

The PhD Discussion Chapter: What It Is & How To Write It
Sep 11, 2023

Your PhD discussion chapter is your thesis’s intellectual epicenter. Think of it as the scholarly equivalent of a courtroom closing argument, where you summarise the evidence and make your case. Perhaps that’s why it’s so tricky – the skills you need in your discussion chapter aren’t skills you’ve likely had to deploy before: it’s where you start to speak like a Doctor.
In this guide, I want to present a comprehensive guide to the PhD discussion chapter. We’ll look at a number of key topics:
What is the purpose of a PhD Discussion Chapter?
- Suggested outlines for a discussion chapter:
Advice for improving your discussion chapter
This is not a normal blog subscription.
Each week we send two short, thought-provoking emails that will make you think differently about what it means to be a PhD student. It is designed to be read in thirty seconds and thought about all day.
The PhD discussion chapter is the place where your findings, research questions, literature, theoretical framework and methodology coalesce into a coherent narrative. A common pitfall is when students see the discussion chapter as a summary of everything that has come before. This isn’t the case. Instead, the PhD discussion chapter offers a deep, analytical synthesis of your research, providing context, interpretation, and evaluation of your findings.
It’s the place in which you engage with existing theories, explore the significance of your work, and directly address the “So What?” question, highlighting the real-world implications and academic contributions of your research.
Let’s dig down into each of these things.
Summarising and explaining the research
Before you launch into the detail, start by laying out your findings in a clear, easy to follow way. This is typically done in the introduction and the first proper section of the chapter.
Starting the PhD discussion chapter by clearly laying out your findings serves as an anchor for your reader and sets the stage for the more complex discussions that follow. This foundational step ensures that the reader is equipped with all the necessary information to fully grasp the significance and implications of your work. It’s akin to laying the groundwork before building a complex structure; without a solid base, the intricate analyses may lose their impact or be misunderstood.
For example, if you’re a PhD student in environmental science studying the effects of a specific pollutant on marine life, begin by presenting the key data points, such as the pollutant concentration levels in various regions and the corresponding health indices of marine species studied. Use tables, figures, or graphs to help visualise the data and make it more accessible.
- Laying out Quantitative Findings : If your research is quantitative, use statistical measures to present your results. Clearly state the metrics you’ve considered, such as means, variances, p-values, etc., and what they imply about your research question.
- Laying out Qualitative Findings : In case of qualitative research, such as ethnographic studies or interviews, narrate the trends, patterns, or themes that have emerged. Use representative quotes or observations as illustrative examples.
- Mixed-Methods Approach : If you’ve used both quantitative and qualitative methods, start by outlining how these different types of data will be integrated in your discussion. This could involve presenting the qualitative findings as a contextual backdrop for quantitative data or vice versa.
Remember, your objective at this initial stage is not to overwhelm the reader with complexity but to build a transparent, easily-followable narrative of what you’ve found. By starting with a clear presentation of your findings, you’re laying the groundwork for a powerful, credible discussion chapter that can tackle sophisticated analyses and weighty implications, underpinned by a comprehensible and compelling dataset.
There will be a necessary degree of overlap and repetition between this section (and the discussion chapter in general) and the findings chapter. However, there’s a subtle difference in the way in which the data is introduced in the findings and discussion chapters .
In the findings chapter, you’re generally presenting raw data or observations without interpreting what they mean. In the Discussion chapter, you take those same findings and begin to explore their implications, relate them to existing theories, and evaluate their significance. The danger, however, lies in creating excessive repetition between the two chapters, which can fatigue the reader and dilute the impact of your arguments.
To mitigate this, consider employing the following strategies:
- Selective Highlighting : Choose only the most critical findings to revisit in the Discussion chapter. You don’t need to regurgitate every data point, only those central to the questions you aim to answer in this chapter.
- Narrative Framing : When you bring up a finding in the Discussion chapter, introduce it as a stepping stone to a broader point or argument, rather than an isolated fact. This technique helps the reader understand why you’re revisiting this information and what new aspects you’ll be unveiling.
- Use Different Presentation Formats : If the Findings chapter is heavy on tables and figures, consider summarising key points in a narrative form in the Discussion chapter or vice versa.
By thoughtfully selecting what to revisit and framing it within a new context, you can transform what might appear as repetition into a coherent and evolving narrative that adds value to your thesis. Read more about the difference between the findings and discussion chapters here .
Interpreting and Contextualising Results
It’s in the discussion chapter that you offer the interpretation and context for your research findings.
Here, you transition from being a data ‘gatherer’ to a data ‘interpreter’, weaving together the threads of research questions, data, methods, literature and theory to tell a complex story. While the Results chapter may offer the “what,” the PhD discussion chapter sheds light on the “why” and “how.”
For example, if you’re a social scientist studying the effects of social media on mental health, your results chapter might show statistical data indicating a correlation between social media use and anxiety. However, it’s in your discussion chapter that you would compare these findings to existing literature, perhaps linking them to existing theories or debates. This adds a layer of depth and context that transcends the numerical data, inviting academic dialogue and potential future research avenues.
There are three ways in which you can synthesise your findings:
- Interpretation : Begin by interpreting your findings. Use comparisons, contrasts, and correlations to explain the significance of the results. This is where you should also address any unexpected outcomes and explain them.
- Contextualisation : After interpretation, provide a context to situate your findings within the existing body of knowledge. Link back to your Literature Review and Theoretical Framework to show how your research aligns with or diverges from previous work. More on this below.
- Evaluation : Finally, critically evaluate your own research. Discuss its limitations, the implications of your findings, and offer recommendations for future research.
Whether you’re in natural sciences exploring a new chemical compound or in humanities dissecting a piece of classical literature, the discussion chapter is your opportunity to show that your research not only answers specific questions but also contributes to a wider understanding of your field. It’s not enough to say, for instance, that a new drug successfully reduced symptoms of depression in 60% of study participants. You must explore what that 60% means.
- Is it a statistically significant improvement over existing treatments?
- What might be the physiological or psychological mechanisms at work?
- Could your research method have influenced these outcomes?
There’s an art to explaining and synthesising your findings [Link to “How to Explain Your Findings”], but think of it this way: this is where you shine a light on the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of your findings, delving into the nuances that raw data can’t express.
Evaluating Existing Theories and Models
Beyond explaining your findings, the PhD discussion chapter allows you to evaluate the existing theories and models that you’ve cited in your literature review and/or theory framework chapter (not sure of the difference? Click here) . Your results could either reinforce established theories or challenge them, both of which significantly contribute to your field.
- For instance, did your research on renewable energy technologies confirm the economic theories suggesting that green energy can be cost-effective?
- Or did your social research provide empirical evidence that contradicts widely held beliefs in your field?
The PhD discussion chapter therefore serves as the space where the theories, concepts, ideas and hypotheses that make up and informed your theory framework and which you touched upon in your literature review intersect with the empirical data you’ve presented.
You’re not just mapping your findings onto the theories and models; you’re dissecting them, affirming or challenging them, and potentially even extending or refining them based on what you’ve discovered.
For instance, if you’re working on a thesis in psychology concerning cognitive development in early childhood, your Literature Review may have discussed Piaget’s stages of cognitive development. However, let’s say your findings indicate some nuances or exceptions to Piaget’s theories, or perhaps children in a certain demographic don’t follow the stages as previously thought.
Your discussion chapter is where you can make the argument that perhaps Piaget’s model, while generally accurate, might require some modification to account for these cases.
- Affirming Theories : If your data aligns closely with the existing theories and models, the PhD discussion chapter serves to strengthen their credibility. Here, you’re lending empirical support to theoretical frameworks.
- Challenging Theories : Alternatively, your findings might contradict or challenge the prevailing theories. This is not a shortcoming; instead, it opens the door for re-evaluation and progress in the field, which is just as valuable.
- Extending or Refining Theories : Perhaps your research uncovers additional variables or conditions that existing models have not accounted for. In such cases, you’re pushing the envelope, extending the current boundaries of understanding.
As you evaluate existing theories and models, be comprehensive yet nuanced. Draw on varied disciplines if relevant. For example, if your thesis is at the intersection of public health and social policy, integrate models from both fields to offer a multi-faceted discussion. Being interdisciplinary can make your discussion richer and more impactful.
Ultimately, the discussion chapter offers you a platform to voice your scholarly interpretation and judgment. You’re participating in a broader academic dialogue, not just narrating your findings but positioning them in a web of knowledge that spans across time, disciplines, and viewpoints.
Discuss Unexpected Results
The discussion chapter is where you also discuss things that didn’t quite work out as planned. In particular, results that were unexpected.
Sometimes the most perplexing data offers the most valuable insights. Don’t shy away from discussing unexpected results; these could be the starting points for future research or even paradigm shifts in your field.
When your research yields findings that diverge from established theories or commonly held beliefs, you’re offered a unique opportunity to challenge and extend existing knowledge.
Take the field of primary education as an illustrative example. Assume you’re researching the efficacy of a specific teaching methodology that prior studies have lauded. However, your data reveals that while the method works wonders for one subgroup of students, it fails to benefit another subgroup. Far from diminishing the value of your research, this unexpected outcome presents an exciting opening. It beckons further inquiry into why the teaching methodology yielded disparate impacts, which could eventually result in more tailored and effective educational strategies.
In the realm of scientific discoveries, the significance of unexpected results cannot be overstated. Alexander Fleming’s accidental discovery of penicillin originated from what appeared to be a ‘failed’ experiment, but it revolutionised medicine. Similarly, the unintended discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation provided pivotal support for the Big Bang theory. In both instances, what seemed like anomalies paved the way for transformative understanding.
The first task when you encounter unexpected findings is to set them apart from the expected outcomes clearly. Delineate a specific section in your discussion chapter to delve into these anomalies, affording them the attention they merit.
Next, engage in hypothesising why these peculiarities emerged. This could be the point where your years of study and your depth of understanding of your subject really shine. Are there confounding variables that weren’t initially apparent? Could there be an entirely unexplored underlying mechanism at play? Take your reader on this exploration with you, and offer educated guesses based on your literature review and study design.
Lastly, don’t forget to consider and discuss the wider implications of these findings. Could they potentially refute longstanding theories or present the need for a shift in the prevailing school of thought? Or perhaps they hint at previously unthought-of applications or solutions to existing problems? Reflect on how these unexpected results might fit into the broader academic conversation and where future research might take these findings.
By earnestly and transparently tackling unexpected results, you exhibit a commitment to rigorous academic research. The willingness to entertain complexity and to follow the research—even when it leads in unpredictable directions—is a mark of scholarly integrity and courage. This holds true irrespective of your academic discipline, from the humanities and social sciences to STEM fields.
Answering the “so what?” Question
In your findings chapter you would have presented the data. In the discussion chapter, you answer the ‘so what’ question. Make sure to address it explicitly. Why does your research matter? Who benefits from it? How does it advance the scholarly discourse?
As a PhD student, you’ve already invested a substantial amount of time and effort into your research. Therefore, it’s crucial to articulate its importance not only to validate your own work but also to contribute meaningfully to your field and, in some cases, to society at large.
Answering the “so what?” question means connecting the dots between your isolated research findings and the larger intellectual landscape. It requires you to extend your analysis beyond the specifics of your study, considering how it advances the scholarly discourse in your field. For instance, if your research closes a significant gap in the literature, makes a theoretical breakthrough,
Example in Public Health : If your research finds that community-led sanitation programs are far more effective than government-implemented ones, then the “So What?” is clear: policy-makers need to see this data. But that doesn’t mean you don’t still need to discuss it.
Example in Literature : If your research uncovers previously unnoticed patterns of symbolism in 19th-century Russian literature, the “So What?” could be a deeper understanding of how literature reflects societal anxieties of the time.
In order to make your discussion chapter compelling and relevant, it’s imperative to always highlight why your research matters. This goes beyond simply reiterating your findings; you need to connect the dots and show how your research fits into the broader academic landscape. Are you challenging existing theories, confirming previous studies, or offering a new perspective? Establishing the academic importance of your work provides a solid footing for its wider application.
Further to establishing academic relevance, also aim to illuminate the real-world implications of your findings. What are the practical outcomes that could arise from your research? Are there specific scenarios or applications where your research could be a game-changer? For instance, if your study uncovers a more effective method of teaching reading to children with dyslexia, explicitly mention how this could revolutionise educational approaches and improve quality of life for those affected. Providing concrete scenarios enhances the applicability of your research, proving that it doesn’t merely exist in the realm of academic abstraction, but has tangible impacts that can affect change.
Limitations and Future Research
The quest for perfection is more a journey than a destination. This especially holds true in the context of a PhD thesis. Therefore, a well-crafted Discussion chapter should include a section devoted to the limitations of your research, as it establishes the scope, reliability, and validity of your work. Acknowledging limitations is not an act of undermining your research; instead, it embodies scholarly integrity and rigorous academic thinking.
Being upfront about limitations is essentially about being honest, not only with your readers but also with yourself as a researcher. For instance, if you’ve conducted a survey-based study in psychology but only managed to collect a small number of responses, admitting this limitation provides context for your findings. Perhaps the conclusions drawn from such a sample size are not universally applicable but could still offer significant insights into a particular demographic or condition
- Do not shy away from discussing limitations in fear that it might weaken your arguments.
- Clearly delineate the scope of your research, specifying what it does and doesn’t address.
For example, in a medical research study, if your sample size predominantly consists of individuals from a particular age group, admitting this limitation helps frame your research within that context. Or, if you’re a literature student, if your analysis focuses solely on the works of a single author, your findings might not be generalisable to broader literary trends.
Discussing limitations openly doesn’t devalue your work; it adds a layer of trustworthiness. It assures the reader—and the academic community at large—that you have a nuanced understanding of your research context. It demonstrates that you can critically evaluate your own work, a skill that is paramount.

