addition, it will be capable to integrate changes in its algorithm, allowing it to take more actions based on its learning process.
Ultimately, these systems will become as intelligent as humans, enabling them to become digital assistants and further replace human workers in many industries.
The foundation of AI is built on the notion of human intelligence. AI aims to simulate human cognitive activity by mimicking human behavior. The ability of an artificial system to learn and perform tasks better than humans is a key component of AI.
For example, a robot can use fuzzy logic to solve unfamiliar tasks. Likewise, it can apply knowledge from one domain to another.
While researchers and developers are making great strides in developing AI, there are also plenty of skeptics in the field. The issue of replaceability and unchecked power is a fear that strikes most minds.
Nevertheless, the developments in the Artificial Intelligence field and the discussions it is launching are a must-know for all UPSC aspirants. Discussing current affairs in our Artificial Intelligence UPSC essay can make it stand out and highlight our level of awareness about the subject.
The societal and economic advantages of implemented AI are well-acknowledged around the world.
In contrast to China and Japan, which have allowed existing ministries to adopt AI in their various sectoral areas, many nations have established specialized government offices, such as the Ministry of AI in the United Arab Emirates and the Office of AI and AI Council in the United Kingdom.
While the world is still in its infancy, global developments in AI will be an increasingly important factor for economic growth. China forecasts that artificial intelligence would contribute 26% of its GDP by 2030, while the U.K. estimates that AI will contribute 10%.
France and Japan recently released AI strategies, and the U.K. published an industrial strategy in November. As AI tools improve, we can expect to see these countries continue to push the boundaries of this field.
In addition, NITI Aayog has released National AI Strategy Discussion Paper to provide guidance on the research and development of new and developing technologies. On August 24, 2017, Task forces (i.e., a working group) on artificial intelligence were formed.
Artificial intelligence can add significant value to a wide number of industries around the world, and It is expected to be a significant source of competitive advantage for businesses. Along with the advantages, listing out the challenges can be a good way to steer the Artificial Intelligence UPSC essay forward.
Artificial Intelligence can increase the calculation power of conventional computers. AI processes are usually self-learning, so they can work continuously without any rest. This can greatly increase the competitive edge of a company.
Furthermore, AI can predict the future and anticipate what people will need in a variety of fields. This can help in planning infrastructure and decision-making.
In addition, AI can be programmed to identify threats to human life. It is not yet clear how AI will impact the future of our society, however, it has the capacity to transform the way we live.
Listed below are some of its advantages:
- AI is the only solution to avoid human errors . AI technology isn’t susceptible to human error or discrepancies from human interactions. AI is trained to avoid human errors, allowing it to detect and correct mistakes without human assistance. Unlike human doctors, AI-enabled intelligent machines don’t depend on the mood of their operators, allowing them to focus on solving a particular case instead of focusing on a complex problem. For example, Google’s DeepMind can diagnose severe eye diseases as accurately as world-class doctors. Additionally, it can recommend the best treatment in 94% of cases.
- Another advantage of AI is that it’s highly scalable. Instead of being limited by the human brain, AI can integrate itself with scalable intelligent systems, from cell phones to supercomputers. The scalable nature of AI also allows it to perform tasks of varying complexity. Further, AI can improve the decision-making process thereby increasing productivity. Therefore, companies can benefit from AI for convenience, reducing the time required for data analysis.
- In the Healthcare sector, it is used to provide accurate diagnosis way before the disease reaches its acute phase.
- The use of AI in the education domain is expected to improve access to quality education and improve crowd management . It makes rewarding marks and grading automated and time-efficient.
- AI applications are also advancing the way we live and work , making it easier to manage our cities. For example, artificial intelligence can help improve traffic flow and power balancing, making it easier to monitor power outages.
- AI is already being used in the retail sector , with applications including personalized suggestions, image-based product search, and customer demand anticipation. AI guarantees smart mobility as well as improved supply chain management and delivery processes. Aside from improving customer service, AI applications can also be beneficial for retailers to monitor and prevent potential problems. It can also detect broken products and defective objects, notifying the responsible person.
- Many industries are integrating AI into their products to improve their performance. In the advertising world, AI is used to track user statistics and to show advertisements relevant to their interests . The manufacturing sector utilizes AI in its intelligent robots to hasten the automation process and better quality control.
- Similarly, in the agricultural community, AI is used to help buyers choose products . AI can also be used to reduce crop losses by building modern machines to provide advisories for sowing or monitor weather and diseases to avoid future mishaps. This in turn will increase crop yield.
- The e-commerce industry is incorporating artificial intelligence to make purchases and communication easier and more efficient.
- Innovations in gaming are also possible through AI . Technological innovation in strategic games like chess where artificial intelligence can control the opponent’s computer and even play the game for them using neural networks is an example of this.
These futuristic innovations and systems are growing in popularity in the market, but only a few professionals are working on building them. For this reason, there is an increasing demand for AI professionals in the market. However, despite the great potential for AI, it is essential to find a job with this skill set to be successful.
We can finish our Artificial Intelligence UPSC essay by listing out the challenge and what we think can be the way forward. This will show the examiner your opinion on the subject and your problem-solving skills.
Implementing AI tools in Indian educational institutions is a challenge, especially in India, where educational institutions often lack data. Most don’t have an ERP in place and thus can’t pull data in a uniform format. Without such data, AI tools cannot accurately predict student performance.
Additionally, the current lack of data sets makes it impossible to create a single repository to train AI models. Consequently, the implementation of AI is slow and difficult.
Regardless of its promise to propel national progress and wealth, AI in India faces several barriers. Listed below are some of the most significant hiccups, which should be solved before the technology is fully adopted and embraced in the country.
- There is a lack of communication and collaboration between many stakeholders which hinders a natural developmental progression.
- Concerns about d ata privacy and security , as well as a lack of formal regulation regarding data anonymization.
- Lack of awareness about AI. The vast majority of Indians have no idea what Artificial Intelligence (AI) is or how it operates, and the benefits it may provide for businesses, governments, and individuals. This is mainly because AI is only just beginning to enter mainstream consciousness in other countries too.
- Difficulty with adoption is a reality. Indian businesses generally lack the resources required to implement AI systems and complex machines. For example, many companies don’t have enough data scientists on their teams to analyze customer data and build algorithms that can predict future events based on historical data sets.
- Another setback is the lack of resources and resource costs . There is a shortage of trained professionals who are proficient in Artificial Intelligence techniques like machine learning and deep learning(a subset of machine learning). As a result, organizations are unable to hire people with relevant skill sets or develop in-house talent quickly enough to keep up with the competition.
- Computing infrastructure is scarce and generates huge costs, making it difficult to build, train, and deploy AI-based services. Despite its rapid growth, cloud infrastructure has limited capabilities.
These were some of the current issues with AI-based systems in India. Let’s look at what can be the best way forward.
Ways to Harness AI’s Power
Consider Examarly to prepare for UPSC holistically. You will find everything from personalized study strategy to curated study resources under one umbrella, here.
AI has many benefits in our everyday lives, but it is not without its downsides. Many observers are concerned that AI will create an unequal share of the benefits and risks of technological advancement. Some countries will benefit greatly from AI, while other countries will suffer as they do not have the same resources as developed nations.
The developing world is also concerned that AI will reduce the demand for labor and natural resources. This could negatively impact the welfare of workers, and ultimately lower equilibrium wages and welfare.
We expect that India’s “AI for All” agenda emphasizes ethical AI and results in large-scale AI solutions in order to make India a larger ecosystem for AI and a dependable country to which the rest of the world may outsource AI-related work. AI systems created in India will help the entire planet.
Many people believe that AI-based applications will take their sweet time to master the human language and control the human race. Yet, AI is developing at an incredibly fast rate, which is causing some people to worry and have nightmares of a robotic army. This powerful technology can easily grow out of control and become too powerful for human use.
The emergence of complete artificial intelligence, according to Stephen Hawkins, may mean the extinction of the human race.
While this technology will undoubtedly benefit humans, it could also endanger society by increasing the wealth gap. Further, AI could be used for nefarious purposes, including autonomous weapons and malicious AI systems. Thus, the use of AI is only a step in a path that is yet to be disclosed.
Taking an ethical yet progressive approach to this social transformation is commendable while writing the essay on Artificial Intelligence in your UPSC exam. Prepare for UPSC with Examarly and to maximize your chances of acing the prelims. Check out Examarly for the best Civil Service study materials.
How advanced people live and work is changing as a result of revolutionary trends and technology like robotics, the Internet-Of-things (IoT), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence. The fourth industrial revolution is referred to as this. The incorporation of these technologies into industrial procedures is termed “Industry 4.0.”
A number of scientific and technological sectors have seen substantial advancements thanks to artificial intelligence (AI), also referred to as the 4.0 Industrial Revolution.
1. By processing human language rather than computer language, computer software is said to be performing natural language processing (NLP). Consider spam detection, which determines whether an email is rubbish by examining the subject line and the email’s body. 2. Making a system or a group of processes run without human involvement is known as robotic process automation. Robots can be taught to carry out repetitive, elevated operations that would often be carried out manually, and they differ from IT standardization in that they can change course quickly in response to changing conditions.
The future of AI is uncertain, but it is likely that it will continue to play an increasingly important role in many aspects of our lives. It may also lead to the development of new technologies and industries, as well as new ethical and societal challenges.
One of the main concerns with AI is the potential for it to automate jobs and increase unemployment. Additionally, there are concerns about privacy and the ethical implications of AI, such as bias and discrimination in decision-making.
Related Posts

The Sanyasi Revolt: History, Background and Leaders

Which Article Is Heart And Soul Of Indian Constitution

Schedules Of The Indian Constitution

Article 198 Of The Indian Constitution
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Everything you need to know
Last updated on September 11, 2024 by ClearIAS Team
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a hot word these days. In this post, we cover artificial intelligence in detail – its meaning, scope, risks, ethics etc.
Table of Contents
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- To make it simple – Artificial Intelligence is intelligence exhibited by machines.
- It is a branch of computer science that deals with creating computers or machines as intelligent as human beings.
- The term was coined in 1956 by John McCarthy at the Dartmouth conference, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- It is a simulation of human intelligence processes such as learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using the rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction by machines, especially computer systems.
- Nowadays it has become an umbrella term that encompasses everything from robotic process automation to actual robotics.
- Recently it has become widely popular and gained prominence due to its multifaceted application ranging from healthcare to military devices.
Is it possible for a computer to become completely Artificially Intelligent?

- Work is being done in this arena however except in some instances of computers playing games faster than the best human players no success has been achieved.
- For Example: In May 1997, an IBM super-computer called Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Gary Kasparov in a chess match.
- Another recent example of 2016 is, AlphaGo , a program driven by Google’s DeepMind AI, which has won Korean Lee Sedol, one of Go’s most dominant players.
What is the philosophy and ethics of Artificial Intelligence?
- The research and development of AI started with the intention of creating intelligence in machines that we find and regard as high in humans. Thus answering the big question which is can machines think and behave like humans do?
Three main philosophical questions related to Artificial Intelligence
- Are they dangerous to humanity? How can we ensure that machines behave ethically and that they are used ethically?
- Is artificial general intelligence probable? Can a machine decipher any problem that a human being can solve using intelligence? Or are there hard boundaries to what a machine can accomplish?
- Is it possible for machines to have a mind, consciousness, and mental state in the same sense that human beings do? Can a machine be sentient, and thus deserve certain rights? Can a machine intentionally cause harm?
Examples of Artificially Intelligent Technologies
- Robotic process automation : Automation is the process of making a system or process function automatically. Robots can be programmed to perform high-volume, repeatable tasks normally performed by humans and further, it is different from IT automation because of its agility and adaptability to the changing circumstances.
- Natural language processing (NLP ) is the processing of human language and not computer language by a computer program. For Example, spam detection, which looks at the subject line and the text of an email and decides if it’s junk.
- Pattern recognition is a branch of machine learning that focuses on identifying patterns in data.
- Machine vision is the science of making computers visualize by capturing and analyzing visual information using a camera, analog-to-digital conversion, and digital signal processing. It is often compared to human eyesight, but machine vision isn’t bound by biology and can be programmed to see through walls. It is used in a range of applications from signature identification to medical image analysis.
- Machine learning : A field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning and can be thought of as the automation of predictive analytics.
- Robotics is a field of engineering focused on the design and manufacturing of robots. Robots are often used to perform tasks that are difficult for humans to perform or perform consistently.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Healthcare Sector : Machine learning is being used for faster, cheaper, and more accurate diagnosis thus improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. For Example, IBM Watson and chatbots are some of such tools.
- Business Sector : To take care of highly repetitive tasks Robotic process automation is applied which performs faster and effortlessly than humans. Further, Machine learning algorithms are being integrated into analytics and CRM platforms to provide better customer service. Chatbots are being used in websites to provide immediate service to customers. Automation of job positions has also become a talking point among academics and IT consultancies such as Gartner and Forrester.
- Education Sector : AI can make some of the educational processes automated such as grading, rewarding marks, etc. therefore giving educators more time. Further, it can assess students and adapt to their needs, helping them work at their own pace. AI may change where and how students learn, perhaps even replacing some teachers .
- Financial Sector: It can be applied to personal finance applications and could collect personal data and provide financial advice. Today software trades more than humans on Wall Street.
- Legal Sector : Automation can lead to faster resolution of already pending cases by reducing the time taken while analyzing cases thus better use of time and more efficient processes.
- Manufacturing sector : Robots have been used for manufacturing for a long time now, however, more advanced exponential technologies have emerged such as additive manufacturing (3D Printing) which with the help of AI can revolutionize the entire manufacturing supply chain ecosystem.
- Intelligent Robots − Robots can perform the tasks given by a human because of sensors to detect physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure. Moreover, they have efficient processors, multiple sensors, and huge memory, to exhibit intelligence. Further, they are capable of learning from their errors and therefore can adapt to the new environment.
- Gaming – AI has a crucial role in strategic games such as chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where the machine can think of a large number of possible positions based on heuristic knowledge.
- Speech Recognition – There are intelligent systems that are capable of hearing and grasping the language in terms of sentences and their meanings while humans talk to it. It can handle different accents, slang words, noise in the background, changes in human noise due to cold, etc.
- Cyber Security : In the 20 th conference on e-governance in India it was discussed that AI can provide more teeth to cyber security and must be explored.
Read: AI in Elections
What are the downsides and risks of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- The decrease in demand for human labour is due to machines and intelligent robots taking over the jobs in the manufacturing and services sectors. For Example: In China, some customs officers are now robots, In Japan robots such as housemaids is an emerging trend.
- Existential risks : Stephen Hawkins once said “The development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race. Once humans develop artificial intelligence, it will take off on its own and redesign itself at an ever-increasing rate. Humans, who are limited by slow biological evolution, couldn’t compete and would be superseded”.
- AI technologies falling into terrorist hands may unleash modern terror networks including machines and therefore vulnerability of humans may magnify.
- It may lead to moral degradation in society due to decreased human-to-human interactions.
In such an era of rapid and disruptive changes, many questions arise:
- Will these technological changes be accompanied by equally profound economic, social, and cultural changes?
- Will technology destroy jobs at a faster rate than the rate of creation of jobs?
- Will future governments be forced to fork out Universal Basic Income ?
- How could education be redefined with artificial intelligence, big data, augmented reality, and personalized learning pathways?
- Are conventional manufacturing plants under threat with the advent of additive manufacturing?
- What will be the impact on the skills required ?
- After all these changes, do people-to-people communication and socio-economic activities remain the same?
Possible areas for AI applications in Indian conditions
- It can complement Digital India Mission by helping in the big data analysis which is not possible without using AI.
- Targeted delivery of services, schemes, and subsidies can be further fine-tuned.
- Smart border surveillance and monitoring to enhance security infrastructure.
- Weather forecasting models may become proactive and therefore preplanning for any future mishaps such as floods, and droughts and therefore addressing the farming crisis, farmer’s suicide, crop losses, etc.
- By analyzing big data of road safety data and NCRB (National Crime Record Bureau) data for crimes, new policies can be formulated.
- Disaster management can be faster and more accessible with the help of robots and intelligent machines.
- In the counterinsurgency and patrolling operations, we often hear the loss of CRPF jawans which can be minimized by using the robotic army and lesser human personnel.
- AI can be used to automate government processes, therefore, minimizing human interactions and maximizing transparency and accountability.
- It can be applied to study ancient literature on medicines and therefore help in modernizing health care with the juxtaposition of modern machines and ancient techniques.
- In the remotest areas where the last leg of governance is almost broken, AI can do the job. For Example: in the tribal areas and the hilly areas of the northeast.
Which is the nodal organization of the government for the research work on Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (CAIR), is the primary laboratory of DRDO for research and development in different areas of defense, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and is located in Bangalore. It is involved in the Research & Development of high-quality Secure Communication, Command, and Control, and Intelligent Systems.
- CAIR came into existence in 1986.
- Projects: NETRA- software to intercept online communication, SECOS- Secure operating system.
What are the challenges India’s Artificial Intelligence Development is facing?
- AI-based applications are mostly driven largely by the private sector and have been focused largely on consumer goods.
- Public-private funding model which is a success in the United States, China, South Korea, and elsewhere may be considered good for India. Presently it is not present in India.
- Our educational system is not updated to modern technologies and is outdated in today’s economic environment as the nature of jobs shifts rapidly and skills become valuable and obsolete in a matter of years.
- The debate of poverty vs. technology and where to spend the most is more likely to persist until the political class takes a higher interest in real issues than trivial ones.
Latest Developments
March 2024: The UN General Assembly adopted a landmark resolution to promote “safe, secure and trustworthy” artificial intelligence (AI) systems that will also benefit sustainable development for all.
👉 Which year are YOU targeting for success in the IAS/IPS/IFS Exam? 🚀
(1) ⇒ UPSC 2025: Prelims cum Mains
(2) ⇒ UPSC 2026: Prelims cum Mains
(3) ⇒ UPSC 2027 Prelims cum Mains
Tip: Know more about ClearIAS Courses (Online/Offline)
- The Assembly resolved to bridge the artificial intelligence (AI) and other digital divides between and within countries and promote safe, secure and trustworthy AI systems to accelerate progress towards the full realization of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- The United States is spearheading the first United Nations resolution on artificial intelligence, aimed at ensuring that the new technology is “safe, secure and trustworthy” and that all countries, especially those in the developing world, have equal access.
- The resolution aims at closing the digital divide between countries and making sure they are all at the table in discussions on AI — and that they have the technology and capabilities to take advantage of its benefits, including detecting diseases, predicting floods and training the next generation of workers.
Despite these threats and challenges, it would be stupid to argue that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not the future and it’s only a matter of time before machines replace most jobs. It does not mean the end of the road for humanity and we have a history of technological revolutions causing social and political changes in society.
There were bound to be some fears and challenges in the early years, but so was the case with the French Revolution, steam engines, industrial revolutions, and most recently the computers.
Nevertheless, there will be more opportunities in the fields not yet known and there will be more jobs to cater to human needs. In the case of India, Innefu is one such Artificial Intelligence (AI) based company that is still in its nascent phase but soon may challenge global companies and therefore can create an AI ecosystem in India.
Also read: Future of Work and AI; IndiaAI Mission; International AI Treaty
Article by: Nishant Raj. The author is an IIT Kharagpur Alumnus.

Best-Selling ClearIAS Courses
Upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: unbeatable batch 2025 (online), rs.75000 rs.29999, upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: ultimate batch 2025 (online), rs.95000 rs.49999, upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: ultimate batch 2026 (online), rs.115000 rs.59999, upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: ultimate batch 2027 (online), rs.125000 rs.69999.

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
April 2, 2017 at 8:14 pm
Thank you Team for this article.
June 1, 2017 at 11:33 pm
nice article
September 17, 2018 at 11:43 pm
December 28, 2018 at 11:19 am
Nice Article. Especially liked the Possible areas for AI application in Indian conditions. In particular about how weather forecasting models may become proactive and therefore preplanning for any future mishaps such as floods, droughts and therefore addressing the farming crisis, farmer’s suicide, crop losses etc.
July 21, 2019 at 4:45 pm
your Article is also very important for the UPSC (AC) exam 2. thanks to clearIAS team
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2025
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
ClearIAS Programs: Admissions Open
Thank You 🙌
UPSC CSE 2025: On May 25, 2025
Subscribe ClearIAS YouTube Channel

Get free study materials. Don’t miss ClearIAS updates.
Subscribe Now
IAS/IPS/IFS Online Coaching: Target CSE 2025

Cover the entire syllabus of UPSC CSE Prelims and Mains systematically.
Shopping Cart
No products in the cart.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Advantages & Disadvantages
From Current Affairs Notes for UPSC » Editorials & In-depths » This topic
Artificial Intelligence (AI), also known as the Industrial Revolution 4.0 , has been making deep strides in scientific and technological innovation across different fields. It is capable of bringing considerable transformations in the way civilian activities and military operations are conducted. However, there are also concerns regarding the AI’s implications for employment and other ethical issues.

What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- It is a branch of computer science that deals with creating computers or machines as intelligent as human beings.
- It refers to the ability of the machines to perform human intelligence processes like thinking, perceiving, learning, problem-solving and decision making.
- Thus in simple terms, Artificial Intelligence is the intelligence showed by machines.
- The term Artificial Intelligence was coined by John McCarthy in 1956 at the Dartmouth conference, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- There are two subsets under the Umbrella term AI, they are – Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
Express Learning Programme (ELP)
- Optional Notes
- Study Hacks
- Prelims Sureshots (Repeated Topic Compilations)
- Current Affairs (Newsbits, Editorials & In-depths)
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- Post-Independence Indian History
- World History
- Art & Culture
- Geography (World & Indian)
- Indian Society & Social Justice
- Indian Polity
- International Relations
- Indian Economy
- Environment
- Agriculture
- Internal Security
- Disasters & its Management
- General Science – Biology
- General Studies (GS) 4 – Ethics
- Syllabus-wise learning
- Political Science
- Anthropology
- Public Administration
SIGN UP NOW
What is the difference between Machine Learning and Deep Learning?
Machine learning:.
- A subset of artificial intelligence that deals with the creation of algorithms that can modify itself without human intervention to generate desired output- by feeding itself via structured data .
- Machine learning algorithms are built to “learn” to do things by understanding labeled data, then use it to produce further outputs with more sets of data. However, they need to be retrained through human intervention when the actual output isn’t the desired one (errors).
Deep Learning:
- A subset of machine learning where algorithms are created and function similar to those in machine learning, however, there are different layers of these algorithms- each providing a different interpretation to the data it feeds on.
- Such a network of algorithms is known as artificial neural networks , as it imitates the function of the human neural networks present in the brain.
- Deep learning networks do not need human intervention as the nested layers in the neural networks put data via hierarchies of different concepts, which eventually learn from their own errors . But even these are subject to flawed outputs if the quality of data is not good enough.
To put it simply, the key difference between deep learning and machine learning stems from the way data is presented to the system. Machine learning algorithms almost always require structured data, whereas deep learning networks rely on layers of the ANN (artificial neural networks) . Thus Data is the governor here. It is the quality of data which ultimately determines the quality of the result.
Prelims Sureshots – Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims
A Compilation of the Most Probable Topics for UPSC Prelims, including Schemes, Freedom Fighters, Judgments, Acts, National Parks, Government Agencies, Space Missions, and more. Get a guaranteed 120+ marks!
What are some of the examples of Artificial Intelligent Technologies?
- Robotics and Automation: Robots can be programmed to perform high-volume, repeatable tasks normally performed by humans.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the processing of human language by a computer program. For example, spam detectors look at the subject line and text of an email in order to decide whether it is junk.
- Pattern recognition is a subset of machine learning that seeks to identify patterns in data. For example, a machine learning program can differentiate cats from dogs among 1000 images of cats and dogs through pattern recognition like face, whiskers, etc.
- Machine vision is the science of giving computers a vision by capturing and analyzing visual information using a camera, analog-to-digital conversion, and digital signal processing. It is mostly compared to human eyesight, however, machine vision is not constrained by biology = it can even be programmed to see through walls.
What are the applications/advantages of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Self-driving Cars: AI algorithms are one of the primary components that facilitate self-driving cars to make sense of their surroundings, taking in feeds from cameras installed around the vehicle and detecting objects like roads, traffic signs, other cars, and people.
Digital assistants and smart speakers: Siri, Alexa, Cortana, and Google Assistant utilise artificial intelligence to convert spoken words to text and map the text to certain commands. AI assists digital assistants to make sense of various nuances in spoken language and synthesize human-like voices.
Translation: For several decades, translating text between various languages was a pain point for computers. But deep learning created a revolution in services such as Google Translate. But to be precise, AI still has a long way to go before it perfects human language, but so far, the advances are outstanding.
Facial recognition: Facial recognition is one of the most prominent applications of artificial intelligence. It has different uses, including unlocking your phone, paying with your face, and detecting intruders in your home.
- In the medical field also, we will find the wide application of AI. Doctors assess the patients and their health risks with the help of artificial machine intelligence. It educates them about the side effects of various medicines.
- Medical professionals are often trained with artificial surgery simulators. It finds a huge application in detecting and monitoring neurological disorders as it can simulate the brain functions.
- Robotics is often used in helping mental health patients to come out of depression and remain active.
- A popular application of artificial intelligence is radiosurgery. Radiosurgery is used in operating tumours and this can actually help in the operation without damaging the surrounding tissues.
Agriculture Sector: AI can be utilised to predict advisories for sowing, pest control, input control = enable increased income and giving stability for the agricultural community . Image classification tools in addition to remote and locally sensed data can bring a revolutionary change in – utilisation and efficiency of farm machinery, weed removal, early disease identification, harvesting, and grading.
Business Sector:
- In order to take care of highly repetitive tasks – robotic automation is applied which perform faster, effortlessly and tirelessly than humans.
- Moreover, Machine learning algorithms are being integrated into analytics and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) platforms to provide better customer service. Chatbots being used in the websites to provide instant service to customers.
- Automation of job positions has also become a discussion point among academics and IT consultancies like Gartner and Forrester.
Education Sector:
- Artificial Intelligence can make certain educational processes automated like grading, rewarding marks, etc. thus giving educators more time.
- Furthermore, it can analyse students and adapt to their requirements so as to help them work at their own pace.
- AI can change where and how students learn, perhaps even replacing a few teachers.
Financial Sector:
- AI is applied to personal finance applications and could compile personal data and give financial advice. In fact, nowadays software trades more than humans in Wall Street.
- Detection of financial fraud uses artificial intelligence in a smart card-based system.
Legal Sector: Automation can result in a faster resolution of pending cases by minimising the time taken while analyzing cases = better use of time and more efficient legal & judicial processes.
Manufacturing sector: Robots are being utilised for manufacturing since a long time now but more advanced exponential technologies have emerged like additive manufacturing (3D Printing) which with the support of AI can revolutionize the whole manufacturing supply chain ecosystem.
Intelligent Robots: Robots can do the tasks given by a human with the help of sensors to detect physical data from the real world like light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure. Furthermore, they have effective processors, multiple sensors and enormous memory, to showcase intelligence. Also, they can learn from their errors and hence can adapt to the new environment.
Gaming: AI has a significant role in strategic games like chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where the machine can think of a huge number of possible positions according to heuristic rule (A set of rules intended to increase the probability of solving some problem).
Cyber Security : In the 20th conference on e-governance in India it was discussed that AI has the capability to strengthen cybersecurity ecosystem in India and should be explored further.
Smart Cities and Infrastructure: AI is used to monitor patronage and accordingly control associated systems such as pavement lighting, park maintenance, and other operational conditions = lead to cost savings + improving safety and accessibility.
Space sector: Intelligent robots are fed with information and are sent to explore space. Since they are machines with metal bodies, they are more resistant and have a higher ability to endure the space and hostile atmosphere. Because they are created in such a way that they cannot be modified or get disfigured or breakdown in a hostile environment.
Mining sector: Artificial intelligence and the science of robotics can be put to use in mining and other fuel exploration processes. Not only that, these complex machines can be used for exploring the ocean floor and hence overcome the human limitations.
Defence Sector: Artificial Intelligence (AI) based tools would aid the defence forces constructively in areas such as decision support, sensor data analysis, predictive maintenance, situational awareness, accurate data extraction, security, etc. These tools will assist defence personnel in better operations, maintenance, and logistics support.
What are the concerns with the AI?
- Replacement of humans with machines can lead to large-scale unemployment. Unemployment is a socially undesirable phenomenon. People with nothing to do can lead to the destructive use of their creative minds.
- Humans can unnecessarily be highly dependent on the machines if the use of artificial intelligence becomes rampant. They will lose their creative power and will become lazy.
- Also, if humans start thinking in a destructive way, they can create havoc with these machines.
Robot bosses
- If you have an issue with your current human boss, be thankful that he isn’t a cold, emotionless machine because AI is already being used to monitor employee productivity.
- In what seems like the scary nightmares of a dystopian future, IBM’s Watson has been using AI and Watson Analytics to decide if employees are worthy of a pay rise, a bonus or a promotion by looking at the experience and past projects of employees to judge the qualities and skills that individuals might have to serve the company in the future.
Human error
- Although AI can virtually remove human error from processes, it can still exist in the code, along with bias and prejudice.
- Being largely algorithm-based, technology can be coded to have a negative impact on certain demographics and discriminate against people.
- For example, Microsoft’s ill-fated chatbot, Tay Tweets, had to be taken down after only 16 hours after it started to tweet racist and inflammatory content – ideas it repeated from other Twitter users.
- Worryingly, if security is not 100%, hackers can take advantage of AI’s thirst for knowledge.
- Creation of artificial intelligence requires huge costs as they are very complex machines. Their repair and maintenance require huge costs.
- They have software programs which need frequent up-gradation to cater to the needs of the changing environment and the need for the machines to be smarter by the day.
- In the case of severe breakdowns, the procedure to recover lost codes and reinstating the system might require huge time and cost.
Not ethical to replicate Humans:
- Intelligence is believed to be a gift of nature. Therefore an ethical argument continues, whether human intelligence is to be replicated or not.
Cannot replicate Humans:
- Machines do not have any emotions and moral values. They perform what is programmed and cannot make the judgment of right or wrong. They cannot take decisions if they encounter a situation unfamiliar to them. They either perform incorrectly or breakdown in such situations.
- Unlike humans, artificial intelligence cannot be improved with experience. With time, it can lead to wear and tear. It stores a lot of data but the way it can be accessed and used is very different from human intelligence.
- Machines are unable to alter their responses to changing environments.
- In the world of artificial intelligence, there is nothing like working with a whole heart or passionately. Care or concerns are not present in the machine intelligence dictionary. There is no sense of belonging or togetherness or a human touch. They fail to distinguish between a hardworking individual and an inefficient individual.
No Original Creativity:
- While the AI can help you design and create, they are no match to the power of thinking that the human brain has or even the originality of a creative mind.
- Human beings are highly sensitive and emotional intellectuals. They see, hear, think and feel. Their thoughts are guided by the feelings which completely lacks in machines. The inherent intuitive abilities of the human brain cannot be replicated.
Privacy & Security:
The increasing accessibility of facial-recognition technology has also increased concerns with respect to privacy, security, and civil liberties.
What is the global status of AI adoption?
- China and the U.K. estimate that by 2030, about 26% and 10% of their GDPs respectively will be sourced from AI related activities and businesses.
- There have been numerous activities regarding AI policy positions and the development of an AI ecosystem in various countries in recent years.
- Infrastructural supply-side initiatives have been planned by several countries for building a larger ecosystem of AI development.
- Even local/city governments have become increasingly aware of the significance and potential of AI and have committed public investments.
- For creating the future workforce for AI, countries are also significantly increasing the allocation of resources for Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths (STEM) talent development via investment in universities, mandating new courses (e.g., AI and law), and launching schemes to retrain people.
- AI technology development and applications are rapidly evolving with major implications for economies and societies. A study by EY and NASSCOM found that by 2022, about 46 percent of the workforce will be engaged in entirely new jobs.