Your PhD Thesis. On one page.
Example outline for a discussion chapter:.
I’ve included a suggested outline for a PhD discussion chapter. It’s important to note that no two PhDs are alike, and yours may well (probably will) diverge from this. The purpose here is to show how all the various factors we’ve discussed above fit together.
Introduction
- Brief Overview of Research Objectives and Key Findings
- Purpose of the Discussion Chapter
Summary of Key Findings
- Brief Restatement of Research Findings
- Comparison with Initial Hypotheses or Research Questions
Interpretation of Findings
- Contextualisation of Results
- Significance and Implications of the Findings
Evaluation of Existing Theories and Models
- How Your Findings Support or Challenge Previous Work
- Conceptual Contributions of Your Study
- Acknowledgment of Study Limitations
- Suggestions for Future Research
- Summation of Key Points
- Broader Implications and Contributions of the Research
- Final Thoughts and Future Directions
Once you’ve navigated through the complexities of your PhD research, you’re now faced with the challenge of bringing it all together in your discussion chapter. While you’ve already considered various facets like summarising findings, evaluating existing theories, and acknowledging limitations, there are some “easy wins”—small, yet impactful steps—that can help strengthen this critical chapter.
The Power of a Well-Structured Narrative
Begin with a well-structured narrative that clearly outlines your arguments. Tell the reader what the destination is at the outset of the chapter, and then make sure each paragraph is a stepping stone to that destination.
Each paragraph should serve a purpose and should logically follow the previous one. This helps in making your discussion coherent and easy to follow.
- Use transition sentences between paragraphs to guide the reader through your argument.
- Make sure each paragraph adds a new dimension to your discussion.
Data Visualisation Tools
Visual aids aren’t just for presentations; they can provide tremendous value in a discussion chapter. Diagrams, charts, or graphs can provide a visual break and help to emphasise your points effectively.
- Use graphs or charts to represent trends that support your argument.
- Always caption your visuals and reference them in the text.
Integrate Feedback Actively
It’s often beneficial to have colleagues, advisors, or other experts review your discussion section before finalising it. They can offer fresh perspectives and may catch gaps or ambiguities that you’ve missed.
- Seek feedback but also know when to filter it, sticking to advice that genuinely enhances your work.
- Don’t wait until the last minute for feedback; give reviewers ample time.
Highlight the Broader Implications
While you’ll delve into this more in your conclusion, don’t shy away from previewing the broader implications of your work in your discussion. Make it clear why your research matters in a wider context.
- State the broader implications but keep them tightly related to your research findings.
- Avoid making grand claims that your research can’t support
In the journey toward a PhD, learning ‘how to write like a doctor’ is more than mastering grammar or honing your prose; it’s about flexing your academic muscles with confidence and authority. It is in the discussion chapter that you really start flexing, and which you really can and need to speak like a doctor.
For many, this is the first instance of challenging the hegemony of existing literature, refuting established theories, or proposing innovative frameworks. It’s an intimidating task; after all, these are the ideas and research paradigms you’ve been learning about throughout your educational journey. Suddenly, you’re not just absorbing knowledge; you’re contributing to it, critiquing it, and perhaps even changing its trajectory. If it feels challenging, remember that’s because it’s new, and that’s why it’s hard. However, you’ve made it this far, and that alone testifies to your academic rigour and capability. You’ve earned the right to be heard; now it’s time to speak with the academic authority that has been years in the making. So, don’t hold back—flex those academic muscles and carve your niche in the scholarly conversation.

Share this:
Submit a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 21, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 18, 2023.

The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results .
It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review and paper or dissertation topic , and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion. It should not be a second results section.
There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your writing around these key elements:
- Summary : A brief recap of your key results
- Interpretations: What do your results mean?
- Implications: Why do your results matter?
- Limitations: What can’t your results tell us?
- Recommendations: Avenues for further studies or analyses
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What not to include in your discussion section, step 1: summarize your key findings, step 2: give your interpretations, step 3: discuss the implications, step 4: acknowledge the limitations, step 5: share your recommendations, discussion section example, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about discussion sections.
There are a few common mistakes to avoid when writing the discussion section of your paper.
- Don’t introduce new results: You should only discuss the data that you have already reported in your results section .
- Don’t make inflated claims: Avoid overinterpretation and speculation that isn’t directly supported by your data.
- Don’t undermine your research: The discussion of limitations should aim to strengthen your credibility, not emphasize weaknesses or failures.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarizing your major findings. To speed up the process you can use a summarizer to quickly get an overview of all important findings. Don’t just repeat all the data you have already reported—aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research question . This should be no more than one paragraph.
Many students struggle with the differences between a discussion section and a results section . The crux of the matter is that your results sections should present your results, and your discussion section should subjectively evaluate them. Try not to blend elements of these two sections, in order to keep your paper sharp.
- The results indicate that…
- The study demonstrates a correlation between…
- This analysis supports the theory that…
- The data suggest that…
The meaning of your results may seem obvious to you, but it’s important to spell out their significance for your reader, showing exactly how they answer your research question.
The form of your interpretations will depend on the type of research, but some typical approaches to interpreting the data include:
- Identifying correlations , patterns, and relationships among the data
- Discussing whether the results met your expectations or supported your hypotheses
- Contextualizing your findings within previous research and theory
- Explaining unexpected results and evaluating their significance
- Considering possible alternative explanations and making an argument for your position
You can organize your discussion around key themes, hypotheses, or research questions, following the same structure as your results section. Alternatively, you can also begin by highlighting the most significant or unexpected results.
- In line with the hypothesis…
- Contrary to the hypothesized association…
- The results contradict the claims of Smith (2022) that…
- The results might suggest that x . However, based on the findings of similar studies, a more plausible explanation is y .
As well as giving your own interpretations, make sure to relate your results back to the scholarly work that you surveyed in the literature review . The discussion should show how your findings fit with existing knowledge, what new insights they contribute, and what consequences they have for theory or practice.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support existing theories, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge existing theories, why do you think that is?
- Are there any practical implications?
Your overall aim is to show the reader exactly what your research has contributed, and why they should care.
- These results build on existing evidence of…
- The results do not fit with the theory that…
- The experiment provides a new insight into the relationship between…
- These results should be taken into account when considering how to…
- The data contribute a clearer understanding of…
- While previous research has focused on x , these results demonstrate that y .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Even the best research has its limitations. Acknowledging these is important to demonstrate your credibility. Limitations aren’t about listing your errors, but about providing an accurate picture of what can and cannot be concluded from your study.
Limitations might be due to your overall research design, specific methodological choices , or unanticipated obstacles that emerged during your research process.
Here are a few common possibilities:
- If your sample size was small or limited to a specific group of people, explain how generalizability is limited.
- If you encountered problems when gathering or analyzing data, explain how these influenced the results.
- If there are potential confounding variables that you were unable to control, acknowledge the effect these may have had.
After noting the limitations, you can reiterate why the results are nonetheless valid for the purpose of answering your research question.
- The generalizability of the results is limited by…
- The reliability of these data is impacted by…
- Due to the lack of data on x , the results cannot confirm…
- The methodological choices were constrained by…
- It is beyond the scope of this study to…
Based on the discussion of your results, you can make recommendations for practical implementation or further research. Sometimes, the recommendations are saved for the conclusion .
Suggestions for further research can lead directly from the limitations. Don’t just state that more studies should be done—give concrete ideas for how future work can build on areas that your own research was unable to address.
- Further research is needed to establish…
- Future studies should take into account…
- Avenues for future research include…

If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
In the discussion , you explore the meaning and relevance of your research results , explaining how they fit with existing research and theory. Discuss:
- Your interpretations : what do the results tell us?
- The implications : why do the results matter?
- The limitation s : what can’t the results tell us?
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/discussion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a results section | tips & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

How to Write a Perfect Discussion Chapter for a PhD Thesis
Discussion chapter of a PhD thesis focuses on explaining and analyzing what you have researched, presenting how it is associated with the existing literature. It is also a place for argument supporting your entire discussion. We often find that people seek thesis writing help from experienced editing and proofreading services to prepare a flawless PhD discussion chapter. However, following 9 essential tips can help you design a perfect PhD thesis with an excellent discussion chapter.

This article provides 9 effective tips for writing a flawless discussion chapter for a PhD thesis. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
Writing a flawless PhD thesis requires much more than only subject matter expertise. It requires expertise, experience, and in-depth thinking, along with sharp intelligence. Though most students add a discussion chapter in their thesis or dissertation, many of them end up messing up the essay or missing out the central issues.
A discussion chapter in a PhD thesis is a place where you have the chance to delving into the analysis, importance, and relevance of your research. This section focuses on explaining and analyzing what you have researched, presenting how it is associated with the existing literature. It is also a place for argument supporting your entire discussion. We often find that people seek thesis writing help from experienced editing and proofreading services to prepare a flawless PhD discussion chapter. However, the following 9 essential tips can help you design a perfect PhD thesis with an excellent discussion chapter.
1. Understand the objective of your PhD thesis
Before setting out to conduct a PhD thesis, researchers design and plan a study with objective(s) in mind. Such objectives inform how the dissertation is conducted. For example, no researcher would just commence by administering questionnaires or setting up laboratory equipment without an objective. It also informs the questions and necessary procedures to undertake. To write a well-conveyed discussion section in PhD thesis, the author must review and ascertain whether the conducted study addressed these objectives. It takes the understanding of the objective to assess the achievement of the objective clearly. Based on the assessment, the author finds the direction of his discussion. The comprehension of this objective is critical to crafting a focused discussion section in scholarly writing.
2. Determine a clear structure
The first step in organizing a perfect discussion chapter for a PhD thesis is to divide them into separate sections that move from a particular result to implications. However, depending on your PhD thesis topics, you may utilize the followings:
Analyze and summarize your main findings.
Evaluate how the results reflect the literature review.
Show if the discussion impacts the original hypothesis and, if yes, how it affects your hypothesis.
3. Usage of grammar and tense
The proper usage of grammar and tense is a key to a seamless PhD thesis. The improper use of grammar and tense can have the worst impact on the entire dissertation, along with the discussion chapter . Depending on the context, the usage of past and present tense should be made. When you are referring to specific data, the present tense can be used. For instance, when the light increases, speed decreases. However, while summarizing the result or concluding something, past tense can be used. For example, between 2013 and 2016, the number of car accidents decreased visibly. However, depending on the context, you can combine two tenses. Also, bear in mind that different manuals might require different tenses.
The tense adopted by the study should be uniform. Try to write the discussion chapter of your PhD thesis in the required tense format of your guideline. For instance, The APA Publication Manual provides suggestions on which verb tense is appropriate for various sections of a thesis:
Past tense or present perfect tense for the literature review and "the description of the procedure if the discussion is of past events."
"Use past tense to describe the "
"Use the present tense to discuss the implications of the results and to present the conclusions. By reporting conclusions in the present tense, you allow all readers to join you in deliberating the matter at hand."
As much as possible, try to be consistent with your chosen verb tense within a section as doing so "can help ensure smooth expression."
It is always best to check with your manual to get their opinion on the best approach for your thesis.
4. Referring to hypotheses and literature review
The primary purpose of referring to the literature review is to contextualize your discussion chapter as a part of the debate. For instance, suppose you introduce a theory claiming that speed cameras have zero effect on a road’s fatalities. You need to describe how your findings relate to this assumption. The same applies while making a hypothesis. Never forget this fact while discussing your results.
5. Evaluate your results and compare them with existing studies
While writing the discussion chapter of your PhD thesis, you need to analyze your results rather than just simplifying it. Don’t forget to do complete research on if your results agree or conflict with the previous studies. You need to evaluate if there are any differences and, if yes, what the differences are. Comparing the development with existing studies helps your research to connect any existing debate. It also offers a solid base of conclusions.
In a well-written discussion chapter of a PhD thesis, an author should compare his/her findings with those of other studies reported in the literature. This aspect is different from a literature review in the sense that the author has data at hand to compare, as against the general overview made about a thesis’s objectives prior to the investigation. In comparing, the author is able to pronounce the authenticity of the results, especially when similar procedures were used in other studies. Any differences in findings can be explained using the different peculiarities between the author’s study and others. If this consideration is carefully made and implemented, the author may likely find evidence-based explanations for his/her findings. Even for novel findings, an author may still find relevant literature that formed the rudiments of the present study to discuss the progress, contribution, and novel dimension of the study.
6. Why should the findings of your PhD thesis matter?
After discussing the study results, the author, as part of his goal, must propose the impact of the study’s findings on the problem that informed the idea of the thesis. The reader will be better served if the author describes a roadmap for solving the problem based on the findings. Depending on the nature of the problem, an author may propose solutions to affect policy, behavioral change, or conventional practice. Only after making this contribution will a discussion section expose readers to the specific and general impacts of a PhD thesis.
7. Understand the limitation of your research
It is one of the most important things to evaluate when writing a discussion chapter for your PhD thesis. The discussion chapter of your research paper should involve some acknowledgment of the study limitations. Suppose you have critically assessed similar studies in the literature review; you are free to compare your work against their weakness or strength.
8. Don’t be afraid to be unique
The focus on research may change and evolve with time if you are working on a long-term project. The key to adjusting the focus on the literature review is to reflect these changes. Suppose you may find that specific themes are more prominent than others; it is helpful if you review your literature review and tweak them to emphasize the themes. Never be afraid to be unique to bring the changes.
9. Don’t forget to avail a professional thesis editing and proofreading service
Last but not least, you can seek assistance from professional editing and proofreading services. Taking PhD thesis help from professional editing and proofreading services doesn’t only facilitate the writing process but also helps you execute a flawless PhD thesis with a well-formed and informative discussion chapter. When highly qualified writers take responsibility for your research paper, you don’t need to worry about structure, consistency, flow, tone, grammar, and accuracy.
Writing a PhD thesis is not an easy task. However, systematic thinking and structure can make the process easier. From the introduction to the demonstration of your argument, literature review, and analysis of the result, everything is vital to prepare an outstanding PhD thesis. However, if you want to seek assistance from a professional editing and proofreading service provider to write a seamless discussion chapter and thesis, feel free to contact us. We will be happy to help you.

Why choose Best Edit & Proof for thesis editing and proofreading services
If you need thesis/dissertation editing or proofreading, our services are always credible and highly approved by recognized scholars and researchers. Our editing and proofreading experts adhere to all the guidelines and rules from all eminent universities. All the editors and proofreaders are seasoned doctorally qualified scholars with experience in editing and proofreading manuscripts. Therefore, any students can avail of unmatched thesis editing and proofreading service from Best Edit & Proof.
If you need us to make your thesis and dissertation shine, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering manuscripts with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized styles of writing. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English thesis/dissertation formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for thesis/dissertation editing and proofreading now!
Kindly visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.
24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have an active live chat module to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Avoid Anthropomorphism in Your Dissertation?
How to Write a Research Methodology Section for a Dissertation and Thesis
How to Write a Theoretical Framework for a Dissertation and Thesis?
How to Write Literature Review for a Dissertation and Thesis
How to Write a Dissertation and Thesis Introduction
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

As a student or anyone in the academic field, you need to know about your text even before you start writing it. In academic writing, there are so many rules, regulations, styles, and guides that you need to follow. Naturally, to write a good piece of work, you need to make sure that you know about what you are writing. Similarly, it is important to know about the different types of academic writing before you get started on it. This guide discusses the various types of scholarly writing.

Writing for academic purposes entails writing literature that is formal in tone, objective, structure-wise complex and contains a fair amount of academic jargon. As such, there are certain words and phrases, collectively called taboo words, that academic writers omit when writing manuscripts. Academic writing encourages their elimination to maintain the “formality” of academic documents. This article discusses the definition of taboo words to avoid and examine their use cases.
Whenever you use words, facts, ideas, or explanations from other works, those sources must be cited. Academic referencing is required when you have copied texts from an essay, an article, a book, or other sources verbatim, which is called quotation. You also need referencing when you use an idea or a fact from another work even if you haven’t used their exact expression.
Writing a research paper involves scrutinizing a plethora of research material to bring forth plausible conclusions. However, no matter the degree of impeccability and thoroughness of the research, successfully transmuting it into words takes a grave amount of practice and endurance. Thus, it is not uncommon to see amateur and even veteran scholarly writers commit research writing mistakes in their papers now and then. Following the narrative, this article will describe 5 research writing mistakes that frequently blemish the works of academic writers. It will also shed some much-needed light on the tips to amend and avoid these mistakes.

You have been working hard on your research paper and want to write an excellent dissertation/thesis. You have researched all the materials, and your data are perfect— all you need to do is put them together in a dissertation or thesis. But how do you manage that? While working on the research is not easy, it’s structuring a dissertation or thesis that the main issue lies with. Therefore, if you are struggling with structuring your dissertation or thesis, this article may be of help.

Writing a thesis can be an overwhelming task for many college and graduate students. Managing all the elements associated with a thesis while ensuring that the quality is not compromised can be challenging. However, what is even more strenuous is deciding on a thesis's layout. "How to structure a thesis" is a question that several final-year students struggle to answer. And understandably so, as all colleges and universities have their guidelines for drafting a thesis. However, there is an immutable structure that's common for every thesis. In this brief guide, we will take a look at this structure and analyze each of its components.

We may define a study variable as an attribute of an object of study. Suppose you wish to establish a sound experimental design. In that case, selecting variables to measure is exceedingly crucial.
Editorial Manager, our manuscript submissions site will be unavailable between 12pm April 5, 2024 and 12pm April 8 2024 (Pacific Standard Time). We apologize for any inconvenience this may cause.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
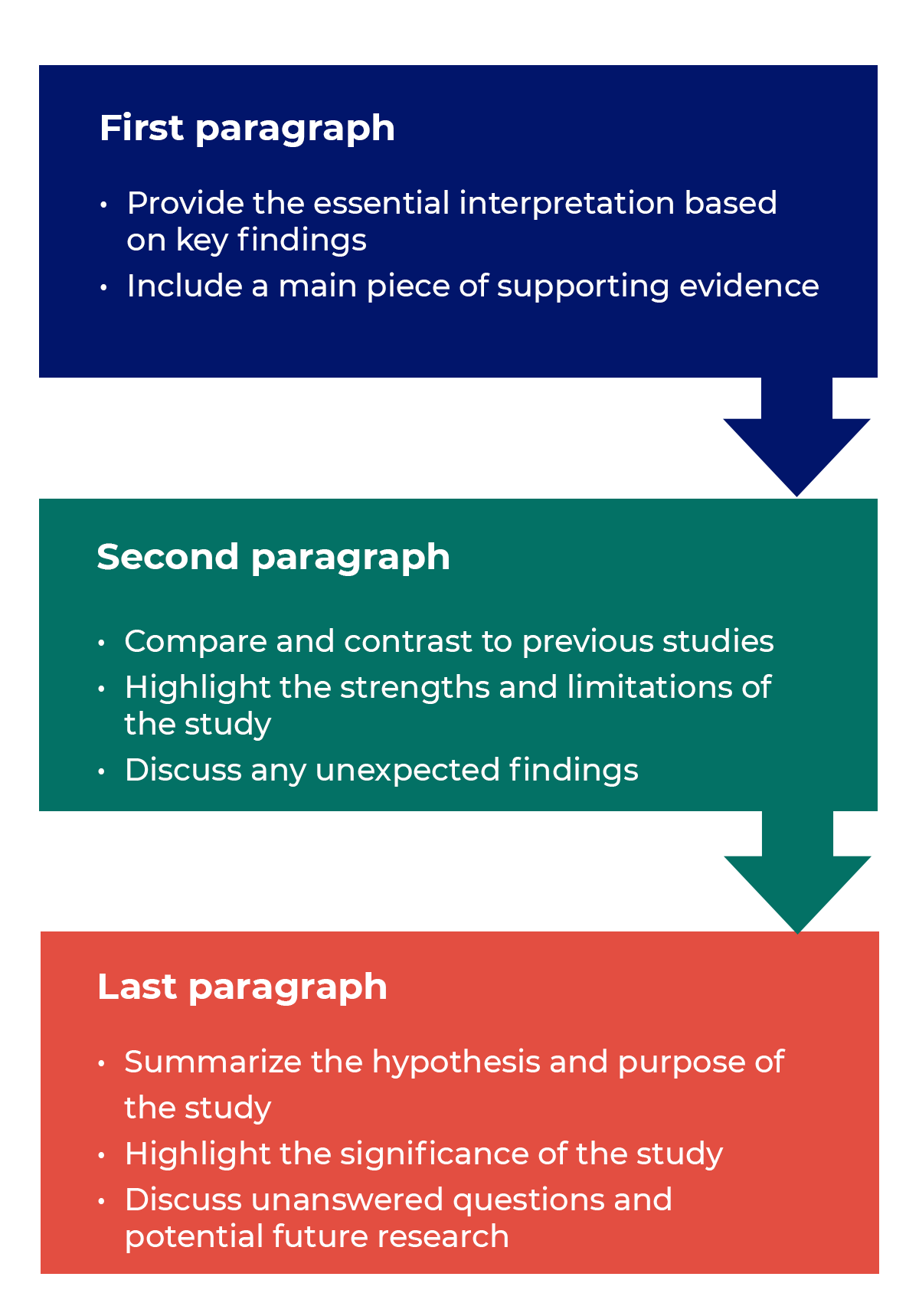
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- How it works
How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter – A Quick Guide with Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
Dissertation discussion is the chapter where you explore the relevance, significance, and meanings of your findings – allowing you to showcase your talents in describing and analyzing the results of your study.
Here, you will be expected to demonstrate how your research findings answer the research questions established or test the hypothesis .
The arguments you assert in the dissertation analysis and discussions chapter lay the foundations of your conclusion . It is critically important to discuss the results in a precise manner.
To help you understand how to write a dissertation discussion chapter, here is the list of the main elements of this section so you stay on the right track when writing:
- Summary: Start by providing a summary of your key research findings
- Interpretations: What is the significance of your findings?
- Implications: Why are your findings important to academic and scientific communities, and what purpose would they serve?
- Limitations: When and where will your results have no implications?
- Future Recommendations : Advice for other researchers and scientists who explore the topic further in future.
The dissertation discussion chapter should be carefully drafted to ensure that the results mentioned in your research align with your research question, aims, and objectives.
Considering the importance of this chapter for all students working on their dissertations, we have comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation discussion chapter.
The discussion and conclusion chapters often overlap. Depending on your university, you may be asked to group these two sections in one chapter – Discussion and Conclusion.
In some cases, the results and discussion are put together under the Results and Discussion chapter. Here are some dissertation examples of working out the best structure for your dissertation.
Alternatively, you can look for the required dissertation structure in your handbook or consult your supervisor.
Steps of How to Write Dissertation Discussion Chapter
1. provide a summary of your findings.
Start your discussion by summarising the key findings of your research questions. Avoid repeating the information you have already stated in the previous chapters.
You will be expected to clearly express your interpretation of results to answer the research questions established initially in one or two paragraphs.
Here are some examples of how to present the summary of your findings ;
- “The data suggests that”,
- “The results confirm that”,
- “The analysis indicates that”,
- “The research shows a relationship between”, etc.
2. Interpretations of Results
Your audience will expect you to provide meanings of the results, although they might seem obvious to you. The results and their interpretations should be linked to the research questions so the reader can understand the value your research has added to the literature.
There are many ways of interpreting the data, but your chosen approach to interpreting the data will depend on the type of research involved . Some of the most common strategies employed include;
- Describing how and why you ended up with unexpected findings and explaining their importance in detail
- Relating your findings with previous studies conducted
- Explaining your position with logical arguments when/if any alternative explanations are suggested
- An in-depth discussion around whether or not the findings answered your research questions and successfully tested the hypothesis
Examples of how you can start your interpretation in the Discussion chapter are –
- “Findings of this study contradict those of Allen et al. (2014) that”,
- “Contrary to the hypothesized association,” “Confirming the hypothesis…”,
- “The findings confirm that A is….. even though Allen et al. (2014) and Michael (2012) suggested B was …..”
3. Implications of your Study
What practical and theoretical implications will your study have for other researchers and the scientific community as a whole?
It is vital to relate your results to the knowledge in the existing literature so the readers can establish how your research will contribute to the existing data.
When thinking of the possible consequences of your findings, you should ask yourself these;
- Are your findings in line with previous studies? What contribution did your research make to them?
- Why are your results entirely different from other studies on the same topic?
- Did your findings approve or contradict existing knowledge?
- What are the practical implications of your study?
Remember that as the researcher, you should aim to let your readers know why your study will contribute to the existing literature. Possible ways of starting this particular section are;
- “The findings show that A….. whereas Lee (2017) and John (2013) suggested that B”, “The results of this study completely contradict the claims made in theories”,
- “These results are not in line with the theoretical perspectives”,
- “The statistical analysis provides a new understanding of the relationship between A and B”,
- “Future studies should take into consideration the findings of this study because”
“Improve your work’s language, structure, style, and overall quality. Get help from our experienced dissertation editors to improve the quality of your paper to First Class Standard. Click here to learn more about our Dissertation, Editing, and Improvement Services .
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue, then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across various disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

4. Recognise the Limitations of your Research
Almost every academic research has some limitations. Acknowledging them will only add to your credibility as a scientific researcher.
In addition to the possible human errors, it’s important to take into account other factors that might have influenced the results of your study, including but not limited to unexpected research obstacles, specific methodological choices , and the overall research design.
Avoid mentioning any limitations that may not be relevant to your research aim, but clearly state the limitations that may have affected your results.
For example, if you used a sample size that included a tiny population, you may not generalise your results.
Similarly, obstacles faced in collecting data from the participants can influence the findings of your study. Make a note of all such research limitations , but explain to the reader why your results are still authentic.
- The small sample size limited the generalisability of the results.
- The authenticity of the findings may have been influenced by….
- The obstacles in collecting data resulted in…
- It is beyond the framework of this research…
5. Provide Recommendations for Future Research
The limitations of your research work directly result in future recommendations. However, it should be noted that your recommendations for future research work should include the areas that your own work could not report so other researchers can build on them.
Sometimes the recommendations are a part of the conclusion chapter . Some examples;
- More research is needed to be performed….
The Purpose of Dissertation Discussion Chapter
Remember that the discussion section of a dissertation is the heart of your research because a) it will indicate your stance on the topic of research, and b) it answers the research questions initially established in the Introduction chapter .
Every piece of information you present here will add value to the existing literature within your field of study. How you structured your findings in the preceding chapter will help you determine the best structure for your dissertation discussion section.
For example, it might be logical to structure your analysis/discussions by theme if you chose the pattern in your findings section.
But generally, discussion based on research questions is the more widely used structure in academia because this pattern clearly indicates how you have addressed the aim of your research.
Most UK universities require the supervisor or committee members to comment on the extent to which each research question has been answered. You will be doing them a great favour if you structure your discussion so that each research question is laid out separately.
Irrespective of whether you are writing an essay, dissertation, or chapter of a dissertation , all pieces of writing should start with an introduction .
Once your readers have read through your study results, you might want to highlight the contents of the subsequent discussion as an introduction paragraph (summary of your results – as explained above).
Likewise, the discussion chapter is expected to end with a concluding paragraph – allowing you the opportunity to summarise your interpretations.
The dissertation analysis & discussion chapter is usually very long, so it will make sense to emphasise the critical points in a concluding paragraph so the reader can grasp the essential information. This will also help to make sure the reader understands your analysis.
Also Read: Research Discussion Of Findings
Useful Tips
Presentation of graphs, tables, and figures.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, students spent days creating graphs and charts for their statistical analysis work . Thanks to technology, you can produce even more accurate graphs and figures today in a shorter period.
Using Microsoft Word, STATA, SPSS, Microsoft Excel and other statistical analysis software, we can now draw beautiful-looking figures, tables , and graphs with just a few clicks and make them appear in our document at the desired place. But there are downsides to being too dependent on technology.
Many students make the common mistake of using colours to represent variables when really they have to print their dissertation paper final copy in black and white.
Any colours on graphs and figures will eventually be viewed in the grayscale presentation. Recognizing different shades of grey on the same chart or graph can sometimes be a little confusing.
For example, green and purple appear as pretty much the same shade of grey on a line chat, meaning your chart will become unreadable to the marker.
Another trap you may fall into is the unintentional stuffing of the dissertation chapter with graphs and figures. Even though it is essential to show numbers and statistics, you don’t want to overwhelm your readers with too many.
It may not be necessary to have a graph/table under each sub-heading. Only you can best judge whether or not you need to have a graph/table under a particular sub-heading as the writer.
Relating to Previous Chapters
As a student, it can be challenging to develop your own analysis and discussion of results. One of the excellent discussion chapter requirements is to showcase your ability to relate previous research to your research results.
Avoid repeating the same information over and over. Many students fall into this trap which negatively affects the mark of their overall dissertation paper .
Concise and to-the-point information will help you effectively convey your point to the readers.
Although you must demonstrate how your findings relate to previous research, it is equally important to ensure you are not simply rewriting what has already been said in the introduction and literature review chapters.
The best strategy is to use examples from previous sections to postulate an argument.
Hyperlinks are recommended to take the reader from one section to another. This is especially important for submitting electronic documents as .word or .pdf files. Hyperlinking is tedious and time-consuming, so you should allow for this in your dissertation timeline to avoid rushing in the closing stages.
Also read: How to Write the Abstract for the Dissertation.
Using Subsections and Subheadings
You might want to reflect on the structure of the discussion in your organizstion of the dissertation discussion chapter, and for that, you will need to create sub-sections.
It is essential to keep subsections to the point and as short as possible. Use a layer of subheadings if possible.
For example
Subsection 4.1 of Chapter 4- Discussion can be further divided into sections 4.1.1 and 4.2.2. After three numerical layers (4.1.1, 4.2.2, and 4.2.3), any subheadings need not appear in the contents table.
The titles of all subsections will appear on your table of contents so choose the wordings carefully. A title too long or too short might confuse the reader. A one or two-word subheading will not give the reader enough information to understand the section.
Likewise, using a research question or long sentences in the subheading is not recommended. It might help to examine how other researchers and writers create these subheadings.
Critical Thinking
Your critical thinking skills are the crux of your dissertation discussion chapter. You will do yourself a great disservice if you fail to put the critical thinking element into the equation.
After all, this exercise aims to showcase clarity in your thoughts and arguments. Markers of the dissertation give more importance to the analysis and discussion chapter. But you could be marked negatively if this particular chapter lacks critical thinking.
Many students struggle to distinguish between fundamental descriptive analysis and critical thinking with their opinions on the research topic.
Critical thinking is a skill developed over time, and it might be daunting for you to come to terms with the idea of critical thinking and its use in your analysis. But even if you are no expert, you must try your best.