What are the possible areas for AI applications in Indian conditions?
- India has the potential to position itself among leaders on the global AI map – with a unique brand of #AIforAll.
- It can complement Digital India Mission by helping in the big data analysis which is not possible without using AI.
- Targeted delivery of services, schemes, and subsidy can be further fine-tuned.
- Smart border surveillance and monitoring to enhance security
- Weather forecasting models may become proactive and therefore preplanning for any future mishaps such as floods, droughts and therefore addressing the farming crisis, farmer’s suicide, crop losses, etc.
- By analyzing big data of road safety data and NCRB (National Crime Record Bureau) data for crimes , new policies can be formulated.
- Disaster management can be faster and more accessible with the help of robots and intelligent machines.
- In the counterinsurgency and patrolling operations, we often hear the loss of CRPF jawans which can be minimized by using the robotic army and lesser human personnel.
- AI can be used to automate government processes , therefore, minimizing human interactions and maximizing transparency and accountability.
- It can be applied to study ancient literature upon medicines and therefore help in modernizing the health care with the juxtaposition of modern machines and ancient techniques.
- In the remotest areas where the last leg of governance is almost broken, AI can do the job. For Example: in the tribal areas and the hilly areas of the northeast.
What are the measures taken by the government to promote AI?
- A Task Force on Artificial Intelligence (AI) for India’s Economic Transformation was constituted on 24 th August 2017. The Task Force gave its report on 19 th January 2018. It has recommended an Inter-Ministerial National Artificial Intelligence Mission to act as a nodal agency for coordinating AI related activities in India.
- NITI Aayog unveiled its discussion paper on national strategy on AI which seeks to guide research and development in new and emerging technologies. NITI has identified 5 sectors – healthcare , agriculture , education , smart cities and infrastructure , and transportation – to focus its efforts on the implementation of AI. The paper focusses on how India can leverage transformative technologies to ensure social and inclusive growth .
- Committee on platforms and data for AI,
- Committee on leveraging AI for identifying National Missions in key sectors,
- Committee on mapping technological capabilities, key policy enablers, skilling, re-skilling and R&D
- Committee on cybersecurity, safety, legal and ethical issues.
- Task Force created by the Ministry of Defence has studied research and innovation in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and outlined its adoption in defence sector including a future roadmap on how to integrate and embed AI strategy with a core defence strategy.
- In addition, the Defence Public Sector Undertakings and Ordnance Factories have been assigned a roadmap for developing AI-enabled products.
- Centre for artificial intelligence and robotics (CAIR), is the main laboratory of DRDO for research and development in various areas of defense, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and is located in Bangalore. It is involved in the Research & Development of high-quality Secure Communication, Command, and Control, and Intelligent Systems.
- Projects: NETRA- software to intercept online communication, SECOS- Secure operating system.
- India joined the league of leading countries including USA, UK, EU, Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Mexico, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Singapore to launch the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI or Gee-Pay) . GPAI is an international and multi-stakeholder initiative to guide the responsible development and use of AI in line with human rights, inclusion, diversity, innovation, and economic growth.
What are the challenges to India’s Artificial Intelligence Development?
- Lack of enabling ecosystems for data collection and usage.
- The low intensity of AI research.
- Insufficient availability of AI expertise, manpower and skilling opportunities.
- High resource cost and low awareness for adopting AI in business processes.
- Unclear privacy, security and ethical regulations.
- Unattractive Intellectual Property regime to incentivise research and adoption of AI.
What needs to be done?
- Incentivising the creation of jobs in AI fields that could constitute the new service industry.
- Recognition and standardisation of informal training institutions.
- Creation of open platforms for learning and financial incentives for reskilling of employees.
- The lack of qualified faculty that poses a serious problem in the present scenario can be addressed through innovative measures such as MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses).
- Acceptability and adoption of these decentralised teaching mechanisms can be ensured through prescribed certification in collaboration with the private sector and educational institutions.
- Additional investment and collaboration with the private sector and educational institutions in order to meet the market demand.
- To encourage the development of sustainable AI solutions at an appropriate price point for sectors such as health, education, and agriculture, it is necessary that a level playing field is ensured and an enabling environment be created for all players in the value chain.
- AI is a highly collaborative domain, and any framework aimed at promoting AI needs to be aligned accordingly. A multipronged approach, involving various stakeholders and promoting a collaborative approach is required for promoting the development of AI tools as well as the adoption of AI in various fields of activity.
- UNESCO’s Global Agreement on the Ethics of AI can guide governments and companies alike.
Way forward
Despite the threats and challenges, it would be foolish to argue that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not the future and it’s only a matter of time that machines will replace most of the jobs. It is because AI is not the end of the road for humanity as we have a history of technological revolutions resulting in positive social and political changes in society such as steam engines, industrial revolutions and most recently the computers and internet. Nonetheless, there will be several opportunities in the fields not yet known and there will be more jobs to serve human needs.

If you like this post, please share your feedback in the comments section below so that we will upload more posts like this.
GET MONTHLY COMPILATIONS
Related Posts

[Premium] Surrogacy Regulation in India: The Big-Picture Analysis
Add AIRAWAT. As always very very good article. Your efforts shows. Your site has become one stop solution for topics you cover. Thank you. Really appreciate your hard work, intelligence and presentation. Good luck.
Thank you so much. This article is so helpful and knowledgeable
Your article is really great. Thanks for sharing valuable information with us.
There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.


Artificial Intelligence: Types, Advantages & Disadvantages|UPSC Notes
Artificial Intelligence: It is changing the world as it has come to exist. It refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines so that they can think like humans and make intelligent decisions about their actions in many fields of study. Such technology has been applied across all fields: healthcare, finance, and so many more, which continue to evolve into new possibilities and challenges. AI operates on algorithms that learn and adapt to data hence their performance improves successively. This has drastically transformed what is witnessed today, especially because AI is very proportional to our daily lives.
- It makes machines identify sounds and make decisions.
- It can analyze huge amounts of data and give good information.
- There are two types of artificial intelligence namely; narrow AI and general AI.
- AI is a technology that makes users’ experiences come alive in applications such as virtual assistants and recommendation systems.
Table of Contents
What is Artificial Intelligence?
The term Artificial Intelligence refers to the development of systems or machines that are in some way mimicked from human intelligence, enabling the development of tasks such as reasoning, problem-solving, and learning. AI is built on machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks that automatically interpret data for better performance in due course. Technologically speaking, the fuel is a culmination of voice recognition systems, autonomous vehicles, and even complex medical diagnostics.
This Brief History of Artificial Intelligence traces back to when the scientist was probing into the simulation possibility of machine learning. Some of the early pioneers include Alan Turing and John McCarthy. In 1956, the term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined by McCarthy at the Dartmouth Conference to formally begin AI studies. Ever since its inception, AI has undergone boom-winter cycles many times with upsurges of rapid progress followed by a period of stagnation. However, recent technological breakthroughs have revived interest in AI and made it a mainstream phenomenon.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence will benefit many aspects of industries and individual lives. This is in healthcare, for example, where AI applications help doctors check diseases and suggest applicable treatments. In finance, AI algorithms can comb through market trends and make investment recommendations. A few examples include how artificial intelligence is shaping lives and jobs. Some of the Advantages of Artificial Intelligence include:
- Efficiency : AI has greater speed in processing huge databases than a human. This leads to more efficient processes, and therefore improvement in the decision-making processes in sectors like healthcare and finance.
- Accuracy : AI eliminates human error, which leads to better decisions.
- Automation : AI enables most repetitive tasks to be automated, thus saving resources and time.
- 24/7 Availability : Machines cannot get tired, so they are available to work on a 24/7 basis.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Despite its advantages, AI has drawbacks. Moreover, the cost of developing and sustaining AI is not within the reach of small businesses or developing countries. The Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence are as follows:
- Job Loss : AI will replace a human worker for the most repetitive and resource-intensive jobs; they lose their job.
- Bias and Discrimination : AI systems can perpetuate biases present in the data they are trained on out of error.
- Security Threats: AI technologies can be exploited to make the case of deepfakes or cyber-attacks.
- Lack of Emotional Intelligence : AI does not possess human emotions and consequently cannot have the empathetic decision-making capability that is so often required in many fields.

Types of Artificial Intelligence
There are several forms of Artificial Intelligence, each suited to different applications. Each form of AI has defined potentials and corresponding risks. Currently, Narrow AI is by far the most used form; however, researchers work on further developing much more advanced forms of AI. There are examples of some of the types next down below:
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI has a particular use; for example, it may consist of voice recognition or image processing. It possesses only a specific set of predefined conditions and performs exceptionally well on jobs that could be defined as virtual assistants or recommendation systems. Narrow AI lacks general intelligence or awareness beyond the task.
General AI, also known as Strong AI
General AI may understand, learn, and apply knowledge in an almost human range of tasks. It may perform any intellectual task a human can. To date, it remains a theoretical concept with no practical implementations. It requires a highly advanced level of self-awareness and adaptability.
Superintelligent AI
Superintelligent AI describes machines that are significantly advanced in every aspect of human intelligence, in terms of creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making. This form of AI has been thought to be only explored in science fiction in general but seems to surpass humans in every form of cognitive task. To date, it remains more theoretical and brings some very important ethical concerns and risks.
Reactive AI
Reactive AI is sensitive to particular stimuli and does not provide memories from previous experiences for later use. It simply executes pre-programmed instructions; it does not learn or adjust to new situations. Applications involving reactive AI include chess-playing programs and voice-activated assistants, which operate within set boundaries.
Little Memory AI
In deciding, the Limited Memory AI can learn from past data. It is that kind of AI that uses historical data to predict outcomes and to make adjustments, based on new information, after new data has arrived. Self-driving cars and fraud detection systems are only but a few examples of this AI, continually improving through the analysis of large datasets over time.
Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI is still under development and aims to understand human emotions, beliefs, and intentions. This type of AI will interact with people on a more implicit level due to its ability to track mental states and then form adequate responses based on them. It allows for human-like communication and decision-making but is yet to be fully realized.
Self-Aware AI
Self-knowing AI would have consciousness and self-awareness so that it will know its existence and environment. It would feel emotions, think, and introspect. This type of AI remains purely hypothetical, of course, involving major ethical, social, and technical challenges that need to be overcome before it can become possible.
India and Artificial Intelligence
In recent times, India has emerged as the hub for developing AI. India should be linked with Artificial Intelligence because the country is investing significantly in AI technologies to boost its economy. With the right investment, India can surely be at the forefront of AI globally. In addition, AI is anticipated to play a crucial role in helping India overcome challenges in health care delivery, and education access, as well as increasing productivity in agriculture. The government is working on the National AI Strategy to support the country in becoming a hub for the development of AI.
- AI Startups: Most of the AI startups in India operate mainly in the health, agriculture, and education sectors.
- Government Initiatives : Some government initiatives are targeting the development of talent and infrastructure.
- Challenges : Though India is a big player in progress, India is found to be challenged in a few areas, having very few AI professionals, and a lack of infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence in Daily Life
What AI does is simply get merged into the lives of people. Voice assistants help in scheduling, algorithms of social media curating personal content, and so much more – AI has upgraded the user’s experience. Applications on a daily level of AI are such that it can change or revolutionize whole industries or even change the way one interacts with technology. A few examples of how AI affects the daily life of an individual:
- Virtual Assistants : Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are AI-driven systems where they assist people in their daily work and provide answers.
- Recommendation Systems : AI has recommended movies, music, and products on Netflix and Amazon based on user preference.
- Healthcare : AI is used in medicine to diagnose diseases. By analyzing the medical data collected, AI suggests proper treatment to doctors.
Artificial Intelligence is indeed one of the most powerful tools that can revolutionize industries and help people lead quality lives. However, it brings risks to the table, to be managed considerably. Understanding what is Artificial Intelligence, its benefits, and also its challenges will prepare us well to face the future where AI plays a very big role in shaping our world.
Post navigation
Previous post.