“Still unsure about how to write a dissertation discussion chapter ? Why not take advantage of our UK-based dissertation writing service ? Your dissertation is essential to your degree, so you cannot risk failing it.
With our custom writing service , you are guaranteed to have all your dissertation paper elements put into the right place. Our expert academics can help you with your full dissertation paper or a part of it. Click here to learn more about our dissertation services.
Duplication of Content
Another critical error students make reaffirming the point the graph/chart was supposed to make. Writing out the same information as presented in the graph defeats the whole purpose of having them in the first place.
You will be expected to form your opinions and arguments based on the findings (as presented by the graphs), so keep an eye on this mistake. Finally, avoid simply inserting a graph without any explanation whatsoever.
It should be noted that there is no correct or incorrect number of charts/figures one can use in the dissertation findings and discussion chapter. A balance must be struck.
Avoid Over Interpretation
This is a major no-no when writing a dissertation discussion. Do not make an argument that isn’t backed by your collected data.
The results and interpretations that cannot be supported should not be mentioned. Your research will be deemed unauthentic and will also be questioned by your supervisor if you do so. Results should be interpreted without any bias.
How to Write the Findings of a Dissertation.
Do not Speculate
Speculation in the discussion chapter of your dissertation is discouraged. Your dissertation’s discussion is based on your collected data and how it relates to your research questions. Thus, speculating here will undoubtedly undermine your research’s credibility.
Also, try not to generalise your findings. If your research is based on a specific population, do not state that the same findings might apply in every case. As indicated previously, it is essential to acknowledge the limitations of your research.
On the other hand, if you think your discussion needs to address other populations as well, start your sentence like this ‘We speculate that..’ or ‘It is speculated that..’ This will keep you from getting into any trouble.
What are the elements of the Dissertation Discussion?
The list of the main elements of the discussion chapter are:
- Implications : Why are your findings important to academic and scientific communities, and what purpose would they serve?
- Future Recommendations: Advice for other researchers and scientists who explore the topic further in future.
What are the steps of writing a Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
- Write a summary of the findings
- Provide a summary of your findings
- Interpretations of Results
- Recognise the Limitations of your research
- Provide Recommendations for Future Research.
Can we use graphs and charts in the Dissertation Discussion Chapter?
Yes, using graphs to aid your statistical results and enhance presentation is essential, but do not overwhelm it with a lot of graphs in multiple colours.
You May Also Like
Finding it difficult to maintain a good relationship with your supervisor? Here are some tips on ‘How to Deal with an Unhelpful Dissertation Supervisor’.
How to Structure a Dissertation or Thesis Need interesting and manageable Finance and Accounting dissertation topics? Here are the trending Media dissertation titles so you can choose one most suitable to your needs.
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?
Reflecting on and Comparing Your Data, Recognising the Strengths and Limitations
- First Online: 19 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Sue Reeves ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3017-0559 3 &
- Bartek Buczkowski ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4146-3664 4
275 Accesses
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with subsections and paragraphs. We also present a list of points to do and avoid when writing the discussion together with a Discussion chapter checklist.
- Critical Writing
- Key results
- Limitations
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Braun V, Clarke V (2013) Successful qualitative research: a practical guide for beginners. SAGE Publications, London
Google Scholar
McGregor SLT (2018) Understanding and evaluating research: a critical guide. SAGE Publications, Los Angeles, CA
Book Google Scholar
PLOS (2023) Author resources. How to write discussions and conclusions. Accessed Mar 3, 2023, from https://plos.org/resource/how-to-write-conclusions/ . Accessed 3 Mar 2023
Further Reading
Cottrell S (2017) Critical thinking skills: effective analysis, argument and reflection, 3rd edn. Palgrave, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Roehampton, London, UK
Manchester Metropolitan University, Manchester, UK
Bartek Buczkowski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Reeves, S., Buczkowski, B. (2023). How Do I Write the Discussion Chapter?. In: Mastering Your Dissertation. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-41911-9_9
Published : 19 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-41910-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-41911-9
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

How To Write A Discussion Chapter In Your PhD Discussion
If you’re here, you probably got to the part in your thesis or dissertation where you have to work on the discussion chapter. Don’t worry; we’re here to help! In this article, we’ll break down the discussion chapter in simple language and give you lots of examples to make it easier to understand.”
What is the discussion chapter?
The discussion chapter plays a vital role in your thesis or dissertation.
Unlike the results chapter, which presents your analysis findings, whether they are qualitative or quantitative, this chapter is where you really dig into your results.
Here, you’ll interpret and explain your research findings, exploring their significance and implications.
In this section, you’ll connect your research findings with your research questions or hypotheses and link them back to previous studies and literature, as you did in your literature review chapter.
You’ll also assess the relevance and importance of your findings to your field of study and make a persuasive argument for the conclusions you’ve drawn from your analysis.
In essence, the discussion chapter is your opportunity to engage with and elucidate your research findings in a comprehensive and cohesive manner.
What to Incorporate in the Discussion Chapter?
Let’s start with the basics: in certain studies, the results and discussion chapters are merged into a single chapter.
Whether this applies to your work depends on the type of study you conducted, including its nature and chosen methodology, as well as the guidelines set by your university.
In essence, your discussion chapter’s primary purpose is to dissect, delve into the meaning of, and establish the significance of the data you presented in the results chapter. Here, you will infuse your results with significance by critically evaluating and interpreting them.
This process aids in addressing your research questions, achieving your research objectives, and bolstering your overall conclusions. Therefore, your discussion chapter should squarely focus on findings that are directly relevant to your research objectives and questions.
Since this chapter mirrors your results chapter, it’s imperative that you refrain from introducing any new findings.
In simpler terms, you should avoid making claims in this section if you haven’t already presented the pertinent data in the results chapter.
Hence, ensure that each discussion point you raise in this chapter corresponds to the data analysis covered in the results chapter.
Crafting the Discussion Chapter: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you’ve grasped the essence of the discussion chapter and its essential elements let’s delve into structuring this pivotal chapter. In a broad sense, you can break down this chapter into six key components, which serve as sequential steps in the chapter-writing journey.
Step 1: Reiterate Your Research Problem and Questions
When you begin writing your discussion chapter, the first thing to do is remind your reader about what your research is all about, like the main problem you’re trying to solve and what questions you’re trying to answer. This reminder is important because, after reading a bunch of stuff, your reader might forget what your research was really about or get distracted by other things.
Step 2: Sum Up The Main Discoveries
Moving ahead, it’s time to sum up the most important thing you found in your results chapter. Now, this might look different if you did qualitative or quantitative research. Qualitative research could be all about themes and connections, while quantitative research might talk about things like correlations and reasons behind everything happening.
Usually, this part doesn’t need to be long, just a paragraph or two, depending on how many research questions you had. Try to keep it short because you’ll go into more detail later on in the chapter.
Here are some examples of what you might say:
The analysed data suggest that…
The data support/oppose the defined theory that…
The detailed analysis identifies…
Remember, these are just examples. What you say here depends on the questions you were trying to answer in your research, so make sure you address them correctly.
Step 3: Interpret your results
Once you’ve started your research problem and questions and given a quick rundown of what you found, it’s time to explain your discoveries by looking at your results more closely.
But remember, only talk about what you already told them in the results part – don’t bring in new information.
From a structure point of view, it might be a good idea to organise this chapter, kind of like how you did the results one. This makes it easier for your reader to follow along and understand your points better.
Here are a few things to think about while you’re explaining your findings:
- How do your results match up with what other studies found?
- If your results are different from other studies, why do you think that happened?
- What do your results add to your field of research?
- Are there any other reasons your findings could be the way they are?
When you’re explaining your findings, make sure not to say anything that doesn’t have proof. Every idea you put out there should have something to back it up, like data or facts (and you already put that in the results chapter).
Step 4: Admit the Flaws in Your Research
Now, in the fourth step of making your discussion chapter, it’s time to fess up about the things that didn’t go so well in your study. These could be problems in any part of your study, like how big or small it was, the theories you used, how you did your analysis or even the group of people you studied.
Some folks might feel like talking about what went wrong is like shooting themselves in the foot. But that’s not true! Actually, one of the signs of doing really good research is being honest about what didn’t work out. So, saying what went wrong is actually a strong move, not a weak one.
Step 5: Offer Some Suggestions for What Comes Next
Now, after you’ve talked about your findings and owned up to what didn’t go perfectly, it’s time to think about two important things:
- How can other students use your findings in real life? Basically, what good can come out of your research in the field or industry? Where can people put this info to use, and how would they do it?
- What about future research? How can other researchers take what you’ve done and build on it? Maybe they can make your findings even better by dealing with the issues you mentioned earlier. While you’re at it, check if your results match up with what other studies have found, and if not, figure out why.
Final Words
By adhering to these fundamental principles, you will not only construct a well-organised discussion chapter but also contribute significantly to the ongoing discourse in your field. This, in turn, elevates the impact and relevance of your research within the broader academic community.
Recent Posts
- Dealing with Academic Rejection: Coping Strategies for Overcoming Setbacks
- Time Management Strategies: Balancing Research, Writing, Teaching Responsibilities, and Personal Life
- Innovative Research Methodologies: Navigating the Future of Academic Inquiry
- Top UK Law Thesis Writing Services: A Must Read for Students
- Excelling in Nursing Thesis: Best Writing Service in UK
Your Dissertation Proposal Is Completely Secured And Never Reused For Another Client.
Work Done On Order Specifications With 0% Plagiarism And 100% Ordinally

Our Customer Support Agents Are Available Round The Clock To Answer Your Queries

Have Any Confusions Regarding Your Essay? Consult Our Experts For Better Guidance
What’s Included: Discussion Template
This template covers all the core components required in the discussion/analysis chapter of a typical dissertation or thesis, including:
- The opening/overview section
- Overview of key findings
- Interpretation of the findings
- Concluding summary
The purpose of each section is explained in plain language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. The template also includes practical examples to help you understand exactly what’s required, along with links to additional free resources (articles, videos, etc.) to help you along your research journey.
The cleanly formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
PS – if you’d like a high-level template for the entire thesis, you can we’ve got that too .
FAQ: Thesis Discussion Template
What types of dissertations/theses can this template be used for.
The discussion chapter template follows the standard format for academic research projects, which means it will be suitable for the majority of dissertations, theses and research projects (especially those within the sciences).
Keep in mind that the exact requirements for the discussion chapter/section will vary between universities and degree programs. For example, your university may require that the discussion chapter and conclusion chapter are merged into one, or that the results and discussion are covered together (this is often the case with qualitative research). So, be sure to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalise your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Master or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a dissertation, thesis or research project at any level of study. Doctoral-level projects typically require the discussion chapter to be more extensive/comprehensive, but the structure will typically remain the same. Again, be sure to check your university’s requirements and norms in terms of document structure.

How long should the discussion chapter be?
This can vary a fair deal, depending on the level of study (undergrad, Master or Doctoral), the field of research, as well as your university’s specific requirements. Therefore, it’s best to check with your university or review past dissertations from your program to get an accurate estimate.
Can I share this template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template in its original format (no editing allowed). If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, please reference this page as your source.
What format is the template (DOC, PDF, PPT, etc.)?
The dissertation discussion chapter template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
Do you have templates for the other chapters?
Yes, we do. We are constantly developing our collection of free resources to help students complete their dissertations and theses. You can view all of our template resources here .
Can Grad Coach help me with my discussion/analysis?
Yes, we can provide coaching-based assistance with your discussion chapter (or any other chapter). If you’re interested, get in touch to discuss our private coaching services .

- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Writing a compelling integrated discussion: a guide for integrated discussions in article-based theses and dissertations
- Krystina B. Lewis , Ian D. Graham , Laura Boland and Dawn Stacey
Article-based theses and dissertations are increasingly being used in nursing and the health sciences as an alternate format to the traditional five-chapter monograph. A unique chapter in the article-based thesis is the integrated discussion, which differs in breadth and depth as compared to the discussion for a traditional thesis monograph or journal article. For many students and faculty, the integrated discussion is a challenging chapter to write, with minimal or no published guidance available. In this article, we offer a four-step approach with templates for planning and writing an integrated discussion. We also share several lessons learned with examples from published theses and dissertations. Writing an integrated discussion can be facilitated and written more efficiently by developing a clear and detailed outline of the chapter and broad discussion points prior to drafting the text, to achieve a higher-level synthesis, analysis, and interpretation of the overall significance of the thesis findings.
Introduction
An increasing number of university graduate programs in nursing and the health sciences offer the option of writing an article-based thesis or dissertation as an alternate format to the traditional five-chapter monograph ( De Jong, Moser, & Hall, 2005 ; Graves et al., 2018 ; Robinson & Dracup, 2008 ; Smaldone, Heitkemper, Jackman, Joanne Woo, & Kelson, 2019 ). This format has gained traction internationally to facilitate the earlier and more frequent publication of graduate student research for the timelier advancement of knowledge and impact on clinical practice ( Evans, Amaro, Herbert, Blossom, & Roberts, 2018 ; Maynard, Vaughn, Sarteschi, & Berglund, 2012 ; Smaldone et al., 2019 ). An article-based thesis, also known as the manuscript option, thesis-by manuscript, integrated thesis, or PhD by published works, typically includes one or more articles suitable for publication in peer-reviewed journals and bounded together with an introduction chapter and integrated discussion chapter ( Baggs, 2011 ). The integrated discussion is a unique chapter in an article-based thesis. Integrated (2020) is defined as “ many different parts [that] are closely connected and work successfully together ” (“Integrated,” 2020). The general purpose of the integrated discussion chapter is to provide an overall synthesis and demonstrate high level abstraction, analysis, and interpretation of the thesis findings. It is an opportunity to showcase the thesis’ findings, the student’s reflections about the findings, and its implications ( Smith, 2015 ).
Requirements and expectations for the integrated discussion chapter vary by institution and department. Supervising faculty within individual institutions may also have differing approaches and expectations. We found no general rules or expectations in the literature for writing an integrated discussion. An inquiry of select institutional guidance documents in various international jurisdictions revealed that academic institutions provide few details about this chapter. Descriptions focus more on the overall contribution of the integrated discussion chapter to the thesis, rather than guidance on how to write it ( Table 1 ).
Examples of institutional guidelines for the integrated discussion chapter in an article-based thesis.
Writing a compelling integrated discussion can be challenging, and there is a scarcity of resources, instructions, or published guidance for students and supervising faculty on this subject. Existing guidance is focused primarily on writing discussions for a single journal article or a traditional thesis monograph. Yet, the integrated discussion chapter differs in breadth and depth. In journal articles, a discussion usually consists of a statement of the main findings, interpretation of the results in the context of the broader literature, strengths and limitations of the study, and implications for potential users of the findings (clinicians, administrators, policy makers, and others), the discipline, and future research ( Makar, Foltz, Lendner, & Vaccaro, 2018 ). The discussion section of the traditional monograph thesis has a similar format to that of a journal article as it discusses a single study but is often more detailed. In comparison, the integrated discussion chapter of the article-based thesis provides students with a space in which to weave the results and discussion points from the individual articles comprising the thesis, elaborate on the logic and linkages between them, and convincingly argue for the unified, coherent, and original nature of their findings and contributions to the field-at-large. Smith (2015) refers to this as the golden thread. Grant (2011) refers to it as the logic of connectivity . Ultimately, it is about how the student links the key ideas from the individual papers and articulates the connectedness between them, so as to make readers understand the thesis’ broader meaning which make it accessible to a larger audience ( Smith, 2015 ).
The educational value of conceptualizing and writing an integrated discussion can be best classified at the highest level of Bloom’s revised taxonomy of educational objectives, to Create — formerly known as Synthesis in Bloom’s original taxonomy — whereby parts are combined in novel ways to produce a coherent whole and to formulate new points of view ( Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001 ; Bloom, 1956 ). According to the taxonomy, the integrated discussion represents the pinnacle of cognitive tasks and processes by requiring higher-order thinking and critical reflections expected of graduate level students. Hence, the integrated discussion chapter provides the graduate student an opportunity to synthesize, integrate, and raise the discussion to a higher level of abstraction; allowing them to demonstrate the coherence between all articles reported in the thesis. It is often in the integrated discussion where thesis advisory committee members and examiners can assess the student’s depth of theoretical and applied knowledge of the subject matter, capacity for critical inquiry, and judge the overall value of the student’s conclusions and contributions to the substantive area of study ( Gould, 2016 ). Specifically in nursing, this higher-level thinking can be articulated by discussing how the knowledge generated advances nursing practice, education and research, and how it contributes to the delivery of high quality health care, and improved health and health system outcomes ( Institute of Medicine [US] Committee on the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Initiative on the Future of Nursing, 2011 ). Yet, with little guidance available on how to think about and write an integrated discussion, graduate students may miss the opportunity to engage in this higher-order thinking and critical reflections.
In this paper, we offer a practical four-step approach with templates for writing an integrated discussion for article-based theses. KBL initially developed the steps and templates as she conceptualized and wrote her integrated discussion for her PhD dissertation. The steps and templates were refined as a result of (a) her own integrated discussion writing process; (b) discussion with her thesis supervisor and thesis advisory committee members; and, (c) feedback from several graduate students who have used it successfully. As recent doctoral graduates and faculty supervisors, we are sharing this approach and our lessons learned with examples from published theses and dissertations.
Writing an integrated discussion chapter
Step 1: outlining the integrated discussion chapter.
To begin, we propose drafting an outline for the integrated discussion chapter with six major sections ( Table 2 ). First, provide an opening paragraph introducing the information to be presented in the chapter. Second, present a summary of the overall purpose of the thesis as a unified piece of work and a brief summary of each individual article prepared for publication. Each article summary should include the study aim, study design, and key results. Keep in mind that by the time supervisors, thesis advisory committee members, and examiners read the integrated discussion chapter, they have probably just finished reading the previous chapters and articles, so there is no need to repeat information in detail. Rather, the purpose of this section is to refresh the readers’ focus and to begin demonstrating how the articles logically link to each other. Third, outline the main points of the integrated discussion as clearly and concisely as possible (see Step 2 and 3 for more details). Fourth, discuss the strengths and limitations of the thesis, as a whole, if applicable. Typically, strengths and limitations are only presented at the individual article level, but if there are broader strengths or limitations that apply to the thesis, they can be discussed in this chapter. Fifth, discuss the implications of the thesis for the specific discipline (e.g., nursing, medicine, population health, epidemiology, rehabilitation) in terms of the findings’ applicability to practice, education, leadership, and/or policy. Sixth, describe implications for future research. Finally, this chapter should end with a strong, clear, and logical conclusion summarizing the entire work across all elements of the thesis. The conclusions should clearly state the original contribution(s) to the advancement of knowledge and overall significance for the field at-large.
Suggested structure for an integrated discussion.
a Approximate length based on 12-point type font, double spacing, left-justified, 1-inch margins, and format for 8 ½ × 11 paper.
Step 2. Mapping individual articles’ findings to inform the integrated discussion
The next step is to draft the main integrated discussion points. Using Template I, capture the main discussion points from each individual article ( Table 3 ). If there is only one article in the thesis, these can be generated from the literature review, guiding theoretical framework, and/or chosen methodology. This exercise is intended to facilitate the student’s thinking about how to build convincing overarching discussion points and explore the key messages they want readers to come away with after reading the thesis.
Template I to summarize individual article discussion points to identify overarching discussion points.
a If there is only one article in the thesis, additional discussion points/contributions/implications can come from the literature review, guiding theoretical framework, and/or chosen methodology. b Whether these implications are included in the individual article or not, this explicitly offers a starting point to think of the implications arising from individual articles.
The last row in this template is reserved for listing the actual and potential disciplinary implications arising from each article, which may address any of the following domains: practice, education, leadership, policy and/or research. Depending on journal requirements, these implications may be directly discussed in the individual articles. If not, this section offers the student a starting point for thinking about the disciplinary implications arising from their thesis as a whole.
Completing Template I as individual articles are finalized, and sharing it with a faculty supervisor or thesis advisory committee can facilitate discussion about the evolving integrated discussion points. It can also facilitate requisite critical thinking and reflection necessary for linking findings across the individual articles.
Step 3. Drafting the main integrated discussion points
Consider the discussion points and disciplinary implications across all individual articles of the thesis to identify commonalities or differences;
Draft main integrated discussion points, logically connecting the individual articles;
Identify findings from, ideally, two individual articles that support (or refute) the proposed main integrated discussion points (aiming for evidence from two articles helps achieve a higher level integrated discussion); and
Identify and classify theoretical and empirical literature relevant to the main integrated discussion points. Select regional, national, and international empirical studies, theoretical works, clinical practice guidelines, technical reports, and/or policy documents; highlight what the thesis adds to the field (of knowledge) and how it will enhance understanding of the subject.
Template II to build the main integrated discussion points from the individual articles and summarize implications.
a If there is only one article in the thesis, the supporting contributions/arguments can come from the literature review, guiding theoretical framework, and/or chosen methodology. b Broader literature can include empirical studies, theoretical works, practice guidelines, technical reports, and/or policy documents. c List the disciplinary implications identified across all articles. This explicitly offers a starting point to think of the disciplinary implications arising across the individual articles’ findings and discussion points.
This exercise is intended to help organize the content of the integrated discussion early in the writing process. We recommend sharing the evolving Templates I and II with the faculty supervisor or thesis advisory committee and use it as a tool for discussion before writing the integrated discussion chapter. As supervisors (DS, IDG), we also initiate Template I in discussion with our graduate students – often using a blank piece of paper. This reflective exercise may save time in the long run, as it facilitates staying focused on the key points and avoids repeating elements of the discussions within the individual papers. The more detailed the completed templates, the more content is available to transform into text.
Step 4. Writing the integrated discussion chapter
The final step is to turn the planned outline (Step 1) and the drafted main integrated discussion points (Step 3) into narrative prose. To remain focused, start by adding subheadings from the outline and lower level subheadings for each of the main integrated discussion points. A compelling integrated discussion is often preceded by multiple revisions. It should not be written when rushing to meet the thesis submission deadline as writing this chapter requires considerable reflection and introspection. For these reasons, we remind students that the integrated discussion is the last chapter their examiners will read, and it will leave a lasting impression. Getting this chapter right allows the student to demonstrate their mastery of the totality of their thesis work and sets the stage for the examination. In our experience, when an integrated discussion is well-written, the examiners’ comments indicate that the integrated discussion chapter tied all elements of the thesis together and helped them understand the thesis in its entirety.
Lessons learned
When applying this approach for writing our own integrated discussions, or when guiding graduate students through the process, we have learned several lessons. To exemplify these lessons, we offer examples of published theses and dissertations in nursing and other health professions.
Lesson 1. Use stepwise approach with templates to plan and structure the chapter
Using the attached templates and proposed stepwise approach to structure the writing process reduces the inclination to simply repeat the discussion points found in the individual articles. The templates may also help graduate students overcome procrastination resulting from not knowing where to start with the integrated discussion. Further, Templates I and II may be used to guide discussions between graduate student and faculty supervisor, allowing for progress to be monitored prior to writing. Another advantage to doing this early is that some supervisors are less familiar with the article-based thesis format and may have little experience guiding their students in writing the integrated discussion. As such, using the template to walk through this process may be helpful for both parties.
Lesson 2. Think ahead
Avoid delaying until all the individual thesis articles are written before thinking about the integrated discussion. We recommend filling out the templates as individual articles are completed. When analyzing the results for individual articles and thinking about the discussion sections for these, we often identified relevant discussion points that were too broad for the articles. Keeping a log of discussions with faculty supervisors and thesis advisory committee members throughout the thesis writing process, and keeping record of personal reflections that were beyond the scope of individual articles, may help gather ideas early. For example, when first considering her integrated discussion, Hoefel (2019) chose the Walker and Avant (2011) theory testing approach to validate the decisional needs concept and test the main hypothesis of the Ottawa Decision Support Framework ( O’Connor et al., 1998 ). For her thesis, Hoefel (2019) wrote two articles based upon this framework. Her first was a systematic review article on decisional needs of people making health decisions and the second was a sub-analysis of a systematic review on patient decision aids. Hence, evidence from these articles contributed to the higher level discussion about validating the concepts and testing the hypotheses in the framework.
Lesson 3. Dedicate sufficient time
Dedicating sufficient time to writing the integrated discussion is important. For many students, the integrated discussion is a challenging chapter to write. It calls for a different style of writing than that which is required for individual research study articles. It requires conveying abstract and conceptual ideas to generate broader insights. Prior to developing and using these templates, our experience with many students has been that it can take many months of re-writing the integrated discussion chapter for it to adequately reflect the breadth and depth of the student’s thesis work and its vital contribution to the field. We have found that our stepwise approach involves more careful planning and conceptualizing of the integrated discussion prior to drafting the chapter, and therefore results in a more efficient writing and editing process.
Lesson 4. Consider theoretical and methodological implications
Theoretical and methodological implications may be considered as integrated discussion points. A student may choose to closely examine their selected theoretical perspective in light of their thesis findings. For example, in Lewis’ (2018) integrated discussion, she provided a discourse on the use of complementary theoretical frameworks across individual studies: the Ottawa Decision Support Framework ( O’Connor et al., 1998 ) and Normalization Process Theory ( May et al., 2009 ). This provided a link between intervention development and implementation planning, proposing a novel theory-informed approach for the development of decision support interventions ( Lewis, 2018 ). Likewise, methodological implications may be discussed in cases where a student’s thesis advances methods, or to discuss the influence of chosen methodology on key findings where similar research questions are answered using distinct study designs. Wu’s (2014) integrated discussion focused on the methods used for conducting a survey for data collection. He used a set of reminders, with the last reminder being a courier package and return envelope. He then discussed how testing this reminder strategy in his thesis study contributed to survey design methods.
Lesson 5. An integrated discussion is feasible with one article
In cases where there is only one article comprising an article-based thesis, key findings from a more detailed literature review, a theoretical framework guiding the entire research project, or chosen methodology can provide the additional linkages to build the main integrated discussion points. For instance, in her Master of Nursing thesis integrated discussion, Demery Varin (2018) compared and contrasted her secondary analysis findings on the predictors of nurses’ research use in long-term care settings (as reported in one published article) with her review of the literature on the individual and contextual factors to nurses’ research use in all settings.
Lesson 6. Integrated discussions are publishable
The integrated discussion (or elements of it) may be publishable in its own right. When written well, the integrated discussion often results in an important academic contribution to the body of knowledge. Some graduate students have used the integrated discussion as the basis for a commentary paper or an updated theoretical framework paper. In her integrated discussion chapter of her doctoral thesis, Jull (2014) described the development of a collaborative framework for community-research partnerships co-produced by First Nations, Inuit, and Metis women’s community members and researchers. This framework was based on her findings and experience conducting the studies comprising her thesis. Jull et al. (2018) subsequently published a paper based on her integrated discussion.
Lesson 7. Integrated discussions can lay the foundation for subsequent research
Many students who are completing a Master’s or PhD thesis also intend to pursue further research. A well thought out and articulated integrated discussion can inform subsequent research projects, grant proposals, or programs of research. For example, Boland (2018) drew from her PhD integrated discussion to identify evidence-practice gaps and potential solutions in pediatric shared decision-making, which she used to underpin a successful Canadian Institutes of Health Research post-doctoral fellowship and guide the establishment of her research program.
In this paper, we propose an approach to writing an integrated discussion chapter for an article-based thesis. Our advice provided in this paper is intended to position graduate students to adequately plan and produce a unified, coherent, and higher-level synthesis of the articles comprising their thesis. Challenges in writing an integrated discussion include avoiding repetition of discussion points already included within the individual articles comprising the thesis and achieving a higher-level discussion to integrate findings across the individual articles. Writing an integrated discussion can be facilitated by developing a clear and detailed outline of the chapter and, in particular, by identifying broader, more overarching points of discussion, than those presented within the individual articles. We encourage graduate students, faculty supervisors and thesis advisory committees to use the templates provided and share their experiences.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the graduate students who have used this approach, reported that it was useful, and offered feedback to improve it. The authors also wish to thank the reviewers. Their critical read and constructive comments strengthened this manuscript.
Research funding: The authors received no financial support for the authorship and publication of this manuscript. IDG is a recipient of a CIHR Foundation Grant (FDN# 143237). DS holds a University Research Chair in Knowledge Translation to Patients at the University of Ottawa.
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
Competing interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Aarhus University . (2020). Guidelines for assessment of PhD dissertation and PhD defence . Retrieved from https://phd.health.au.dk/doingaphd/dissertation/assessment/guidelinesforassessmentofphddissertationandphddefence/ . Search in Google Scholar
Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (2001). A taxonomy for teaching, learning, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives . New York, NY: Longman. Search in Google Scholar
Baggs, J. G. (2011). The dissertation manuscript option, internet posting, and publication. Research in Nursing & Health , 34 (2), 89–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.20420 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Bloom, B. S. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives, handbook I: The cognitive domain . New York: David McKay Co Inc. Search in Google Scholar
Boland, L. (2018). Implementation of shared decision making in pediatric clinical practice [PhD in Population Health]. Ottawa, Canada: University of Ottawa. Search in Google Scholar
Carter. (2009). Old lamps for new: Mnemonic techniques and the thesis. Arts and Humanities in Education , 8 , 56–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/1474022208098302 . Search in Google Scholar
De Jong, M. J., Moser, D. K., & Hall, L. A. (2005). The manuscript option dissertation: Multiple perspectives. Nurse Author & Editor , 15 (3), 3–4, 7–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-4910.2005.tb00554.x . Search in Google Scholar
Deakin University . (2019). Thesis structure options: Thesis by publication . Retrieved from https://www.deakin.edu.au/students/research/your-thesis-and-examinations/thesis-structure-options . Search in Google Scholar
Demery Varin, M. (2018). Modeling the predictors of nurses’ research use in Canadian long-term care homes [Masters of Science degree in Nursing]. Ottawa, Canada: University of Ottawa. Search in Google Scholar
Evans, S. C., Amaro, C. M., Herbert, R., Blossom, J. B., & Roberts, M. C. (2018). “Are you gonna publish that?” Peer-reviewed publication outcomes of doctoral dissertations in psychology. PloS One , 13 (2), e0192219. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192219 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Gould, J. (2016). Future of the thesis. Nature , 535 , 26–28. https://doi.org/10.1038/535026a . Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Grant, C. (2011). Diversifying and transforming the doctoral studies terrain: A student’s experience of a thesis by publication. Alternation , 18 (2), 245–267. Search in Google Scholar
Graves, J. M., Postma, J., Katz, J. R., Kehoe, L., Swalling, E., & Barbosa-Leiker, C. (2018). A national survey examining manuscript dissertation formats among nursing PhD programs in the United States. Journal of Nursing Scholarship , 50 (3), 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnu.12374 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Hoefel, L. (2019). 20th Anniversary update of the Ottawa Decision Support Framework: Evidence syntheses of needs assessments and trials of patient decision aids [Masters of Science degree in Nursing]. Ottawa, Canada: University of Ottawa. 10.1177/0272989X20924645 Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Institute of Medicine Committee on the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Initiative on the Future of Nursing . (2011). The future of nursing: Leading change, advancing health . Washington (DC): National Academies Press. Search in Google Scholar
Integrated. (2020). https://www.oxfordlearnersdictionaries.com/definition/english/integrated [Accessed 3 Dec 2020]. Search in Google Scholar
Jull, J. (2014). Cultural adaptation of a shared decision-making intervention to address the needs of first Nations, Métis and Inuit women [PhD in Population Health]. Ottawa, Canada: University of Ottawa. Search in Google Scholar
Jull, J., Giles, A., Boyer, Y., & Stacey, D., & Minwaashin, Lodge. (2018). Development of a Collaborative Research Framework: An Example of a Study Conducted By and With a First Nations, Inuit and Métis Women’s Community and Its Research Partners. ACME: An International Journal for Critical Geographies , 17 (3), 671–686. https://acme-journal.org/index.php/acme/article/view/1317 . Search in Google Scholar
Lancaster University . (2020). Manual of academic regulations and procedures: Postgraduate graduate research regulations . Retrieved from https://www.lancaster.ac.uk/media/lancaster-university/content-assets/documents/student-based-services/asq/marp/PGR-Regs.pdf . Search in Google Scholar
Lewis, K. B. (2018). Development and preliminary evaluation of decision support for patients to accept or decline implantable cardioverter-defibrillator replacement at the time of battery depletion [PhD in Nursing]. Ottawa, Canada: University of Ottawa. Search in Google Scholar
Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical Spine Surgery , 31 (8), 345–346. https://doi.org/10.1097/bsd.0000000000000687 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed
May, C. R., Mair, F., Finch, T., MacFarlane, A., Dowrick, C., Treweek, S., … Montori, V. M. (2009). Development of a theory of implementation and integration: Normalization process theory. Implementation Science , 4 , 29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-4-29 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Maynard, B. R., Vaughn, M. G., Sarteschi, C. M., & Berglund, A. H. (2012). Social work dissertation research: Contributing to scholarly discourse or the file drawer? British Journal of Social Work , 44 , 1045–1062. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcs172 . Search in Google Scholar
O’Connor, A. M., Tugwell, P., Wells, G. A., Elmslie, T., Jolly, E., Hollingworth, G., … Drake, E. (1998). A decision aid for women considering hormone therapy after menopause: Decision support framework and evaluation. Patient Education and Counseling , 33 (3), 267–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0738-3991(98)00026-3 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Robinson, S., & Dracup, K. (2008). Innovative options for the doctoral dissertation in nursing. Nursing Outlook , 56 (4), 174–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.outlook.2008.03.004 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed
Smaldone, A., Heitkemper, E., Jackman, K., Joanne Woo, K., & Kelson, J. (2019). Dissemination of PhD dissertation research by dissertation format: A retrospective cohort study. Journal of Nursing Scholarship , 51 (5), 599–607. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnu.12504 . Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
Smith, S. (2015). PhD by published work: A practical guide for success . London, UK: Palgrave. Search in Google Scholar
Stellenbosch University . (2019). General information on doctoral studies . [Available upon request]. Search in Google Scholar
University of Ottawa . (2020). Monograph thesis and thesis by article(s) – regulations . Retrieved from https://www.uottawa.ca/graduate-studies/students/theses/writing . Search in Google Scholar
University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing . (n.d.). PhD handbook . Retrieved from https://www.nursing.upenn.edu/student-services/resources/handbooks-forms-policies/phd-handbook/dissertation/ . Search in Google Scholar
Walker, L. O., & Avant, K. C. (2011). Strategies for theory construction in nursing . Boston: Prentice-Hall. Search in Google Scholar
Wu, R. C. (2014). Evaluation of a rectal cancer patient decision aid and the factors influencing its implementation in clinical practice [Masters of Science in Epidemiology]. Ottawa, Canada: University of Ottawa. 10.1186/1471-2482-14-16 Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2021 Krystina B. Lewis et al., published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- X / Twitter
Supplementary Materials
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
Journal and Issue
Articles in the same issue.
How do I write the discussion section?
Some time ago, on the advice of my good friend and efficiency guru Jason Downs , I read The 80/20 principle: how to achieve more by doing less by Richard Koch.
To be fair, Jason did tell me, in the spirit of efficiency, that I didn’t really need to read the book. The main message, he said, was in the title – and he was right. Koch claims that 80% of value comes from 20% of the work effort. The trick to an efficient work life, Richard Koch contends, is to identify ‘high value’ work and just do that as much as possible. High value work for me is writing and talking to people; low value work is email. As with most self help books, I finished it and did nothing different.
Then, late last year, my friend Jonathon, one half of the fantastic Research Whisperer team , sent me a spreadsheet analysis of all their blog search terms. His analysis showed lots of people were looking for how to make a simple Gantt Chart. Jonathan’s excellent analysis left me wondering: what do readers think is ‘high value work Thesis Whisperer work’ based on their search behaviour?
I immediately dropped everything to repeat the method on Thesis Whisperer, using 10 years of search data from well over 9 million visits. Here’s what I found out:
- Thesis Whisperer has great brand recognition: around 50% of people find their way here through typing variations of the name of the blog (far less people come here by typing in my actual name, Inger Mewburn).
- As I expected, the next most popular search type was writing problems, in various manifestations.
- Third most common search term was ‘How to look clever’, which is both funny and sad. I’m guessing this leads people to this old post here, which is a personal favourite
I drilled down a bit to try and find out: what exactly is troubling people about writing? I thought I would find concerns about productivity, feedback, literature reviews, style and voice, perhaps grammar, but it wasn’t: 75% of the thousands of writing related searches were questions and anxieties about the discussion section. I’ve only written about the discussion section twice in 10 years. That’s not 20% of the effort producing 80% of the reward – It’s more like 0.003% of the effort!
I’ve been teaching writing for over 15 years and reviewed lots of development programs at other universities. I see very few workshops that focus on the discussion section as a separate piece of writing. I guess we assume that supervisors are helping out, but my search data suggests maybe not. I get the anxiety, I really do. The discussion section of the thesis is the heart of the creative endeavour: it’s where you have to be MOST original. Even if you don’t have a section in your thesis called ‘discussion’ (I didn’t) there will still be places in your thesis where you must explicitly make new knowledge in relation to the data you have collected and your analysis.