Artificial Intelligence
Pre-cum-Mains GS Foundation Program for UPSC 2026 | Starting from 14th Nov. 2024 Click Here for more information
The NITI-Aayog has put forward a discussion paper on artificial intelligence in India
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
- Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or software perform human-like tasks.
- It refers to the ability of machines to perform cognitive tasks like thinking, perceiving, learning, problem solving and decision making.
- There are two subsets under the umbrella term AI: Machine learning and Deep learning
- Machine Learning involves the use of algorithms to parse data and learn from it. This enables making a determination or prediction.
- Deep learning is technique for implementing machine learning.
- The term was coined in 1956 by John McCarthy

Evolution of AI

Categorization of AI:

Advantages of AI
- No leisure time required
- Lower error rate compared to humans. Better precision and accuracy. Eg: Robotic radio surgery
- Better speed
- Not affected by surrounding environment
- Replace humans in repetitive, tedious tasks
- Better user experience through predictive technology e.g. Help in predicting what a user will type, ask, search, and do. Can easily act as assistants and recommend actions.
- Interact with humans for entertainment or a task. E.g. Sophia robot
- Logical – devoid of emotions. Can make rational decisions with less or no mistakes.
Disadvantages:
- Initial cost too high
- Cannot take decisions if they encounter a situation unfamiliar to them.
- Repair costs are high
- May lead to destruction, if put in the wrong hands. E.g. terrorists
- May have Impact on employment
- Ethical concerns:

Application of AI:
Agriculture:
Application of AI in agriculture can help in increasing crop yield by providing real-time advisory, early detection of pest attacks, prediction of crop prices, precision farming etc.
- PEAT – Machine Vision for Diagnosing Pests / Soil Defects
Berlin-based agricultural tech start-up PEAT has developed a deep learning application called Plantix that reportedly identifies potential defects and nutrient deficiencies in soil.
- CROPTIX- diagnose crop diseases in the field and alert rural farmers in Kenya
It is a new mobile app that uses artificial intelligence to accurately diagnose crop diseases in the field
- Microsoft -ICRISAT AI Sowing App: The app sends sowing advisories to participating farmers on the optimal date to sow
- Healthcare:
Can be used in diagnosis, treatment design, imaging diagnosis, early detections of disease outbreaks, robot assisted surgeries, virtual nurse assistants etc.
- Sensely’s “Molly” – an AI-powered nurse used by UCSF and the UK’s NHS to interact with patients
- Recently, researchers at an Oxford hospital developed AI that can diagnose scans for heart disease and lung cancer
- Can be used for developing tools for customised learning, interactive and intelligent tutoring systems, and predicting tools- for example predicting dropouts
- Can also be used in developing automated teacher posting and transfer systems, using analytics based on demand – supply gaps across schools
Pearsons’ WriteToLearn software:
It uses natural language processing technology to give students personalised feedback, hints, and tips to improve their writing skills
- Urban planning:
Can be used for optimizing infrastructure in cities, service delivery, crowd management, cyber security, public safety and water and waste management
In Kerala, engineers have developed sewer-cleaning robots to put an end to manual scavenging
- Transportation:
- Can be used in developing AI-based traffic management system including sensors, CCTV cameras, automatic number plate recognition cameras, speed detection cameras, signalised pedestrian crossings
- Can help in predictions in public transport journeys
- Can help in optimising parking
Intelligent traffic signals at Pittsburgh
Smart parking garages in USA
Can be used in customer demand anticipation, improved inventory management, efficient delivery management, interaction with customers etc
Japan’s Pepper:
It is a humanoid robot that can interact with customers and “perceive human emotions”.
- Manufacturing:
Can be used in supply chain management, predictive maintenance, logistics, and quality assurance
General Electric’s Brilliant Manufacturing:
Designed to make the entire manufacturing process more efficient and thus reduce costs.
Can be used in energy system modelling, predictive analysis, demand and infrastructure management, renewable management, building energy efficient buildings, etc
EWeLiNE, Germany:
It can work as an early-warning system for grid-operators to assist them in calculating renewable-energy output over the next 48 hours using AI
Areas of application of AI in defence include:
- Intelligent and Autonomous Unmanned Weapon Systems
- Tactical artificial intelligence: Tactical AI analyzes the battlefield and acts on information by creating a Course of Action that exploit the weaknesses in enemy’s position
- AI-Enabled Data Fusion, Information Processing, and Intelligence Analysis
- Cyber defence and cyber warfare
AI powered planning tool, USA
Global Developments:
Various initiatives taken by countries to promote and develop artificial intelligence

Artificial Intelligence in India
Why does India need AI?
- To reap economic benefit
- According to a research by Accenture, AI can boost India’s annual growth rate by 1.3 percentage points by 2035.
- Business opportunities: Can host enterprises and institutions globally to develop AI technology which can be easily implemented in the rest of the developing and emerging economies
- Social development and inclusive growth
AI developments in India:
- There has been an increase in AI focused start-ups
- According to a PwC research, 36 percent large financial establishments in India have invested in AI technologies
- Artificial Intelligence Industry in India is currently estimated to be $180 Million annually in revenues
- Center for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (CAIR) in DRDO conducts research in artificial intelligence
- Indian Army already has Wheeled Robot with Passive Suspension, Snake Robot, Legged Robot, Wall-Climbing Robot, and Robot Sentry,
- CAIR has been working on a project to develop a Multi Agent Robotics Framework (MARF)- will have array of robots functioning as human soldiers
Health Sector:
- NITI Aayog is working with Microsoft and Forus Health to introduce a technology for early detection of diabetic retinopathy as a pilot project
- 3nethra developed by Forus Health for detecting common eye problems
- NITI Aayog and IBM have partnered to develop a crop yield prediction model using AI to provide real time advisory to farmers.
- Andhra Pradesh government has collaborated with Microsoft to predict drop-outs and address the issue
Urban infrastructure and Transport:
- Pune Street Light Project- energy efficient street lights: can be remote controlled through a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems.
- Surat has collaborated with Microsoft to develop solutions for water management and urban planning.
- Traffic Management System based on radar-based monitoring with the help of AI to be used in Delhi
- Kamakoti Committee:
AI Task Force headed by V.Kamakoti was set up to to explore possibilities to leverage AI for development across various fields.
Key recommendations:
- Set up digital data banks, marketplaces and exchanges to ensure availability of cross-industry information
- Data ombudsman: to address data-related issues and grievances.
- Ensure availability of funds for R&D
- Setting up National Artificial Intelligence Mission (N-AIM)
10 domains need attention:
- Manufacturing
- Agriculture
- Retail/Customer engagement
- Public utility services
- Aid for differently-abled persons/Accessibility technology
- Environment
- National security
- Education and awareness
National strategy on artificial intelligence
- NITI Aayog in its recent discussion paper addresses the national strategy on artificial intelligence.
- It identifies 5 cores areas for application of artificial intelligence:
- Healthcare : increased access and affordability of quality healthcare
- Agriculture : enhanced farmers’ income, increased farm productivity and reduction of wastage
- Education : improved access and quality of education
- Smart Cities and Infrastructure : efficient and connectivity for the burgeoning urban population
- Smart Mobility and Transportation : smarter and safer modes of transportation and better traffic and congestion problems
Challenges to Adoption in India
- Unavailability of proper data ecosystem
- Insufficient funding and research in AI.
- Inadequate availability of AI expertise, manpower and skilling opportunities
- High resource cost
- Low awareness for adopting AI in business processes
- Lack of proper privacy, security and ethical regulations
- Unattractive Intellectual Property regime. This hinders research and adoption of AI
- Unemployment issues
Way Forward
- Two-tiered structure for AI research:
- Centre of Research Excellence (CORE) focused on developing a better understanding of existing core research and pushing technology frontiers through creation of new knowledge
- International Centres of Transformational AI (ICTAI) for developing and deploying application-based research. Private sector collaboration is considered to be a key aspect of ICTAIs.

- Increased public sector spending.
- Private investment
- Achieve excellence in AI research
Best Practice:
- EU’s Robotics Public Private Partnership, 2013:
- One of the biggest civilian research programme- has helped Europe in emerging among top robot manufacturers.
- Skilling and Re-skilling of workforce, help in adoption of AI
- Facilitating creation of large foundational annotated data sets
- Partnership of Industries and Academia
- Supporting start-ups
- Spreading awareness on advantages of AI
- Taxing of Robots: Bill Gates had suggested that governments should tax companies using robots. This tax could be used for funding human services.

Type your email…
Search Articles
Prelims 2024 current affairs.
- Art and Culture
- Indian Economy
- Science and Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- International Relations
- Polity & Nation
- Important Bills and Acts
- International Organizations
- Index, Reports and Summits
- Government Schemes and Programs
- Miscellaneous
- Species in news
Post-Mains Strategy Session by Mr. Ayush Sinha | ForumIAS
Civilsdaily
No. 1 UPSC IAS Platform for preparation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Breakthrough
Artificial intelligence (ai): understanding its potential, risks, and the need for responsible development.
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important :
Prelims level: AI applications, Artificial General Intelligence, and latest developments
Mains level: AI's potential, Concerns and need for responsible development and deployment
Central Idea
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) has garnered considerable attention due to its remarkable achievements and concerns expressed by experts in the field. The Association for Computing Machinery and various AI organizations have emphasized the importance of responsible algorithmic systems. While AI excels in narrow tasks, it falls short in generalizing knowledge and lacks common sense. The concept of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) remains a topic of debate, with some believing it to be achievable in the future.
AI Systems: Wide Range of Applications
- Healthcare : AI can assist in medical diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized medicine, patient monitoring, and data analysis for disease prevention and management.
- Finance and Banking: AI can be utilized for fraud detection, risk assessment, algorithmic trading, customer service chatbots, and personalized financial recommendations.
- Transportation and Logistics : AI enables autonomous vehicles, route optimization, traffic management, predictive maintenance, and smart transportation systems.
- Education : AI can support personalized learning, intelligent tutoring systems, automated grading, and adaptive educational platforms.
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants improve customer interactions, provide real-time support, and enhance customer experience.
- Natural Language Processing : AI systems excel in speech recognition, machine translation, sentiment analysis, and language generation, enabling more natural human-computer interactions.
- Manufacturing and Automation: AI helps optimize production processes, predictive maintenance, quality control, and robotics automation.
- Agriculture : AI systems aid in crop monitoring, precision agriculture, pest detection, yield prediction, and farm management.
- Cybersecurity: AI can identify and prevent cyber threats, detect anomalies in network behavior, and enhance data security.
- Environmental Management: AI assists in climate modeling, energy optimization, pollution monitoring, and natural disaster prediction.

Some of the key limitations of AI systems
- Lack of Common Sense and Contextual Understanding: AI systems struggle with common sense reasoning and understanding context outside of the specific tasks they are trained on. They may misinterpret ambiguous situations or lack the ability to make intuitive judgments that humans can easily make.
- Data Dependence and Bias : AI systems heavily rely on the data they are trained on. If the training data is biased or incomplete, it can result in biased or inaccurate outputs. This can perpetuate societal biases or discriminate against certain groups, leading to ethical concerns.
- Lack of Explainability : Deep learning models, such as neural networks, are often considered “black boxes” as they lack transparency in their decision-making process. It can be challenging to understand why AI systems arrive at a specific output, making it difficult to trust and verify their results, especially in critical domains like healthcare and justice.
- Limited Transfer Learning: While AI systems excel in specific tasks they are trained on, they struggle to transfer knowledge to new or unseen domains. They typically require large amounts of labeled data for training in each specific domain, limiting their adaptability and generalization capabilities.
- Vulnerability to Adversarial Attacks: AI systems can be susceptible to adversarial attacks, where input data is manipulated or crafted in a way that causes the AI system to make incorrect or malicious decisions. This poses security risks in applications such as autonomous vehicles or cybersecurity.
- Ethical and Legal Considerations: The deployment of AI systems raises various ethical and legal concerns, such as privacy infringement, accountability for AI-driven decisions, and the potential impact on human employment. Balancing technological advancements with ethical and societal considerations is a significant challenge.
- Computational Resource Requirements : Training and running complex AI models can require substantial computational resources, including high-performance hardware and large-scale data storage. This can limit the accessibility and affordability of AI technology, particularly in resource-constrained environments.
What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
- AGI is a hypothetical concept of AI systems that possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks and domains, similar to human intelligence.
- Unlike narrow AI systems, which are designed to excel at specific tasks, AGI aims to achieve a level of intelligence that surpasses human capabilities and encompasses general reasoning, common sense, and adaptability.
- The development of AGI is considered a significant milestone in AI research, as it represents a leap beyond the limitations of current AI systems.
Concerns and Dangers Associated with the Development and Deployment of AI systems
- Superhuman AI : One concern is the possibility of highly intelligent AI systems surpassing human capabilities and becoming difficult to control. The fear is that such AI systems could lead to unintended consequences or even pose a threat to humanity if they were to act against human interests.
- Malicious Use of AI: AI tools can be misused by individuals with malicious intent. This includes the creation and dissemination of fake news, deepfakes, and cyberattacks. AI-powered tools can amplify the spread of misinformation, manipulate public opinion, and pose threats to cybersecurity.
- Biases and Discrimination : AI systems are trained on data, and if the training data is biased, it can lead to biased outcomes. AI algorithms can unintentionally perpetuate and amplify societal biases, leading to discrimination against certain groups. This bias can manifest in areas such as hiring practices, criminal justice systems, and access to services.
- Lack of Explainability and Transparency : Deep learning models, such as neural networks, often lack interpretability, making it difficult to understand why an AI system arrived at a specific decision or recommendation. This lack of transparency can raise concerns about accountability, trust, and the potential for bias or errors in critical applications like healthcare and finance.
- Job Displacement and Economic Impact: The increasing automation brought about by AI technologies raises concerns about job displacement and the impact on the workforce. Some jobs may be fully automated, potentially leading to unemployment and societal disruptions. Ensuring a smooth transition and creating new job opportunities in the AI-driven economy is a significant challenge.
- Security and Privacy: AI systems can have access to vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy breaches and unauthorized use of sensitive information. The potential for AI systems to be exploited for surveillance or to bypass security measures poses risks to individuals and organizations.
- Ethical Considerations: As AI systems become more advanced, questions arise regarding the ethical implications of their actions. This includes issues like the responsibility for AI-driven decisions, the potential for AI systems to infringe upon human rights, and the alignment of AI systems with societal values.
The Importance of Public Oversight and Regulation
- Ethical and Moral Considerations: AI systems can have significant impacts on individuals and society at large. Public oversight ensures that ethical considerations, such as fairness, transparency, and accountability, are taken into account during AI system development and deployment.
- Protection against Bias and Discrimination: Public oversight helps mitigate the risk of biases and discrimination in AI systems. Regulations can mandate fairness and non-discrimination, ensuring that AI systems are designed to avoid amplifying or perpetuating existing societal biases.
- Privacy Protection: AI systems often handle vast amounts of personal data. Public oversight and regulations ensure that appropriate safeguards are in place to protect individuals’ privacy rights and prevent unauthorized access, use, or abuse of personal information.
- Safety and Security: AI systems, particularly those used in critical domains such as healthcare, transportation, and finance, must meet safety standards to prevent harm to individuals or infrastructure. Public oversight ensures that AI systems undergo rigorous testing, verification, and certification processes to ensure their safety and security.
- Transparency and Explainability: Public oversight encourages regulations that require AI systems to be transparent and explainable. This enables users and stakeholders to understand how AI systems make decisions, enhances trust, and allows for the detection and mitigation of errors, biases, or malicious behavior.
- Accountability and Liability: Public oversight ensures that clear frameworks are in place to determine accountability and liability for AI system failures or harm caused by AI systems. This helps establish legal recourse and ensures that developers, manufacturers, and deployers of AI systems are accountable for their actions.
- Social and Economic Impacts: Public oversight and regulation can address potential negative social and economic impacts of AI, such as job displacement or economic inequalities. Regulations can promote responsible deployment practices, skill development, and the creation of new job opportunities to ensure a just and inclusive transition to an AI-driven economy.
- International Cooperation and Standards: Public oversight and regulation facilitate international cooperation and the establishment of harmonized standards for AI development and deployment. This promotes consistency, interoperability, and the prevention of global AI-related risks, such as cyber threats or misuse of AI technologies.
Way Ahead: Preparing India for AI Advancements
- Awareness and Education: Foster awareness about AI among policymakers, industry leaders, and the general public. Promote education and skill development programs that focus on AI-related fields, ensuring a skilled workforce capable of driving AI innovations.
- Research and Development : Encourage research and development in AI technologies, including funding for academic institutions, research organizations, and startups. Support collaborations between academia, industry, and government to promote innovation and advancements in AI.
- Regulatory Framework: Establish a comprehensive regulatory framework that balances innovation with responsible AI development. Create guidelines and standards addressing ethical considerations, privacy protection, transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI systems. Engage in international discussions and cooperation on AI governance and regulation.
- Indigenous AI Solutions: Encourage the development of indigenous AI solutions that cater to India’s specific needs and challenges. Support startups and innovation ecosystems focused on AI applications for sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, education, governance, and transportation.
- Data Governance : Formulate policies and regulations for data governance, ensuring the responsible collection, storage, sharing, and use of data. Establish mechanisms for data protection, privacy, and informed consent while facilitating secure data sharing for AI research and development.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Foster collaborations between academia, industry, and government entities to drive AI research, development, and deployment. Encourage public-private partnerships to facilitate the implementation of AI solutions in sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and governance.
- Ethical Considerations : Promote discussions and awareness about the ethical implications of AI. Encourage the development of ethical guidelines for AI use, including addressing bias, fairness, accountability, and the impact on society. Ensure that AI systems are aligned with India’s cultural values and societal goals.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Improve infrastructure and connectivity to support AI applications. Enhance access to high-speed internet, computing resources, and cloud infrastructure to facilitate the deployment of AI systems across the country, including rural and remote areas.
- Collaboration with International Partners: Collaborate with international partners in AI research, development, and policy exchange. Engage in global initiatives to shape AI standards, best practices, and regulations.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly monitor the implementation and impact of AI systems in various sectors. Conduct evaluations to identify potential risks, address challenges, and make necessary adjustments to ensure responsible and effective use of AI technologies.
- The journey towards AGI is still uncertain, but the risks posed by malicious use of AI and inadvertent harm from biased systems are real. Striking a balance between innovation and regulation is necessary to ensure responsible AI development. India must actively engage in discussions and establish a framework that safeguards societal interests while harnessing the potential of AI for its development.
Get an IAS/IPS ranker as your 1: 1 personal mentor for UPSC 2024

JOIN THE COMMUNITY
Join us across social media platforms., your better version awaits you.
- AI Education in India
- Speakers & Mentors
- AI services
The transformative impact of artificial intelligence on the UPSC essay
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a prominent and intriguing topic in today’s advanced technological world. With the rapid development and implementation of AI systems, the relevance of artificial intelligence for the UPSC examination has come into focus. This essay will explore the significance of AI in the UPSC exam and its impact on various aspects of the examination process.
Artificial intelligence, as a field of study, encompasses various technologies and algorithms that allow machines to exhibit human-like intelligence. For the UPSC exam, AI offers numerous advantages. One of the key benefits is the ability of AI systems to analyze vast amounts of data and provide valuable insights. This can be particularly useful in the analysis of previous question papers and the prediction of potential question patterns.
Furthermore, AI can assist in the evaluation and assessment of answer scripts. By utilizing machine learning algorithms, AI systems can analyze and grade answer scripts, reducing the subjectivity and bias that can be inherent in manual evaluation. This can lead to a fair and objective evaluation process, ensuring that all candidates are treated equally.
In addition, AI-powered chatbots can be developed to provide instant and accurate answers to queries related to the UPSC exam. This can be immensely helpful for candidates who require quick clarification or guidance. The availability of such chatbots can enhance the accessibility and support provided to aspirants, ultimately improving their chances of success in the examination.
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination has the potential to revolutionize and enhance various aspects of the exam. From data analysis and prediction to evaluation and support, AI can play a pivotal role in ensuring a fair and efficient examination process. As technology continues to advance, it is imperative for UPSC to explore and embrace the benefits that artificial intelligence brings to the table.
Definition of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that focuses on the creation of intelligent machines that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. AI is characterized by the ability of machines to exhibit traits such as learning, problem-solving, perception, and understanding natural language. While the field of AI has been evolving for several decades, it has gained significant attention and relevance in recent years.
Relevance of Artificial Intelligence
The relevance of artificial intelligence in the context of the UPSC examination cannot be understated. As technology continues to advance and permeate every aspect of society, it is vital for aspiring civil servants to have a comprehensive understanding of AI. The application and implications of AI in areas such as governance, healthcare, finance, defense, and education are immense, and policymakers and administrators must be equipped to make informed decisions about its implementation.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Society
Artificial intelligence has the potential to revolutionize various sectors, bringing about both benefits and challenges. While the automation of routine tasks can increase efficiency and productivity, it also raises concerns about job displacement and income inequality. The ethical implications of AI, such as privacy and bias, also need to be carefully considered and addressed.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence is a rapidly growing field with significant implications for society and the UPSC examination. Aspiring civil servants must acquire a deep understanding of AI and its various dimensions to navigate the complex challenges and opportunities that it presents.
Importance of Artificial Intelligence in UPSC Exam
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become an essential part of modern society, and its relevance in the field of education and examination cannot be overlooked. UPSC examination, being one of the most prestigious and competitive exams in the country, can greatly benefit from the integration of AI.
AI technology can be utilized in various aspects of the UPSC exam, starting from the initial application process to the evaluation of answer scripts. With the help of AI algorithms, the examination authorities can ensure a fair and transparent evaluation process, reducing the chances of bias and human error.
AI-powered essay evaluation systems can provide instant feedback to the candidates, helping them improve their writing skills. These systems can analyze the content, grammar, and structure of the essays, allowing the candidates to understand their strengths and weaknesses. This would enable the candidates to focus on areas that need improvement, ultimately enhancing their performance in the UPSC exam.
Furthermore, AI can be used to monitor and detect instances of plagiarism in the examination. With the ability to compare thousands of essays within seconds, AI algorithms can provide accurate reports on the originality of the content. This would discourage the use of unethical practices and ensure the integrity of the examination.
AI can also assist in personalized learning, where it can provide tailored study materials and resources to each candidate based on their strengths and weaknesses. This would enable candidates to receive targeted guidance and support, improving their overall preparation for the UPSC exam.
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence in the UPSC exam is of utmost importance. Its potential to enhance the examination process, provide personalized learning, and ensure fairness and transparency makes it a valuable tool for the UPSC aspirants. As technology continues to evolve, its role in the education sector will only become more significant, and the UPSC examination should embrace the benefits that AI can offer.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Society
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a significant part of modern society, and its relevance is evident in various spheres such as education, healthcare, business, and governance. In the competitive world of the UPSC examination, AI has made a significant impact.
UPSC, or the Union Public Service Commission, is responsible for conducting one of the toughest examinations in India. The exam is known for its rigorous selection process and covers a wide range of subjects and topics. With the advent of AI, the examination process has become more efficient and effective.
AI-powered systems assist examiners in managing the examination process. These systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and provide insights to help in decision-making. They can automate administrative tasks such as verifying eligibility criteria, managing applications, and generating admit cards. By reducing manual workload, AI improves the overall efficiency of the examination process.
Furthermore, AI can also play a role in enhancing the accuracy and fairness of the examination. AI algorithms can be used to analyze past question papers, identify patterns, and generate model answers. This helps in setting appropriate question patterns and evaluating the answers of candidates objectively. AI-powered systems can also detect anomalies or instances of cheating during the examination, maintaining the integrity of the process.
Another area where AI can be beneficial is in providing personalized learning resources for UPSC aspirants. AI-powered platforms can analyze the strengths and weaknesses of candidates and recommend specific study materials and strategies to help them improve their performance. This personalized approach can significantly enhance the learning experience and increase the chances of success in the examination.
In conclusion, the role of artificial intelligence in modern society cannot be underestimated, especially in the context of UPSC examinations. Its ability to streamline administrative processes, enhance accuracy, and provide personalized learning resources makes it a valuable tool. As technology continues to advance, the use of AI in the UPSC examination will undoubtedly increase, leading to a more efficient and fair selection process.
UPSC Essay Topic on Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) has gained significant relevance in the modern world. It is a technology that imitates human intelligence, enabling machines to think, learn, and perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence. The UPSC examination, being a crucial exam for aspiring civil servants, holds great importance for the field of AI.
Relevance of Artificial Intelligence for the UPSC Exam
The UPSC exam evaluates candidates on various aspects, including knowledge, analytical abilities, decision-making skills, and adaptability. These are precisely the areas where AI can play a significant role. With the use of AI, the UPSC exam can utilize advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms to assess candidates more effectively.
AI can assist in the examination process by automating tasks such as evaluation of subjective answers, generating personalized study recommendations, and analyzing vast amounts of data for pattern recognition. This automation can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of the evaluation process, saving time and effort for both candidates and evaluators.
The Benefits of AI in the UPSC Examination
Integrating AI in the UPSC examination has several advantages. Firstly, it can help in customizing the exam experience for individual candidates. Through AI-driven adaptive learning systems, the exam can identify candidates’ strengths and weaknesses and generate personalized study plans to maximize learning outcomes. This personalized approach can significantly improve the efficiency of the exam preparation process.
Secondly, AI can provide valuable insights and analytics to both candidates and evaluators. By analyzing past exam data, AI algorithms can identify patterns, trends, and key areas of improvement for candidates. This information can be used to guide candidates in their preparation and provide targeted feedback and suggestions.
Lastly, AI can minimize human biases in the evaluation process. By removing human subjectivity, AI algorithms can ensure a fair and unbiased examination. This is particularly important in a highly competitive exam like the UPSC, where even the slightest bias can have a significant impact on a candidate’s success.
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination holds great promise. By leveraging AI technologies, the exam can become more efficient, personalized, and fair. With the rapid advancements in AI, it is crucial for the UPSC and other examination bodies to embrace this technology and adapt to the changing landscape. AI can revolutionize the examination process and contribute to the overall improvement of the assessment system.
Artificial Intelligence and its Impact
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a topic of examination and relevance in various fields, including UPSC. Its potential to transform industries, societies, and our daily lives cannot be underestimated. In this essay, we will explore the impact of AI on different aspects of society.
1. Economy and Industry
AI has the potential to revolutionize the economy and industries in numerous ways. With its ability to analyze vast amounts of data and make predictions, AI can help businesses make informed decisions and improve efficiency. It can also automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more complex tasks. However, there are concerns about job displacement and the need for re-skilling the workforce to adapt to a more AI-driven economy.
2. Healthcare
AI is transforming the healthcare industry by improving diagnostics, treatment, and patient care. AI-powered algorithms can analyze medical records and images to detect diseases early and accurately. This can lead to faster diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. AI can also assist doctors and surgeons in decision-making, reducing errors and increasing success rates. However, ethical considerations and data privacy issues need to be addressed to ensure the responsible use of AI in healthcare.
3. Education
AI has the potential to revolutionize education by personalizing learning experiences for students. Intelligent tutoring systems can adapt to the individual needs and pace of each student, enhancing engagement and improving learning outcomes. AI can also automate administrative tasks for teachers, allowing them to focus more on instructional activities. However, there are concerns about data privacy and the need for skilled educators to effectively integrate AI in the classroom.
4. Ethics and Society
The rise of AI brings about ethical considerations and societal impact. AI algorithms can reinforce existing biases or create new ones, leading to discrimination and inequality. There are concerns about privacy, transparency, and accountability in AI systems. It is crucial to ensure that AI is developed and used in a way that is fair, transparent, and respects human values.
In conclusion, the impact of artificial intelligence on different aspects of society is vast and transformative. While AI brings immense potential for advancement, it also requires careful consideration and regulation to address the associated challenges. Policymakers, industry leaders, and society as a whole must work together to harness AI for the benefit of all.
Benefits of Studying Artificial Intelligence for UPSC
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become increasingly relevant in today’s world, and its examination for UPSC holds great significance. Studying AI can provide numerous benefits for aspiring UPSC candidates, helping them in various aspects of the exam.
1. Enhances Problem-solving Skills:
Studying artificial intelligence equips candidates with advanced problem-solving abilities. The field of AI focuses on developing algorithms and models that can replicate human intelligence to solve complex problems. By learning AI, UPSC aspirants can enhance their analytical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are crucial for cracking the examination.
2. Keeps Candidates Updated:
AI is experiencing rapid advancements, with new technologies and approaches being developed continuously. By studying artificial intelligence, UPSC candidates can stay updated with the latest trends and developments in the field. This knowledge can be highly advantageous in the exam, as it allows candidates to provide relevant and up-to-date examples in their essays or answers, showcasing their awareness of current issues.
Moreover, AI is increasingly being integrated into various sectors and governance systems. Understanding its applications and implications can provide UPSC aspirants with insights into the changing dynamics of governance and policymaking, which can prove valuable in answering questions related to governance and current affairs.
Conclusion:
Studying artificial intelligence can benefit UPSC candidates by enhancing their problem-solving skills and keeping them updated with the latest trends and developments. It provides them with a deeper understanding of the relevance and impact of AI on various sectors, which can be instrumental in answering questions related to governance, technology, and current affairs. In an ever-evolving world, staying ahead with knowledge of artificial intelligence can give UPSC aspirants a competitive edge in the examination.
Current Trends in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence has become an extremely relevant topic in the current era, especially in the field of education. The use of AI technologies, such as natural language processing and machine learning, has revolutionized the way examinations are conducted, including the UPSC examination.
One of the main trends in AI is the development of intelligent exam assessment systems. These systems are capable of grading essays and short answers, providing a fair and unbiased evaluation of students’ knowledge and understanding. This is particularly relevant for the UPSC examination, where essay writing plays a crucial role in the selection process.
AI technologies have also made it possible to conduct online examinations, making the process more convenient and accessible for candidates. This has eliminated the need for physical examination centers and has allowed for greater flexibility in scheduling the exams. Additionally, AI algorithms can detect cheating attempts and ensure the integrity of the examination.
The relevance of AI for the UPSC examination
Artificial intelligence has significantly transformed the UPSC examination by introducing innovative assessment methods and improving the overall examination experience. With the use of AI, the UPSC can efficiently evaluate the knowledge and skills of a large number of applicants, ensuring fairness and transparency in the selection process.
Moreover, AI technologies have enabled the automation of administrative tasks, such as application processing and document verification. This has reduced the burden on administrative staff and improved the efficiency of the examination process.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence has brought numerous advancements to the field of education and has had a profound impact on the UPSC examination. With its ability to assess exams, detect cheating, and automate administrative tasks, AI has made the examination process more streamlined, efficient, and fair for all candidates.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) has grown exponentially in relevance over the past few decades. With its rapid advancements in technology and its potential to revolutionize various industries, AI has become a topic of study and discussion, especially for UPSC exam aspirants. However, along with its benefits, AI also poses significant challenges and ethical considerations that need to be addressed.
1. Bias and Discrimination
One of the major challenges in AI is the issue of bias and discrimination. AI systems are trained on large datasets, but these datasets often contain biases that exist in society. As a result, AI algorithms can inadvertently amplify existing biases and discriminate against certain groups of people. It is essential to ensure that AI systems are developed and trained in a way that is fair and unbiased.
2. Data Privacy and Security
Another challenge in AI is the protection of data privacy and security. AI systems require vast amounts of data to learn and make accurate predictions. However, this data often includes sensitive and personal information. It is crucial to establish proper regulations and mechanisms to protect the privacy of individuals and prevent misuse or unauthorized access to their data.
Furthermore, AI systems themselves can be vulnerable to cyber attacks and hacking. As AI becomes more prevalent in various sectors, the potential for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities in AI systems and manipulate them for their gain increases. Therefore, ensuring the security of AI systems is paramount.
In conclusion, the field of artificial intelligence presents immense opportunities and challenges. Aspirants preparing for the UPSC examination must understand the relevance and importance of these challenges and ethical considerations in the development and deployment of AI systems. Addressing issues such as bias and discrimination, as well as data privacy and security, is essential to ensure that AI benefits society as a whole.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Various Fields
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a revolutionary technology with vast applications in different fields. This essay explores the diverse range of applications and the impact that AI has made in these areas.
One of the major areas where AI has been extensively used is in healthcare. Medical professionals are now able to leverage AI to enhance diagnosis, treatment planning, and drug discovery. AI algorithms can analyze medical data, such as patient scans and records, and provide accurate predictions and recommendations. This has led to faster and more efficient healthcare delivery, saving lives and improving patient outcomes.
Another field where AI has shown immense potential is in the financial sector. AI-based systems can analyze large amounts of financial data and detect patterns and trends that humans may miss. This helps in making accurate predictions about stock market trends, investment opportunities, and risk assessment. AI-powered chatbots are also being used by banks to provide customer support and personalized financial advice.
AI is also making waves in the field of transportation and logistics. Self-driving cars, which rely on AI algorithms to navigate and make decisions on the road, are being developed and tested by major automobile companies. AI is also being used in optimizing routes, predicting traffic patterns, and managing the supply chain logistics of delivery companies. This has the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry and make it more efficient and sustainable.
Furthermore, AI has also found applications in the field of education. Intelligent tutoring systems can adapt to each student’s learning style and provide personalized guidance and feedback. AI-powered virtual reality simulations can create more engaging and interactive learning experiences. AI algorithms can also analyze large amounts of educational data to identify areas of improvement and suggest interventions for better learning outcomes.
These are just a few examples of how AI is being utilized in various fields. The potential of AI is vast, and its impact on society and economy is only expected to grow in the coming years. As we embrace this technology, it is crucial to address ethical and privacy concerns and ensure that AI is used for the benefit of humanity and not in a detrimental manner.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Science
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a rapidly growing field that has gained immense popularity in recent years. In the digital age, the vast amount of data generated every day has created a need for advanced techniques to analyze and interpret this data. This is where the relevance of artificial intelligence and data science comes into play.
Artificial Intelligence in Examination
In the context of examinations, artificial intelligence has the potential to address various challenges faced by students and educators alike. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict outcomes, and provide personalized learning plans. These tools can help students improve their performance by providing targeted feedback and recommendations based on their individual needs.
AI can also be used to detect cheating and plagiarism during examinations. By analyzing patterns in students’ responses and comparing them with a vast database of known answers, AI systems can identify instances of academic dishonesty and flag them for further investigation. This can help maintain the integrity of the examination process and ensure a level playing field for all students.
Data Science and its Relevance for Artificial Intelligence
Data science plays a crucial role in the development and deployment of artificial intelligence systems. It involves the collection, processing, and analysis of large amounts of data to extract valuable insights and make informed decisions. Without data science, the field of artificial intelligence would not be able to leverage the power of data to drive innovation and provide meaningful solutions.
Data scientists use various techniques and tools to clean, transform, and analyze data. They apply statistical methods, machine learning algorithms, and other advanced techniques to extract patterns, make predictions, and gain a deeper understanding of the data. This information is then used to train and improve artificial intelligence models, enabling them to perform complex tasks with accuracy and efficiency.
Furthermore, data science helps in addressing the ethical and social implications of artificial intelligence. By analyzing the data and considering factors like fairness, bias, and accountability, data scientists can develop AI systems that are more transparent, equitable, and reliable. This ensures that the benefits of artificial intelligence are realized without compromising ethical principles.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence and data science are intrinsically linked and complement each other. While AI enables machines to mimic human intelligence, data science provides the necessary tools and techniques to process and analyze the vast amount of data available. Together, they have the potential to revolutionize various fields, including examinations, by improving accuracy, efficiency, and fairness.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are two rapidly growing fields in the world of technology. UPSC, the Union Public Service Commission, conducts the examination to select candidates for various administrative positions in India.
With the advent of AI and ML, the relevance of these technologies for the UPSC examination and its candidates has become more prominent. AI, the capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior, has the potential to transform the way UPSC conducts its examination and selects candidates.
Machine Learning, a subset of AI, focuses on the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. By harnessing ML techniques, UPSC can leverage the vast amounts of data generated during the examination process to improve the accuracy and efficiency of evaluating candidate performance.
The use of AI and ML in the UPSC examination holds significant promise. It can assist in automating administrative tasks, such as the evaluation of answers and the generation of results, thereby reducing the burden on human resources. This automated approach can also facilitate a more objective and standardized evaluation process.
Furthermore, AI and ML can help identify trends and patterns in candidate performance, enabling UPSC to develop personalized learning paths for aspirants. By analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of individuals, the examination can be tailored to address specific areas of improvement, ensuring a more efficient preparation process for candidates.
However, while AI and ML offer great potential, their implementation in the UPSC examination should be handled judiciously. It is essential to address concerns related to data security, privacy, and fairness to ensure a transparent and unbiased evaluation process.
In conclusion, the integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the UPSC examination has the potential to revolutionize the selection process and benefit both the commission and the candidates. By embracing these technologies, UPSC can enhance its efficiency, accuracy, and fairness, ultimately selecting the most deserving candidates for administrative positions in India.
Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
Artificial intelligence (AI) is an area of computer science that focuses on creating intelligent machines that can perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence. Robotics, on the other hand, is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
In the UPSC examination, the topic of artificial intelligence and its relevance is of great importance. The exam tests the knowledge and understanding of candidates in various subjects, including emerging technologies like AI and robotics.
The Relevance of Artificial Intelligence in the UPSC Exam
Artificial intelligence has become increasingly important in today’s world, and its impact on various fields cannot be overlooked. This is why the UPSC exam includes questions on AI, as it is crucial for aspiring civil servants to understand the potential applications and implications of this technology.
AI can be used in areas like governance, public service delivery, and policy making, which are all important aspects of the civil services. It can help in data analysis, decision making, and automation of administrative tasks, which can greatly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the government.
Moreover, AI can also be utilized in areas like defense and security, where it can assist in tasks like surveillance, threat detection, and predictive analysis. It can help in identifying patterns and anomalies in large sets of data, which can be crucial in maintaining national security.
AI and Robotics: A Promising Combination
The combination of artificial intelligence and robotics is particularly exciting in terms of the advancements it can bring. With AI, robots can become more intelligent, adaptable, and autonomous. They can learn from their environment, make decisions, and perform tasks with precision and accuracy.
This combination has the potential to revolutionize various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and transportation. Robots can be used in factories for tasks that require precision and repetitive actions. In healthcare, they can assist in surgeries, patient care, and rehabilitation. In agriculture, they can help in planting, harvesting, and monitoring crops. In transportation, they can be utilized in self-driving vehicles, making travel safer and more efficient.
Overall, artificial intelligence and robotics hold immense potential and can greatly impact various industries and sectors. Understanding their relevance and applications is crucial for aspirants appearing for the UPSC exam, as it reflects the need for adapting to the changing technological landscape and harnessing its benefits for the betterment of society.
Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized various domains, including natural language processing (NLP). NLP is a subfield of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and human language. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to understand, analyze, and generate human language.
Relevance of NLP in UPSC Examination
NLP plays a crucial role in the context of the UPSC examination. The examination, one of the most competitive in India, requires candidates to have a strong command over language and information processing skills. As a result, the integration of AI and NLP can provide several benefits for both the candidates and the examination process itself.
Firstly, NLP can enhance the evaluation process by automating the assessment of essay and answer writing. With AI-powered NLP algorithms, evaluators can save time and effort by efficiently analyzing the quality of the candidate’s responses. This can lead to quicker and more accurate evaluation, ensuring fairness and impartiality in the examination.
Secondly, NLP can be utilized to improve the accessibility of examination materials. AI-powered NLP technologies can convert complex study materials and question papers into simpler language, making it easier for candidates with language barriers or learning disabilities to understand and engage with the content. This inclusivity promotes equal opportunities for all aspirants.
The Future of NLP and AI in the UPSC Examination