I reviewed the two posts to see what else I might have to say. In How do I start my discussion section I offer a description of what the discussion section should contain, how to decide if you need one or not and a grab bag of tactics to go about getting started – each one of which should probably have its own blog post. In The difficult discussion section I describe the section as the ‘problem child’ of the thesis. In that post, I try to walk people through a step by step process for making sense of the mess of writing, findings and analysis that you can end up with towards the end of your degree.
But what should actually go in the discussion section and how should you write it?
I’m indebted to my colleague Josta Heylingers for pointing me at the literature on functional linguistics. Josta uses this literature to teach people how to write discussion chapters at Auckland University of Technology. To do this, she uses the work of John Swales , and his method of ‘move step analysis’. I touched on this method in my own PhD, and of my PhD students is using move step analysis in her work, so I’ve had to become passingly familiar with the method.
Swales starts by assuming that texts are social things : every reader has been ‘trained’ on what to expect from different kinds of texts. Job applications ‘sound’ different from grant applications, which sound different than a journal article. So readers are familiar with the linguistic ‘moves’ to expect. These linguistic moves are sort of like dance steps that build together to make a socially recognisable text.
Swales’ move step analysis is a way of breaking down the text dance so you can understand which bits go where and how to put them together in an accomplished performance. Think of any dance craze you can name. When I was a teenager, in the 1980s (!) it was ‘ The Nutbush ‘; by the 1990s it was The Macarena . In case you weren’t there, or don’t remember, here’s a helpful video. It’s worth watching, because it’s delightful, and a good way to understand what move step analysis is:
In the video, Jean Eu broke down the Macerana series of steps with the hands, arms and hips, that are put together to form moves. The moves must appear in the right order or sequence to become a dance. If you start with your hands down to your hips instead of out in front of you, you ARE dancing, but it’s NOT the Macarena. People watching you, expecting to see the Macarena, will be confused. If you do the right moves, but not in time with the music, it’s still the Macarena, but anyone watching you will think that you are a bad dancer.
So it is with the Macarena as it is with writing the discussion section of your thesis: use the right steps, build them into a move and do the moves in the right sequence and you will write a ‘socially correct’ text. If you do a socially correct text, the knowledge you are putting forward for consideration can be easily assessed by the reader, because they are not distracted by the bad performance. The steps also give you a formula you can use to give your thoughts about your research findings a shape and form.
So, what does the discussion section dance look like? Let’s start with the big picture. In ‘ The textural organisation of the discussion sections of accounting research articles’, Amnuai says:
“The discussion section is where authors place their ideas about their research findings and consolidate, generalize, and interpret their research outcomes for the benefit of those in their field or for other communities”
Each discipline is different. It’s important to base your moves on what is socially acceptable for your community, but here is a simple list of basic moves that every discussion section needs to have:
- Restate Results (don’t repeat them!)
- Comment on the results
- Evaluate the Results
- Make suggestions based on the results
The helpful Manchester Academic Phrase Bank ‘discussing the findings’ section , gives you some sentences that you can use as the ‘steps’ for each move. Try some of these sentence starters to get you going:
Restate Results: “The current study found that …” “The results of this study show/indicate that …” “The results of this study did not show that …/did not show any significant increase in …”
Comment on the results: “These results further support the idea of … “These results confirm the association between … “These findings are consistent with …” “These match/don’t match those observed in earlier studies…” “These results are in line with those of previous studies…” “These findings are in agreement with those obtained by …”
Evaluate the Results: “There are several possible explanations for this result…” “It seems possible that these results are due to …” “The reason for this is not clear but it may have something to do with…” “These data must be interpreted with caution because …” “The present results are significant in at least two major respects.”
Suggestions “There are still many unanswered questions about …” “There is abundant room for further progress in determining.” “Despite these promising results, questions remain.”
Don’t just confine yourself to these sentences though, go and visit the Manchester Academic Phrase Bank where there are hundreds of sentence starters for all parts of the thesis.
Another way to get started is to take a leaf out of Pat Thomson and Barbara Kamler’s book ‘Helping doctoral students write’ by ‘stripping down’ a paragraph from a writer you admire and using it, almost like a garden trellis, to ‘train’ your own text in the right direction. Here’s the first paragraph from a paper in my library by Wajcman and Rose (2011) Constant Connectivity: Rethinking Interruptions at Work. This paragraph is clearly part of the ‘summarising the results’ move:
The picture that emerges from the analysis above is one of work practices being reshaped as employees negotiate the constant connectivity intrinsic to contemporary knowledge work. We have established a link between mediated communication and short, fragmented work episodes. What is striking is that the predominant mode of communication during the workday is now tech- nologically mediated rather than face-to-face. However, each communication episode tends to be of a short duration – on average a period of five minutes or less.
Kamler and Thomson suggest you strip out the content. I like using the ‘strike through’ setting on my word processor, like so:
The picture that emerges from the analysis above is one of work practices being reshaped as employees negotiate the constant connectivity intrinsic to contemporary knowledge work . We have established a link between mediated communication and short, fragmented work episodes . What is striking is that the predominant mode of communication during the workday is now tech- nologically mediated rather than face-to-face . However, each communication episode tends to be of a short duration – on average a period of five minutes or less.
You can now insert your own findings in to this cleared out structure. This technique works best if you treat the original framework roughly, so that you produce something almost entirely new. Here’s the reworked paragraph using some concepts I am playing with in my latest work (although I haven’t actually proved any of this, so don’t quote me!):
The picture that emerges from the analysis above is one of many missed opportunities, which seems intrinsic to the post PhD job search. We have established a link between previous experience of specific work environments and success in job seeking. What is striking is that the strength of this connection is how little the graduates paid attention to the need to articulate their previous industry experience. Each Graduate tends to be living in a state of what Lovitts calls ‘pluralistic ignorance’.
You might be wondering: is this plagiarism? No because you are not using the original knowledge or ideas, just the structure. You can write a whole discussion section like this if you like, but you would need to find a study with very similar findings. My hunch is that you could have to hijack paragraphs from different texts and stitch them together like a patchwork quilt.
Once you get your head around the idea that there are the ‘right’ and ‘wrong’ kind of textural moves in every kind of academic writing, you have an amazingly powerful writing device that you can deploy on any section of your thesis.
There is so much more to say about the discussion section – I’ll try to get to it again this year. Your question will help me decide what to focus on, so please feel free to leave them in the comments. I’m also interested in your feelings about the discussion section and how you’ve approached constructing them in the past – do you have any suggestions for others?
Related posts
How do I start my discussion section
The difficult discussion section
The textural organisation of the discussion sections of accounting research articles
Analysis of moves, rhetorical patterns and linguistic features in New Scientist articles
Constant Connectivity: Rethinking Interruptions at Work.
Want more content like Thesiswhisperer?