As AI and NLP continue to advance, their potential for the UPSC examination is immense. The integration of these technologies can lead to an adaptive examination system that customizes the assessment process based on the individual’s strengths and weaknesses. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide personalized feedback and guidance to aspirants, helping them improve their performance.
Furthermore, AI and NLP can aid in the analysis of vast amounts of data, such as previous year question papers and syllabus materials. By identifying patterns and trends, these technologies can assist aspirants in understanding the examination requirements better and strategizing their preparation effectively.
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence and natural language processing has significant relevance in the context of the UPSC examination. By harnessing the power of AI and NLP, the examination process can become more efficient, inclusive, and personalized. However, it is essential to address the challenges and ethical considerations associated with these technologies to ensure their responsible and equitable implementation.
Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as one of the most significant technological advancements of our time. With its ability to mimic human intelligence and learn from data, AI has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including computer vision.
Computer vision involves teaching computers to see and interpret visual data, such as images and videos. AI technologies, particularly machine learning algorithms, play a crucial role in enabling machines to analyze and understand visual content.
The relevance of artificial intelligence and computer vision in the UPSC examination cannot be overlooked. As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, the ability to process and extract insights from visual information is becoming more important. AI-powered computer vision can assist in analyzing large volumes of visual data and identifying patterns or anomalies that may not be apparent to human observers.
Moreover, computer vision can aid in various tasks relevant to the UPSC exam, such as image classification, object detection, and facial recognition. For example, AI algorithms can classify images of historical monuments or geographical features, helping aspirants gain a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
The integration of AI and computer vision can also enhance the accuracy and efficiency of evaluating answer sheets. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to assess handwritten answers and provide instant feedback, improving the transparency and objectivity of the examination process.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence and computer vision are interconnected and have immense relevance in the UPSC examination. Leveraging AI technologies can facilitate a more comprehensive and efficient analysis of visual data, enhancing the learning experience and evaluation process. As AI continues to advance, its integration with computer vision will only become more critical in various academic and professional domains.
Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Virtual Reality (VR) are two rapidly advancing technologies that are revolutionizing various aspects of our lives. Both AI and VR are interdisciplinary fields that combine elements of computer science, engineering, psychology, and more to create immersive and intelligent experiences.
The field of AI focuses on developing intelligent machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI systems can analyze data, recognize patterns, make decisions, and learn from their experiences. Virtual Reality, on the other hand, is all about creating a simulated environment that can be similar or completely different from the real world. VR technology allows users to immerse themselves in a virtual world and interact with it.
Artificial intelligence and virtual reality share several commonalities and have a significant impact on each other. AI technologies can enhance the virtual reality experience by providing intelligent and responsive virtual characters, adaptive environments, and personalized interactions. AI can also be used to analyze user behavior and preferences, making virtual environments more immersive and engaging.
Virtual reality, on the other hand, provides a unique platform for AI systems to learn, train, and improve their capabilities. Virtual environments can be designed to simulate real-world scenarios for AI systems to learn from, allowing them to develop skills and knowledge in a controlled and safe environment. This can be particularly useful in areas like robotics, autonomous vehicles, and medical diagnosis.
Given the rapid advancements in AI and VR technologies, their relevance for the UPSC examination cannot be underestimated. The essay on “Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality” can provide a valuable opportunity for candidates to demonstrate their understanding of these cutting-edge technologies and their impact on various fields such as healthcare, gaming, education, and more. Furthermore, discussing the ethical and societal implications of AI and VR can showcase the candidate’s critical thinking and analytical skills.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence and virtual reality are two interconnected fields that hold immense potential for transforming various aspects of our lives. Their relevance for the UPSC examination cannot be overlooked, as they represent key technological advancements with wide-ranging applications. Candidates must grasp the key concepts and implications of AI and VR to effectively address essay topics related to these fields.
Artificial Intelligence and Augmented Reality
In today’s fast-paced world, the role of technology has become increasingly prominent. Artificial intelligence (AI) and augmented reality (AR) are two branches of technology that have gained significant traction in recent years. Both AI and AR are revolutionizing various industries and sectors, including education, healthcare, and entertainment. Their relevance in the UPSC examination cannot be overlooked.
The UPSC exam, known as one of the toughest exams in India, requires candidates to have a comprehensive understanding of various subjects, including current affairs and emerging technologies. As AI and AR continue to advance, it becomes crucial for aspirants to acquaint themselves with these technologies and their applications in different fields.
Artificial intelligence, in simple terms, refers to the ability of machines to simulate human intelligence and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI has proven its significance in the field of data analysis, where it can efficiently process massive amounts of data and derive meaningful insights. In the context of UPSC, AI can be used to analyze trends in historical data, identify patterns, and predict future outcomes based on available information.
Similarly, augmented reality refers to the integration of digital information with the real world, providing an interactive and immersive experience. AR has already made its way into various industries, such as gaming and retail, but its potential goes beyond entertainment. In the UPSC examination, AR can be utilized to create interactive study materials and enhance the learning experience of aspirants. For instance, AR can be used to simulate real-life scenarios, allowing candidates to practice and refine their decision-making skills.
The combination of AI and AR has the potential to transform the way candidates prepare for the UPSC examination. AI-powered virtual assistants can provide personalized study plans, suggest relevant study materials, and track the progress of aspirants. AR can bring subjects to life through immersive visualizations, making complex concepts easier to grasp.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence and augmented reality are not only changing the landscape of various industries, but they are also reshaping the way we approach learning and preparation for examinations like UPSC. As a candidate, understanding the relevance of these technologies and harnessing their potential can give you an edge in the competitive exam. Embracing AI and AR will not only enhance your knowledge but also help you adapt to the changing dynamics of the examination.
Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things
The examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) tests the knowledge and understanding of a wide range of subjects. One such topic that holds immense relevance in today’s world is the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It involves the creation of intelligent machines that can perform tasks without human intervention. AI has the potential to revolutionize various industries and sectors, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and more. It can enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making capabilities.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things, on the other hand, refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity. These devices can collect and exchange data, providing valuable insights and enabling improved efficiency and convenience. The IoT has already begun to transform various aspects of our daily lives, such as smart homes, smart cities, and connected vehicles.
The integration of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things holds tremendous potential for the future. The combination of AI and IoT allows for the creation of intelligent systems that can gather, analyze, and interpret vast amounts of data from connected devices. This enables real-time decision-making, predictive analysis, and automation.
For the UPSC examination, it is crucial to understand the concepts and applications of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. Candidates should be aware of the benefits and challenges posed by these technologies. They should also have a comprehensive understanding of the ethical and legal implications associated with AI and IoT.
- AI and IoT can greatly impact governance and public administration. Governments can leverage these technologies to improve service delivery, disaster management, and urban planning.
- AI and IoT can revolutionize healthcare. Smart devices and sensors can monitor patients’ health, assist in diagnostics, and enable remote patient monitoring, leading to better healthcare outcomes.
- AI and IoT can enhance transportation systems. Autonomous vehicles, traffic management systems, and predictive maintenance can significantly improve road safety and efficiency.
It is important for UPSC aspirants to stay updated with the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. These technologies are shaping the future and will continue to have a significant impact on society, economy, and governance. By understanding their implications, candidates can provide informed perspectives and contribute to the discussions and policies surrounding AI and IoT.
Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
Artificial intelligence has been making significant advancements in various fields, and healthcare is no exception. With the ability to analyze vast amounts of data and extract meaningful insights, AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes.
The relevance of AI in healthcare cannot be overstated. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI systems can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, with a level of accuracy that rivals or even surpasses human experts. This can help speed up the diagnosis process, leading to quicker treatment and improved prognosis.
Furthermore, AI can be used to predict disease progression and patient outcomes based on historical data, facilitating personalized treatment plans. With the capability to process and analyze large datasets, AI can uncover patterns and trends that may not be apparent to human clinicians, leading to more effective treatment strategies.
Another area where AI can have a profound impact is in drug discovery and development. By simulating molecular interactions and predicting their effectiveness, AI-powered algorithms can streamline the drug development process, reducing costs and timeframes. This could potentially lead to the discovery of new treatments for currently incurable diseases.
Moreover, AI can assist healthcare professionals in administrative tasks, lowering the burden of paperwork and allowing them to focus more on patient care. AI chatbots can provide basic medical information and answer common questions, freeing up healthcare personnel’s time and resources.
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence in healthcare holds great promise for improving patient care and outcomes. Its ability to process and analyze large amounts of data, predict disease progression, assist in drug discovery, and streamline administrative tasks highlights its relevance in transforming the healthcare sector. As the UPSC examination focuses on current affairs and emerging technologies, understanding the potential of AI in healthcare becomes crucial for aspiring candidates.
Artificial Intelligence and Education
The field of artificial intelligence has immense potential and unlimited applications in various sectors and industries. One of the areas where artificial intelligence has found its relevance is in the field of education.
With the advancement in technology and the rise of intelligent systems, incorporating AI in education has become a hot topic of discussion. Intelligent systems can revolutionize the way we teach and learn, making education more personalized, interactive, and effective.
Enhanced Learning Experience
Artificial intelligence can provide personalized learning experiences tailored to individual students’ needs and preferences. Intelligent tutoring systems can analyze student data and adapt instructional strategies accordingly, ensuring that each student receives the most effective educational content and support.
Furthermore, AI-powered systems can provide real-time feedback and assessments, enabling students to track their progress and identify areas for improvement. This continuous feedback loop facilitates self-directed learning and helps students develop critical thinking skills.
Efficient Administrative Processes
Another significant impact of artificial intelligence in education is in streamlining administrative processes. AI-powered systems can automate tasks like grading, scheduling, and course planning, reducing the burden on educators and administrators.
By automating routine administrative tasks, educators can focus more on their core teaching responsibilities and provide personalized attention to students. This not only improves efficiency but also enhances the overall learning experience for students.
Future of Education and Examination
As artificial intelligence continues to advance, it is expected to play a significant role in the future of education and examination. AI-powered systems can help create intelligent assessments that evaluate not only factual knowledge but also higher-order thinking skills.
Furthermore, AI can assist in identifying areas where students may need extra support or intervention, enabling educators to provide targeted interventions and personalized learning plans.
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence in education has the potential to revolutionize the way we teach and learn. It enhances the learning experience, streamlines administrative processes, and paves the way for more personalized and effective education. As the world progresses, it is crucial for educational institutions to embrace artificial intelligence and harness its power for the benefit of students and the entire education ecosystem.
Artificial Intelligence and Business
Artificial intelligence is having a significant impact on the business world, and its relevance for the UPSC examination cannot be underestimated. In today’s digital age, businesses are constantly looking for ways to be more efficient, productive, and profitable. AI offers innovative solutions to achieve these goals.
One area where AI is making a difference in business is customer service. Chatbots powered by AI are being used to provide instant responses to customer queries, improving customer satisfaction and reducing the need for human intervention. AI algorithms can also analyze customer data and behavior to personalize marketing campaigns, leading to higher conversion rates and customer retention.
Another application of AI in business is automation. AI-powered robots and machines can perform repetitive and mundane tasks, thereby freeing up human resources to focus on more complex and creative work. This automation not only improves efficiency but also reduces costs for businesses.
AI in decision-making
AI is also playing a crucial role in decision-making for businesses. Advanced AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, enabling businesses to make informed decisions. From inventory management to supply chain optimization, AI is revolutionizing the way businesses operate.
Furthermore, AI is helping businesses in risk management. AI algorithms can detect anomalies and potential threats, enabling businesses to take proactive measures to prevent fraud and other security breaches. This predictive capability of AI is invaluable in today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment.
The future of AI in business
The future of artificial intelligence in the business world is promising. As technology advances, AI is expected to become even more sophisticated and capable. Businesses will be able to leverage AI to gain a competitive edge, improve customer experiences, and streamline operations.
However, there are also concerns about the ethical implications of AI in business. Issues such as privacy, data security, and job displacement need to be carefully addressed to prevent any negative impacts of AI implementation.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence is transforming the way businesses operate. Its potential in improving efficiency, decision-making, and customer service is undeniable. Aspirants for the UPSC examination should be aware of the relevance of AI in the business world and its impact on society as a whole.
Artificial Intelligence and Finance
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing various industries, and finance is no exception. The integration of AI technology into the financial sector has had a significant impact on the way we conduct financial transactions, manage investments, and analyze data.
As financial institutions handle massive amounts of data and complex calculations, AI has emerged as a powerful tool to streamline operations and improve decision-making. AI algorithms can analyze and interpret data much faster than humans, leading to more efficient and accurate financial analysis.
The relevance of AI in the finance industry
AI offers several benefits and applications in the finance industry. One area where AI has proven its relevance is in fraud detection and prevention. AI algorithms can analyze vast volumes of data, identify patterns, and detect anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity. This has helped financial institutions prevent fraud and protect their customers’ assets.
AI also plays a crucial role in risk assessment and management. By analyzing historical data and market trends, AI algorithms can identify potential risks and provide insights that can help financial institutions make informed decisions. This enables them to mitigate risks and optimize their investment strategies.
The future of AI in finance and its implications for UPSC examination
The growing adoption of AI in the finance industry is reshaping the landscape of financial services. As AI becomes more advanced, it has the potential to automate certain financial tasks and workflows, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings. However, this also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for re-skilling the workforce.
For UPSC examination, understanding the implications of AI in finance is crucial. Candidates should be aware of how AI is transforming the financial sector and its implications for various stakeholders, including consumers, regulators, and financial institutions. They should also be able to analyze the benefits and challenges associated with AI adoption and its potential impact on the economy.
In conclusion, AI has emerged as a game-changer in the finance industry, offering numerous opportunities for innovation and growth. Its relevance for the UPSC examination lies in the need for candidates to stay updated with the latest developments in AI technology and understand its implications for the financial sector and the wider economy.
Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity
As the UPSC examination is known for its rigorous evaluation process, it is crucial for candidates to have a comprehensive understanding of various topics to excel in the essay section. One such topic that is highly relevant and gaining traction is the intersection of artificial intelligence and cybersecurity.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence, or AI, refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These systems are designed to process vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on that information. The potential applications of AI are wide-ranging, including healthcare, transportation, finance, and more.
In recent years, AI has gained significant attention and investment due to its promise of optimizing operations, improving efficiency, and enabling automation. However, as the use of AI becomes more prevalent, it also raises concerns regarding its potential impact on cybersecurity.
The Role of AI in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a critical concern in today’s digital world, given the increasing number of cyber threats and attacks. Traditional methods of securing systems and networks are often not sufficient to protect against sophisticated attacks. This is where artificial intelligence can play a crucial role.
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, detect anomalies, and identify potential threats. Machine learning techniques can help improve the accuracy of threat detection by constantly learning and adapting to new attack patterns. AI-powered systems can also automate certain cybersecurity tasks, allowing for faster response times and reducing the burden on human operators.
However, it is important to note that AI is a double-edged sword in the context of cybersecurity. While AI can be used to enhance defense mechanisms, it can also be exploited by malicious actors to launch sophisticated attacks.
The Ethical Considerations
As AI continues to advance, it is crucial to address the ethical considerations associated with its use in cybersecurity. These considerations include transparency, accountability, and bias in AI algorithms. It is essential to ensure that AI-powered cybersecurity systems are fair, unbiased, and transparent in their decision-making process. Additionally, guidelines and regulations must be put in place to govern the use of AI in cybersecurity to prevent its misuse.
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence and cybersecurity is an important topic that candidates should be well-versed in for the UPSC examination. Understanding the potential of AI in improving cybersecurity, as well as the ethical considerations surrounding its use, is crucial in addressing the challenges and opportunities it presents.
Future Prospects of Artificial Intelligence
The relevance of artificial intelligence in various sectors is undeniable. It has the potential to revolutionize industries, improve efficiency, and enhance our lives in countless ways. As the field of AI continues to advance, its future prospects are increasingly promising.
Artificial Intelligence in Education
One of the areas where AI can have a significant impact is education. With the use of intelligent tutoring systems and adaptive learning platforms, AI can personalize the learning experience for students, identify their strengths and weaknesses, and provide tailored guidance. This can greatly improve the effectiveness of education and make learning more engaging and interactive.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
The healthcare industry can benefit tremendously from the integration of AI. From diagnosing diseases to developing personalized treatment plans, AI can analyze vast amounts of medical data and provide valuable insights. AI-powered systems can also assist in the detection of early warning signs, predicting epidemics, and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, AI can automate administrative tasks, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
Furthermore, AI has a significant role to play in the field of medical research. AI algorithms can analyze complex genetic data and help researchers discover new treatments and therapies, leading to groundbreaking advancements.
AI-powered robotic surgery is another area with immense potential. With greater precision, reduced invasiveness, and shorter recovery times, AI can revolutionize surgical procedures and lead to better patient outcomes. The future of healthcare is closely intertwined with artificial intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence in the Workplace
AI is set to transform the way we work. While there may be concerns about job displacement, AI can actually augment human capabilities and create new opportunities. Intelligent automation can eliminate mundane and repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work that requires creativity and problem-solving skills. AI-powered tools can assist professionals in making better decisions, analyzing large datasets, and improving productivity.
Moreover, AI has the potential to improve efficiency in various industries, such as manufacturing, logistics, and customer service. From predictive maintenance to intelligent supply chain management, AI can streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity.
The future of artificial intelligence holds immense possibilities. As technology continues to evolve, AI will become an integral part of our daily lives. Its impact on education, healthcare, and the workplace will continue to grow, making it crucial for individuals to stay updated and adapt to the changing landscape.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence has the potential to revolutionize various sectors and improve the way we live and work. It is important for individuals to recognize its significance and prepare for its integration. As technology continues to advance, the future prospects of artificial intelligence are incredibly promising.
Question-answer:
What is artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It encompasses the ability of a computer or machine to mimic and simulate human intelligence, perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence, and learn from experience.
Why is artificial intelligence relevant for the UPSC examination?
Artificial intelligence is relevant for the UPSC examination because it has the potential to revolutionize various sectors and impact governance, policymaking, and public service delivery. It can enhance efficiency, effectiveness, and transparency in government processes, facilitate data-driven decision-making, and help solve complex problems that governments face. Therefore, having an understanding of artificial intelligence is crucial for aspirants appearing for the UPSC examination.
What are the benefits of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination?
Artificial intelligence can bring several benefits to the UPSC examination. It can assist in automating administrative tasks, such as handling and processing large amounts of data, enabling faster data analysis, and improving accuracy. AI-powered tools can also support exam preparation by providing personalized recommendations and feedback to aspirants, offering adaptive learning platforms, and facilitating the assessment of individual strengths and weaknesses. Moreover, it can help in conducting online examinations securely and efficiently.
Are there any challenges associated with the use of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination?
Yes, there are several challenges associated with the use of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination. Some of the challenges include ensuring the fairness and transparency of AI algorithms, addressing privacy and data protection concerns, managing biases in AI systems, and maintaining public trust in AI-driven decision-making processes. Moreover, there may be technical issues, such as system errors or glitches, that can disrupt the examination process and create disparities among candidates. Therefore, it is important to carefully design and implement AI systems in the UPSC examination while addressing these challenges.
How can aspirants prepare for the impact of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination?
Aspirants can prepare for the impact of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination by staying updated on the latest developments and advancements in AI technology, understanding the potential applications of AI in governance and public administration, and critically analyzing the ethical and social implications of AI. They can also develop digital literacy skills, enhance their understanding of data analysis and interpretation, and familiarize themselves with AI tools and platforms that can aid in exam preparation. Additionally, aspirants should be adaptable and open to embracing new technologies and approaches in their study and exam preparation strategies.
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It involves the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
How is artificial intelligence relevant for the UPSC examination?
Artificial intelligence is highly relevant for the UPSC examination as it has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of governance and administration. AI can be used in areas such as data analysis, decision-making, policy formulation, and public service delivery. It can help in improving efficiency, reducing corruption, enhancing transparency, and promoting inclusive growth. Therefore, having a good understanding of AI is important for aspirants preparing for the UPSC examination.
What are the benefits of artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence offers several benefits, including increased efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. It can automate repetitive tasks, analyze large volumes of data quickly and accurately, and provide valuable insights for decision-making. AI-powered systems can also improve the quality of public services, enhance accessibility, and enable personalized experiences. Additionally, AI has the potential to tackle complex challenges, such as healthcare diagnostics, climate change, and disaster management.
What are the ethical considerations related to artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence raises various ethical concerns, such as privacy, bias, accountability, and job displacement. AI systems often rely on collecting and analyzing large amounts of personal data, which can raise privacy concerns. Biases in data or algorithms used in AI systems can result in biased decisions, perpetuating inequalities. Ensuring accountability and transparency in AI decision-making is another important ethical consideration. Moreover, the potential impact of AI on jobs and the workforce should be carefully analyzed and managed to minimize negative consequences.
Related posts:

About the author
3 months ago
BlackRock and AI: Shaping the Future of Finance
Ai and handyman: the future is here, embrace ai-powered cdps: the future of customer engagement.
Explore Our Affordable Courses
- UPSC Offline
- UPSC Online
- UPSC (Live From Classroom)
- UPSC Optional
- UPPSC Offline
- BPSC Offline
- UPPCS Online
- BPSC Online
- MPSC Online
- MPPSC Online
- WBPSC Online
- OPSC Online
- BPSC (Live from Classroom)
- UPPSC (Live From Classroom)
- UPSC Test Series
- State PSC Test Series
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- SUBJECT WISE CURRENT AFFAIRS
- DAILY EDITORIAL ANALYSIS
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS QUIZ
- Daily Prelims(MCQs) Practice
- Daily Mains Answer Writing
- Prahaar (Mains Wallah) 2024
- Prahaar Summary 2024
- Mains Marks Booster 2024
- Mains Wallah (Q&A)
- Monthly Current Wallah
- Daily Editorial Summary
- NCERT Wallah
- Prelims PYQs
- Optionals PYQs
- NCERT Notes
- Udaan Notes
- UPSC Prelims Answer Key
- UPSC Syllabus
- Topper's Copies
- Delhi – Mukherjee Nagar Centre
- Delhi – Old Rajinder Nagar Centre
- UP – Lucknow Centre
- UP – Prayagraj Centre
- Bihar – Patna Centre
- Galgotia University Centre