Visit The Whisper Collective , a site we built to continuously curate all the best research education material on the web.
Love the ThesisWhisperer?
I cover all the expenses of operating the Thesis Whisperer out of my own pocket. If you’d like to support my work, please consider becoming a $1 a month Patreon or buy a copy of my (cheap!) ebooks: Tame your PhD or The Year of Living Covidly .
Jason Downs and I have our first ‘On the Reg’ podcast book – on TextExpander . This book shows you how to use TextExpander to reduce your everyday cognitive load.
You can find links to print versions – and my other books – on the Buy Books page
Share this:
The Thesis Whisperer is written by Professor Inger Mewburn, director of researcher development at The Australian National University . New posts on the first Wednesday of the month. Subscribe by email below. Visit the About page to find out more about me, my podcasts and books. I'm on most social media platforms as @thesiswhisperer. The best places to talk to me are LinkedIn , Mastodon and Threads.
- Post (606)
- Page (16)
- Product (5)
- Getting things done (257)
- Miscellany (137)
- On Writing (137)
- Your Career (113)
- You and your supervisor (67)
- Writing (48)
- productivity (23)
- consulting (13)
- TWC (13)
- supervision (12)
- 2024 (3)
- 2023 (12)
- 2022 (11)
- 2021 (15)
- 2020 (22)
Whisper to me....
Enter your email address to get posts by email.
Email Address
Sign me up!
- On the reg: a podcast with @jasondowns
- Thesis Whisperer on Facebook
- Thesis Whisperer on Instagram
- Thesis Whisperer on Soundcloud
- Thesis Whisperer on Youtube
- Thesiswhisperer on Mastodon
- Thesiswhisperer page on LinkedIn
- Thesiswhisperer Podcast
- 12,068,741 hits
Discover more from The Thesis Whisperer
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter: Guide & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
How to Write a Dissertation Discussion Chapter: Guide & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker

You may also like

Dissertation discussion section is a chapter that interprets the results obtained from research and offers an in-depth analysis of findings. In this section, students need to analyze the outcomes, evaluate their significance, and compare them to previous research. The discussion section may also explore the limitations of the study and suggest further research perspectives.
If you are stuck with your thesis or dissertation discussion chapter, you are in the right place to complete this section successfully. This article will outline our best solutions and methods on how to write the discussion of a dissertation or thesis. We also will share advanced dissertation discussion examples to help you finalize your PhD work. Feel like academic writing gives you hassles? Remember that you can always rely on academic experts qualified in your field to get professional dissertation help online .
Order dissertation discussion from our proficient writers. They will take a significant burden off of you. Instead, they will carry out high-level academic work in a short time.
FAQ About Dissertation Discussion Chapter
1. where does a discussion section go in a dissertation.
Dissertation discussion section is used to go right after the result chapter. The logic is simple — you share your data and then go to the elaboration and explanation of it. Check the sample thesis we provide to students for details on structure.
2. How long should a dissertation discussion chapter be?
It is not a surprise that dissertation discussion chapter is extremely significant for the research. Here you will go into the details of your study and interpret results to prove or not your hypothesis. It should take almost 25% of your work.
3. What tense should I use in a dissertation discussion?
Thesis or dissertation discussion used to have some rules on using tenses. You need to use the present tense when referring to established facts and use the past tense when referring to previous studies. And check your text before submission to ensure that you did not miss something.
4. What not to include in a dissertation discussion section?
The answer is easy. Discussion section of a dissertation should not include any new findings or describe some unsupported claims. Also, do not try to feel all possible gaps with one research. It may be better to outline your ideas for future studies in recommendations.
Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
First and foremost, students need to have a clear understanding of what dissertation discussion is. This is not the same as your results section , where you share data from your research. You are going deeper into the explanation of the existing data in your thesis or dissertation discussion section. In other words, you illustrate practical implications of your research and how the data can be used, researched further, or limited. What will make your discussion section of a dissertation excellent:
This section should go after research methodology and before the dissertation conclusion . It should be directly relevant to questions posed in your introduction. The biggest mistake you can make is to rewrite your result chapter with other words and add some limitations and recommendation paragraphs. However, this is an entirely different type of writing you need to complete.
A dissertation discussion section is critical to explaining students’ findings and the application of data to real-life cases. As we mentioned before, this section will often be read right after the dissertation methods . It evaluates and elaborates on findings and helps to understand the importance of your performed thesis research. A dissertation discussion opens a new perspective on further research on the same field or topic. It also outlines critical data to consider in subsequent studies. In a nutshell, this is the section where you explain your work to a broad audience.
Let’s start your writing journey of this research part with a clear delineation of what it should include and then briefly discuss each component. Here are some basic things you need to consider for an excellent discussion chapter of dissertation :
One of the most commonly asked questions for our experts is how to write the discussion section of a dissertation or thesis. We understand why it can be complicated to get a clear answer. Students often think that this section is similar to the result chapter and just retells it in other words. But it is not so. Let’s go through all steps to writing a discussion in a dissertation, and share our best examples from academic papers.
Writing the discussion chapter of a dissertation is not a big deal if you understand its aim and each component in a text structure. First of all, you need to evaluate how your results help to answer research questions you defined in the beginning. It is not about repeating the result, you did it in previous paragraphs. However, dissertation or thesis discussion should underline how your findings help to answer the research problem. Start writing from a brief intro by recalling research questions or hypotheses . Then, show how your results answer them or support a hypothesis in your work.
Next part of your discussion for dissertation is to provide a short summary of previous data. But do not respite the same summary paragraphs from results or introduction of a dissertation . Here researchers should be more thoughtful and go deeper into the work’s aims. Try to explain in a few sentences what you get from running research. For instance, starters usually write the statement that “our data proves that…” or “survey results illustrate a clear correlation between a and b that is critical for proving our working hypothesis…”. A discussion chapter of your dissertation is not just a fixation on results but a more profound summary connected to research goals and purpose. Here is an example: Summary of Findings Example
The most critical part of a discussion section is to explain and enact the results you’ve got. It is the most significant part of any text. Students should be clear about what to include in these paragraphs. Here is some advice to make this elaboration structured:
Writing a dissertation discussion chapter can be tough, but here is a great sample to learn from. Example of Interpretations in Disssertation Discussion
Here we came to the implications of your findings for the dissertation discussion. In other words, this is a few sentences on how your work is connected to other studies on the same research topic or what literature gap you are going to fill with the data and research you launched. Remember to mention how your study address the limitations you have discovered while writing a literature review . First, outline how your hypothesis relates to theories or previous works in the field. Maybe, you challenged some theories or tried to define your own. Be specific in this section. Second, define a practical implementation of your work. Maybe, it can support recommendations or change legislation. Discussion chapter of a thesis is a place where you explain your work, make it valuable, and incorporate additional meaning for some specific data. Example of Implications in Disssertation Discussion
It is pretty tricky to conduct research without limitations. You will always have some, which does not mean that your work is not good. When you write a discussion chapter in a thesis or dissertation, focus on what may influence your results and how changing independent variables can affect your data collection methods and final outcomes. Here are some points to consider when you structure your dissertation discussion limitation part:
Critical thinking and analysis can help you to outline possible limitations. It can be the age of the reference group, change of questionnaire in a survey, or specific use of data extraction equipment. Be transparent about what could affect your results. Example of Complications
Writing a dissertation discussion also makes a connection to possible future research. So, other scientists may complete that. While elaborating on possible implementations of your study, you may also estimate future approaches in topic research. Here are some points to consider while your discussion in thesis writing:
Example of Recommendations
You are almost done, the last step is to provide a brief summary of a section. It is not the same as a conclusion for whole research. However, you need to briefly outline key points from the dissertation discussion. To finalize writing the discussion section of a dissertation, go through the text and check if there is no unimportant information. Do not overload the text with relevant data you did not present in the result section. Be specific in your summary paragraphs. It is a holistic view of everything you pointed out. Provide a few sentences to systemize all you outlined in the text. Example of a Concluding Summary in a Dissertation Discussion Section
If we need to share one piece of practical advice, it would be to use thesis or dissertation discussion examples when writing your own copy. StudyCrumb provides the best samples from real students' work to help you understand the stylistic and possible structure of this part. It does not mean you need to copy and paste them into your work. However, you can use a dissertation discussion example for inspiration and brainstorming ideas for breaking writing blocks. Here’s a doctoral thesis discussion chapter example.
Before reading this blog, you should already know how to write a thesis discussion. However, we would share some essential tips you need to have in mind while working on the document.
At this stage, it should not be a question for you on how to write a discussion chapter in a PhD thesis or dissertation. Let’s make it clear. It is not a result section but still a place to elaborate on data and go deeper with explanations. Dissertation discussion section includes some intro, result interpretations, limitations, and recommendations for future research. Our team encourages you to use examples before starting your own piece of writing. It will help you to realize the purpose and structure of this chapter and inspire better texts! If you have other questions regarding the PhD writing process, check our blog for more insights. From detailed instruction on how to write a dissertation or guide on formatting a dissertation appendix , we’ve got you covered.
- clear structure
- practical implication
- elaboration on future work on this topic.
- Brief summary It does not mean copying an introduction section. However, the first few paragraphs will make an overview of your findings and topic.
- Interpretations This is a critical component of your work — elaborate on your results and explain possible ways of using them.
- Implication Research work is not just 100+ pages of text. Students should explain and illustrate how it could be used for solving practical problems.
- Constraints This is where you outline your limitations. For instance, your research was done only on students, and it may have different results with elderly people.
- Recommendations You can also define possible ways of future research on the exact topic when writing a discussion for your thesis or dissertation. Tell readers, for example, that it would be helpful to run similar research in other specific circumstances.
- Identify correlations or patterns in the data for dissertation discussion.
- Underline how results can answer research questions or prove your hypothesis.
- Emphasize how your findings are connected to the previous topic studies.
- Point out essential statements you can use in future research.
- Evaluate the significance of your results and any unexpected data you have.
- What others can learn from your research and how this work contributes to the field.
- Consider any possible additional or unique explanation of your findings.
- Go deeper with options of how results can be applied in practice.
- If results can change in case you change the reference group?
- What will happen with data if it changes circumstances?
- What could influence results?
- Outline questions related to your topic that you did not answer in defined study or did not outline as research questions. There are other possible gaps to research.
- Suggest future research based on limitations. For example, if you define surveyed people’s age as a limitation, recommend running another survey for older or younger recipients.
- Be consistent Your dissertation discussion chapter is a part of bigger research, and it should be in line with your whole work.
- Understand your reader You are writing an academic text that will be analyzed by professionals and experts in the same field. Be sure that you are not trying to simplify your discussion.
- Be logical Do not jump into a new line of discussion if you did not delineate it as a research question at the beginning.
- Be clear Do not include any data that was not presented in the result section.
- Consider word choice Use such terms as “our data indicate…” or “our data suggests…” instead of “the data proves.”
- Use proper format Follow the formatting rules specified by a specific paper style (e.g., APA style format , MLA format , or Chicago format ) or provided by your instructor.
What Is a Dissertation Discussion?
Purpose of a dissertation discussion chapter, structure of a dissertation discussion section, how to write a dissertation discussion chapter, 1. remind your research questions & objectives, 2. sum up key findings, 3. interpret the results, 4. discuss how your findings relate to the literature, 5. mention possible limitations, 6. provide recommendations for further research, 7. conclude your thesis/ dissertation discussion, dissertation discussion example, dissertation discussion writing tips, bottom line on writing a dissertation discussion chapter.
According to the data, implementing the co-orientation theory was successful and can be used for the same circumstances in the future. As we found, most participants agreed with the importance of those theses on the five fundamental reforms. It means that the results identified a successful government work in choosing the messages to communicate about examined reforms. At the same time, the situation is not so favorable with implementing the principles of two-way symmetrical communications. According to the results, people did not feel that the government had a mutual, open, and equal dialogue with the public about the reforms.
Our study underlines the importance of future research on using TikTok for political communication. As discussed above, TikTok is the most commonly used social media platform for many young voters. This means that political discussion will also move to this platform. Our research and typology of political communication content can be used in the future planning of effective political campaigns. For example, we can assume that “play videos” have enormous potential to facilitate complicated topics and provide specific agenda settings. We also identified additional affordances of TikTok used for political communication, such as built-in video editors, playlists for specific topics, a green screen for news explainers, and duets for reflection on news and discussion. It means that these features make TikTok suitable for efficient political communications.
As we pointed out in the literature review, there are few works on using TikTok affordances for political communications, and this topic can be expanded in the future. Government institutions have already understood the importance of this platform for efficient communication with younger audiences, and we will see more political projects on TikTok. That is why expanding research on using TikTok for political communication will be enormous in the following years. Our work is one of the first research on the role of emerging media in war communication and can be used as a practical guide for government's strategic planning in times of emergencies.
Although this study has provided critical first insights into the effects of multimodal disinformation and rebuttals, there are some limitations. First and most importantly, the effects of multimodal disinformation and rebuttals partially depend on the topic of the message. Although fact-checkers reduce credibility of disinformation in both settings, and attitudinal congruence plays a consistent role in conditioning responses to multimodal disinformation, visuals do not have the same impact on affecting the credibility of news on school shootings and refugees.
As we mentioned before, our study has some limitations, as the research was conducted based on data from United State citizens. However, for a better understanding of government communication practices, it would be productive to implement the same research in other countries. Some cultural differences can influence the communication strategies the government uses in times of emergency. Another possible way to examine this topic is to conduct research using a specific period of time. For future studies, it will be beneficial to expand the number of survey recipients.
To summarize, Airbnb has expertise in communicating CSR and CSA campaigns. We defined their communication strategy about the program for Ukrainian refugees as quite successful. They applied all the principles of CSR communication best practices, used dialogic theory to engage with the public on social media, and created clear messaging on applying for the program. Airbnb examples of CSR communication can be used by other businesses to create a communication strategy for unplanned CSR campaigns. Moreover, it can be further researched how Airbnb's CSR campaign influenced the organizational reputation in the future.
Writing the discussion section of a PhD dissertation
The discussion section of your PhD dissertation is one of the final sections in a long line of work representative of years of your life. While most students hasten through this part because it seems like regurgitation—boring, too—it is quite important. It is something you want to work on with care.
- Pull back after you finish your results section and give yourself some time to review the work from a fresh perspective. You want to step back from the finer details and concise points you have worked thus far to explain for your readers, and give them a chance to put your work into the bigger picture.
- Give your readers context. They need to know not just your key findings, but what your findings say. So go back over the literature and try to really dig deeply into what your findings represent, what role they play in the bigger picture, and how you can apply it elsewhere. If your work was clinical in nature, consider what political implications it might have in the future. These are things to address in the discussion section of your PhD dissertation. Without this, readers won’t know why they should care.
Far too often students become concerned with stating all of their flaws, potential issues, or future direction and let this part of the work slide. The result? Readers are left with more questions than answers.
- Mistakes to avoid:
- Starting with your limitations rather than the implications of your work
- Writing too much about the limitations of your work, causing your readers to question the entire legitimacy of your process
- Repeating your introduction
- Not acknowledging your limitations
- Not differentiating between your weak and strong results
- Using causal language when your data is correlational
- Restating your results without links to previous research or interpretations for future work
- Provide no concluding statements
- Presenting new results that belong earlier in your work
- Making strong claims about your weakest results
- While you need to note the limitations of your work, it is best to recommend follow up studies without drawing attention away from your work. You want to highlight where future work could lead, but you do not want your readers to finish the discussion section caring more about future studies than your study.
- Conclude with one of your main points or strongest point in a different fashion than before. Don’t simply copy and paste a previous paragraph or paraphrase it. Leave your mark in the minds of the readers, right here and now. Don’t just summarize, show how your work resolves existing controversies or connects to other literature Give your readers a clear and concise conclusion to read.