- Offline Centres
- UDAAN Notes
- UPSC Prelims PYQs
- UPSC Mains PYQs

Artificial Intelligence
Government agencies and policymakers are using AI tools to analyze patterns, forecast scenarios, and offer informed recommendations. Yet, AI adoption in decision-making has potential downsides.
More on News:
- The biases inherent in AI, often a reflection of the biases in the data they are trained on or the perspectives of their developers, can lead to skewed or unjust outcomes and represent a significant challenge in the integration of AI into governance.
- Prompts about the role of women in leadership positions can generate content that portrays women stereotypically and subordinately, reinforcing gender biases.
About Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- For Example: ChatGPT
Types of Artificial Intelligence
- For Example: Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri.
- For Example: These kinds of systems can be found in applications like self-driving cars or in hospital operating rooms.
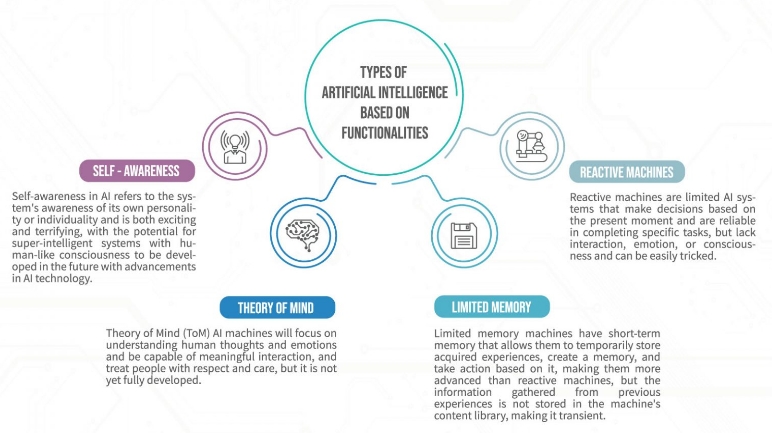
India’s Initiatives for Developing AI:
- NITI Aayog has come with the ‘National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence’ Discussion Paper that focuses on establishing the International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI) in the country through private sector collaboration.
- NITI Aayog is to set up India’s first AI-specific cloud computing infrastructure called AIRAWAT.
- Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) : In 2020, India joined with 15 other countries to form the GPAI to establish frameworks for the responsible utilization of emerging technologies.
Benefits of AI:
- Further, a report from Goldman Sachs Research in April 2023 said that generative AI alone could raise global GDP by 7% or almost $7 trillion over a 10-year period.
- Boosting annual growth rate: The discussion paper’ ‘Towards Responsible#AIForAll ’ by Niti Aayog states that there is a potential for large-scale adoption of AI which can boost the country’s annual growth rate by 1.3 per cent, by 2035.
- For Example: In a study called “Generative AI at Work, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) economists showed that AI tools boosted worker productivity by 14% and improved consumer satisfaction.
- Creation of New Job: AI may result in automating some routine jobs but will also result in job creation in various data science, data curation etc.
- Innovation: A recent survey among employees of LinkedIn’s top 50 companies in the United States shows that almost 70% of them found AI helping them to be faster, smarter, and more innovative.
- Effective Policy Implementation: Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) plans to use Artificial Intelligence technologies to carry out pilot studies for Optimization of Crop Cutting Experiments (CCEs ) in various States.
Ethical Issues associated with Artificial Intelligence:
- For Example: A research paper titled “Robots and Jobs: Evidence from US Labor Markets” by Daron Acemoglu of MIT found that robot adoption has a negative effect on workers, on average — it reduces the labor share, employment and wages.
- AI Bias: AI systems can perpetuate existing biases present in training data, leading to discrimination against certain groups. Ensuring fairness and minimizing bias in AI models is a significant challenge.
- Social Manipulation: AI-powered algorithms can be used to spread misinformation, influence public opinion, and manipulate social behavior.
- Rights of AIs : AIs are still simple and mostly disembodied programs. But, as AIs become more complex and start to have physical, possibly human shapes , and more numerous, what rights they should have is debatable.
- Unintended Consequences : AI systems can produce unexpected outcomes due to their complexity, which can have negative impacts on society.
- For Example: Analysis by Goldman Sachs has suggested that 15%-35% of work in the U.S. economy is exposed to automation.
- Multiple Challenges: AI could create deep challenges for society, including in the labor market, politics, data privacy, crime and warfare; these challenges are difficult to anticipate and plan for.
- Applying Kantian ethics to the use of AI in decision-making within governance could lead to serious concerns.
- If decisions that were once the purview of humans are delegated to algorithms, it could threaten the capacity for moral reasoning.
Way Forward:
- For Example: MeitY has initiated FutureSkills PRIME, an upskilling programme for 10 emerging technologies.
- Integration of AI with Curriculum: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) announced its plan to introduce Artificial Intelligence as an elective for students from classes 9 to 12.
- Stepping up Cyber regulations: Governments would have to step up their cyber regulations with respect to the new challenges posed by AI.
- International Collaboration: Member States should work with international organizations, educational institutions and private and non-governmental entities to provide adequate AI literacy education to the public on all levels in all countries in order to empower people.
- Thus, it would be prudent for India to focus more on education and training in AI; this could be a lot easier now with online education having larger acceptance after the COVID-19 pandemic.
News Source: The Hindu
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.

- Recent Post
- Related Post
- Most Viewed Post

Secularism Is A Core Part of the Constitution: Supreme Court
Big Tech Companies Scouting for Nuclear Power
Role of wetlands in National Biodiversity Strategies at COP1...
5th National Water Awards 2023
India, Pakistan Renew Their Agreement on Kartarpur Corridor
IMF Released World Economic Outlook

Social Stock Exchange
Prime- minister’s egypt state visit, arsenic and fluoride in groundwater, who launches icd 11 – a traditional medicine module 2:..., drug controller general of india, latest comments, recent editorial.
Role Of Family in Incalculation of Values
A major new report makes the case for water as a g...
German Chancellor’s India visit, a Chance fo...
The world needs blue helmets who act as blue helme...
Human Values
Civil society organisations too need to be account...
Popular current affairs
Secularism Is A Core Part of the Constitution: Sup...
Role of wetlands in National Biodiversity Strategi...
India, Pakistan Renew Their Agreement on Kartarpur...
Our Courses

Need help preparing for UPSC or State PSCs?
Connect with our experts to get free counselling & start preparing
THE MOST LEARNING PLATFORM
Learn From India's Best Faculty
Our Initiatives
Beginner’s roadmap, quick links.

PW-Only IAS came together specifically to carry their individual visions in a mission mode. Infusing affordability with quality and building a team where maximum members represent their experiences of Mains and Interview Stage and hence, their reliability to better understand and solve student issues.
Subscribe our Newsletter
Sign up now for our exclusive newsletter and be the first to know about our latest Initiatives, Quality Content, and much more.
Contact Details
G-Floor,4-B Pusa Road, New Delhi, 110060
- +91 9920613613
- [email protected]
Download Our App
Biginner's roadmap, suscribe now form, fill the required details to get early access of quality content..
Join Us Now
(Promise! We Will Not Spam You.)
CURRENT AF.
<div class="new-fform">
Select centre Online Mode Hybrid Mode PWonlyIAS Delhi (ORN) PWonlyIAS Delhi (MN) PWonlyIAS Lucknow PWonlyIAS Patna Other
Select course UPSC Online PSC ONline UPSC + PSC ONLINE UPSC Offline PSC Offline UPSC+PSC Offline UPSC Hybrid PSC Hybrid UPSC+PSC Hybrid Other
</div>



- Insights IAS Brochure |
- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru --> Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2025
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
- Insights IAS Brochure

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

UPSC Editorial Analysis: Universal Basic Income (UBI) in the Indian Context
Source: The Hindu
General Studies-3; Topic: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Introduction:
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) has highlighted global issues of jobless growth, worsened by automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Rising inequality and youth unemployment, particularly in India, have reignited debates around UBI as a tool to provide a social safety net .
Background:
- UBI gained momentum in India after the 2016-17 Economic Survey , which proposed considering UBI to replace inefficient welfare schemes.
- The development of JAM (Jan-Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile) infrastructure has enhanced the feasibility of implementing Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs) for UBI.
UBI as a Safety Net Policy:
- UBI should be viewed as a social safety net policy rather than a solution to employment growth or economic development . It helps individuals manage the consequences of unemployment and poverty.
- Policies need to be evaluated based on their objectives. UBI is designed to provide basic income support , not directly solve structural economic issues like job creation .
key benefits of Universal Basic Income (UBI):
- UBI provides a direct cash transfer to all citizens, ensuring a minimum income floor . This can lift people out of poverty, particularly in regions with high poverty rates, by providing basic financial security.
- Universal transfers ensure fewer intermediaries, reducing administrative costs and minimizing exclusion errors .
- With basic income support , individuals, especially in lower-income groups, will have more purchasing power . This can stimulate aggregate demand , boosting consumption and potentially driving economic growth, especially in times of economic downturn.
- UBI can provide essential financial support to vulnerable populations like the elderly, disabled, and unemployed, who may not benefit from work-based welfare programs like MGNREGS.
- With guaranteed financial support, families are more likely to invest in better healthcare and education for their children, improving overall human development indicators in the long run.
- A guaranteed basic income can reduce the stress and mental health issues associated with financial insecurity. It can also reduce crime rates , as people with stable income are less likely to resort to criminal activities out of desperation.
Feasibility vs. Desirability of UBI:
- Feasibility : UBI may not be financially viable for India, given budgetary constraints.
- Desirability : UBI is desirable as it can provide universal income support, reducing inequality and offering a minimal consumption guarantee.
- A key question is whether a modified UBI that is less ambitious but financially feasible can be explored.
State and Central Government Schemes:
- Rythu Bandhu (Telangana) and KALIA (Odisha) are state-level schemes providing unconditional payments to farmers. The national-level PM-KISAN scheme offers ₹6,000 per year to farmers, aiming to cover 10 crore farming households.
- Challenges : These programs face issues like inclusion and exclusion errors due to logistical challenges (Aadhaar verification, bank rejections).
Financial Feasibility of UBI in India:
- Large-scale UBI proposals range from 3.5% to 11% of GDP, requiring significant budgetary resources or cutting other anti-poverty programs.
- A more feasible approach is a limited UBI , pegged at 1% of GDP , providing around ₹144 per month to every citizen (or ₹500 per household). This amount, while small, can be scaled up gradually, building on programs like PM-KISAN .
Concerns and challenges associated with implementing a Universal Basic Income (UBI)
- One of the primary concerns about UBI is the significant financial burden it places on the government.
- If UBI is implemented by replacing current welfare schemes, there’s a risk that targeted programs that are crucial for vulnerable populations (such as food distribution via the Public Distribution System or MGNREGS) might be eliminated, leaving certain groups worse off.
- Providing a universal cash transfer could potentially lead to inflation , particularly in rural or underdeveloped areas where an increase in demand for basic goods might outpace supply.
- There is concern that UBI could create a disincentive to work , as individuals receiving guaranteed income may opt out of the labor force.
- Biometric failures and network issues have already plagued existing welfare schemes in India, such as PM-KISAN, leading to exclusion errors.
- While UBI may provide short-term financial relief, it does not address the structural issues related to unemployment, education, healthcare, or inequality in the long run.
Way Forward:
- Implementing a full-scale UBI may not be feasible in India due to financial constraints. Therefore, a modified UBI, starting with specific vulnerable groups (such as women, the elderly, the disabled, and landless laborers), could be an effective compromise.
- UBI can be integrated into existing frameworks like MGNREGS (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme) and Public Distribution System (PDS) to ensure comprehensive coverage.
- The JAM (Jan-Dhan, Aadhaar, Mobile) infrastructure is crucial for the smooth rollout of UBI. The government must continue improving banking access in remote areas, addressing issues with Aadhaar-based verification, and ensuring stable internet and mobile connectivity.
- UBI is not a solution to structural unemployment; hence, it must be paired with policies that promote job creation and boost economic growth.
Conclusion:
- UBI has merit as a tool to address poverty and inequality, but its large-scale implementation faces budgetary challenges.
- A modified UBI , gradually rolled out and combined with existing programs, offers a viable strategy for India, ensuring a balanced and comprehensive social safety net for all citizens.
Practice Question:
Universal Basic Income (UBI) has often been seen as a potential solution to address rising inequality and jobless growth in India. Discuss the relevance of UBI in the context of global trends like automation and Artificial Intelligence. How can UBI contribute to India’s social safety net? (250 words)

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Weak AI, Strong AI, Differences Between AI, ML and DL, Types of AI. For Mains: Indigenization of Technology & Developing New Technology, Awareness in Different Fields, Advantages of AI, Disadvantages of AI, Applications of AI in Different Sectors.
Question 1: Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does AI help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to the privacy of the individual in the use of AI in healthcare? (UPSC Prelims 2023) Question 2: With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?
9 min read. “Success in creating AI would be the biggest event in human history. Unfortunately, it might also be the last, unless we learn how to avoid the risks.” —Stephen Hawkins. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the computer science that emphasizes the creation of intelligent machines that work and react like humans.
This article will help you design and write an essay on artificial intelligence UPSC style. The first step to writing an Artificial Intelligence essay UPSC level is to define what AI is. Read on to familiarize yourself with the term AI.
It describes the action of machines accomplishing tasks that have historically required human intelligence. It includes technologies like machine learning, pattern recognition, big data, neural networks, self algorithms etc.
Table of Contents. What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? Is it possible for a computer to become completely Artificially Intelligent? What is the philosophy and ethics of Artificial Intelligence? Three main philosophical questions related to Artificial Intelligence. Examples of Artificially Intelligent Technologies.
17/10/2022. 5 Comments. From Current Affairs Notes for UPSC » Editorials & In-depths » This topic. Artificial Intelligence (AI), also known as the Industrial Revolution 4.0, has been making deep strides in scientific and technological innovation across different fields.
Moreover, the cost of developing and sustaining AI is not within the reach of small businesses or developing countries. The Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence are as follows: Job Loss: AI will replace a human worker for the most repetitive and resource-intensive jobs; they lose their job. Bias and Discrimination: AI systems can perpetuate ...
This article will help you understand the following concepts: Artificial Intelligence in India, challenges, global development, and future prospects of AI. These UPSC Notes on AI are aligned with the UPSC Syllabus and aspirants should prepare this topic for General Studies Paper III. Artificial Intelligence is an important topic as AI has been ...
BYJU'S IAS Comprehensive News Analysis. Artificial Intelligence [UPSC Notes GS III] This article will help you understand the following concepts: Artificial Intelligence in India, challenges, global development, and future prospects of AI.
The concept of Artificial Intelligence is based on the idea of building machines capable of thinking, acting, and learning like humans. What is AI? Artificial intelligence is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans.
Artificial intelligence: Comparing the types and their impacts. GS Paper 3. Syllabus: Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications and Effects in Everyday Life. Source: TH. Context: AI can traditionally be divided into Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI).
Essay on the impact of artificial intelligence in the UPSC examination and its implications for the future. By ai-admin. In AI Blog. 11 months ago. 48 Min Read. E. In the future, technology will play an increasingly significant role in our daily lives.
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or software perform human-like tasks. It refers to the ability of machines to perform cognitive tasks like thinking, perceiving, learning, problem solving and decision making. There are two subsets under the umbrella term AI: Machine learning and Deep learning.
From UPSC perspective, the following things are important : Prelims level: AI applications, Artificial General Intelligence, and latest developments. Mains level: AI's potential, Concerns and need for responsible development and deployment.
Artificial intelligence is the branch of computer science concerned with making computers behave like humans. AI refers to the ability of machines to perform cognitive tasks like thinking, perceiving, learning, problem solving and decision making.
T. Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a prominent and intriguing topic in today’s advanced technological world. With the rapid development and implementation of AI systems, the relevance of artificial intelligence for the UPSC examination has come into focus.
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think like humans and mimic their actions. For Example: ChatGPT. Types of Artificial Intelligence. Weak artificial intelligence: It embodies a system designed to carry out one particular job. For Example: Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri.
AI is defined as the ability of machines and systems to acquire and apply knowledge and to carry out intelligent behaviour. The term "Artificial Intelligence" was coined by John McCarthy, an American computer scientist and cognitive scientist. He was one of the founders of the discipline of AI.
Pune. Ranchi. Sikar. Parikshan New. Digital Current Affairs New. Learn Current Affairs with Ease. Experience on-the-go learning with our all-new digital current affairs ecosystem. Try beta. We've updated VisionIAS.
Source: The Hindu General Studies-3; Topic: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment. Introduction: The International Labour Organization (ILO) has highlighted global issues of jobless growth, worsened by automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Rising inequality and youth unemployment, particularly in India, have ...