Tips for writing a PhD dissertation: FAQs answered
From how to choose a topic to writing the abstract and managing work-life balance through the years it takes to complete a doctorate, here we collect expert advice to get you through the PhD writing process
Campus team
Additional links.

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
A diy guide to starting your own journal, universities, ai and the common good, artificial intelligence and academic integrity: striking a balance, create an onboarding programme for neurodivergent students.
Embarking on a PhD is “probably the most challenging task that a young scholar attempts to do”, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith in their practical guide to dissertation and thesis writing. After years of reading and research to answer a specific question or proposition, the candidate will submit about 80,000 words that explain their methods and results and demonstrate their unique contribution to knowledge. Here are the answers to frequently asked questions about writing a doctoral thesis or dissertation.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
Whatever the genre of the doctorate, a PhD must offer an original contribution to knowledge. The terms “dissertation” and “thesis” both refer to the long-form piece of work produced at the end of a research project and are often used interchangeably. Which one is used might depend on the country, discipline or university. In the UK, “thesis” is generally used for the work done for a PhD, while a “dissertation” is written for a master’s degree. The US did the same until the 1960s, says Oxbridge Essays, when the convention switched, and references appeared to a “master’s thesis” and “doctoral dissertation”. To complicate matters further, undergraduate long essays are also sometimes referred to as a thesis or dissertation.
The Oxford English Dictionary defines “thesis” as “a dissertation, especially by a candidate for a degree” and “dissertation” as “a detailed discourse on a subject, especially one submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of a degree or diploma”.
- Ten platinum rules for PhD supervisors
- Fostering freedom in PhD students: how supervisors can shape accessible paths for doctoral research
- Lessons from students on effective research supervision
The title “doctor of philosophy”, incidentally, comes from the degree’s origins, write Dr Felix, an associate professor at Mahidol University in Thailand, and Dr Smith, retired associate professor of education at the University of Sydney , whose co-authored guide focuses on the social sciences. The PhD was first awarded in the 19th century by the philosophy departments of German universities, which at that time taught science, social science and liberal arts.
How long should a PhD thesis be?
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length ) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) – from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion.
The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social sciences and STEM all have their own conventions), location and institution. Examples and guides to structure proliferate online. The University of Salford , for example, lists: title page, declaration, acknowledgements, abstract, table of contents, lists of figures, tables and abbreviations (where needed), chapters, appendices and references.
A scientific-style thesis will likely need: introduction, literature review, materials and methods, results, discussion, bibliography and references.
As well as checking the overall criteria and expectations of your institution for your research, consult your school handbook for the required length and format (font, layout conventions and so on) for your dissertation.
A PhD takes three to four years to complete; this might extend to six to eight years for a part-time doctorate.
What are the steps for completing a PhD?
Before you get started in earnest , you’ll likely have found a potential supervisor, who will guide your PhD journey, and done a research proposal (which outlines what you plan to research and how) as part of your application, as well as a literature review of existing scholarship in the field, which may form part of your final submission.
In the UK, PhD candidates undertake original research and write the results in a thesis or dissertation, says author and vlogger Simon Clark , who posted videos to YouTube throughout his own PhD journey . Then they submit the thesis in hard copy and attend the viva voce (which is Latin for “living voice” and is also called an oral defence or doctoral defence) to convince the examiners that their work is original, understood and all their own. Afterwards, if necessary, they make changes and resubmit. If the changes are approved, the degree is awarded.
The steps are similar in Australia , although candidates are mostly assessed on their thesis only; some universities may include taught courses, and some use a viva voce. A PhD in Australia usually takes three years full time.
In the US, the PhD process begins with taught classes (similar to a taught master’s) and a comprehensive exam (called a “field exam” or “dissertation qualifying exam”) before the candidate embarks on their original research. The whole journey takes four to six years.
A PhD candidate will need three skills and attitudes to get through their doctoral studies, says Tara Brabazon , professor of cultural studies at Flinders University in Australia who has written extensively about the PhD journey :
- master the academic foundational skills (research, writing, ability to navigate different modalities)
- time-management skills and the ability to focus on reading and writing
- determined motivation to do a PhD.

How do I choose the topic for my PhD dissertation or thesis?
It’s important to find a topic that will sustain your interest for the years it will take to complete a PhD. “Finding a sustainable topic is the most important thing you [as a PhD student] would do,” says Dr Brabazon in a video for Times Higher Education . “Write down on a big piece of paper all the topics, all the ideas, all the questions that really interest you, and start to cross out all the ones that might just be a passing interest.” Also, she says, impose the “Who cares? Who gives a damn?” question to decide if the topic will be useful in a future academic career.
The availability of funding and scholarships is also often an important factor in this decision, says veteran PhD supervisor Richard Godwin, from Harper Adams University .
Define a gap in knowledge – and one that can be questioned, explored, researched and written about in the time available to you, says Gina Wisker, head of the Centre for Learning and Teaching at the University of Brighton. “Set some boundaries,” she advises. “Don’t try to ask everything related to your topic in every way.”
James Hartley, research professor in psychology at Keele University, says it can also be useful to think about topics that spark general interest. If you do pick something that taps into the zeitgeist, your findings are more likely to be noticed.
You also need to find someone else who is interested in it, too. For STEM candidates , this will probably be a case of joining a team of people working in a similar area where, ideally, scholarship funding is available. A centre for doctoral training (CDT) or doctoral training partnership (DTP) will advertise research projects. For those in the liberal arts and social sciences, it will be a matter of identifying a suitable supervisor .
Avoid topics that are too broad (hunger across a whole country, for example) or too narrow (hunger in a single street) to yield useful solutions of academic significance, write Mark Stephan Felix and Ian Smith. And ensure that you’re not repeating previous research or trying to solve a problem that has already been answered. A PhD thesis must be original.
What is a thesis proposal?
After you have read widely to refine your topic and ensure that it and your research methods are original, and discussed your project with a (potential) supervisor, you’re ready to write a thesis proposal , a document of 1,500 to 3,000 words that sets out the proposed direction of your research. In the UK, a research proposal is usually part of the application process for admission to a research degree. As with the final dissertation itself, format varies among disciplines, institutions and countries but will usually contain title page, aims, literature review, methodology, timetable and bibliography. Examples of research proposals are available online.
How to write an abstract for a dissertation or thesis
The abstract presents your thesis to the wider world – and as such may be its most important element , says the NUI Galway writing guide. It outlines the why, how, what and so what of the thesis . Unlike the introduction, which provides background but not research findings, the abstract summarises all sections of the dissertation in a concise, thorough, focused way and demonstrates how well the writer understands their material. Check word-length limits with your university – and stick to them. About 300 to 500 words is a rough guide – but it can be up to 1,000 words.
The abstract is also important for selection and indexing of your thesis, according to the University of Melbourne guide , so be sure to include searchable keywords.
It is the first thing to be read but the last element you should write. However, Pat Thomson , professor of education at the University of Nottingham , advises that it is not something to be tackled at the last minute.
How to write a stellar conclusion
As well as chapter conclusions, a thesis often has an overall conclusion to draw together the key points covered and to reflect on the unique contribution to knowledge. It can comment on future implications of the research and open up new ideas emanating from the work. It is shorter and more general than the discussion chapter , says online editing site Scribbr, and reiterates how the work answers the main question posed at the beginning of the thesis. The conclusion chapter also often discusses the limitations of the research (time, scope, word limit, access) in a constructive manner.
It can be useful to keep a collection of ideas as you go – in the online forum DoctoralWriting SIG , academic developer Claire Aitchison, of the University of South Australia , suggests using a “conclusions bank” for themes and inspirations, and using free-writing to keep this final section fresh. (Just when you feel you’ve run out of steam.) Avoid aggrandising or exaggerating the impact of your work. It should remind the reader what has been done, and why it matters.
How to format a bibliography (or where to find a reliable model)
Most universities use a preferred style of references , writes THE associate editor Ingrid Curl. Make sure you know what this is and follow it. “One of the most common errors in academic writing is to cite papers in the text that do not then appear in the bibliography. All references in your thesis need to be cross-checked with the bibliography before submission. Using a database during your research can save a great deal of time in the writing-up process.”
A bibliography contains not only works cited explicitly but also those that have informed or contributed to the research – and as such illustrates its scope; works are not limited to written publications but include sources such as film or visual art.
Examiners can start marking from the back of the script, writes Dr Brabazon. “Just as cooks are judged by their ingredients and implements, we judge doctoral students by the calibre of their sources,” she advises. She also says that candidates should be prepared to speak in an oral examination of the PhD about any texts included in their bibliography, especially if there is a disconnect between the thesis and the texts listed.
Can I use informal language in my PhD?
Don’t write like a stereotypical academic , say Kevin Haggerty, professor of sociology at the University of Alberta , and Aaron Doyle, associate professor in sociology at Carleton University , in their tongue-in-cheek guide to the PhD journey. “If you cannot write clearly and persuasively, everything about PhD study becomes harder.” Avoid jargon, exotic words, passive voice and long, convoluted sentences – and work on it consistently. “Writing is like playing guitar; it can improve only through consistent, concerted effort.”
Be deliberate and take care with your writing . “Write your first draft, leave it and then come back to it with a critical eye. Look objectively at the writing and read it closely for style and sense,” advises THE ’s Ms Curl. “Look out for common errors such as dangling modifiers, subject-verb disagreement and inconsistency. If you are too involved with the text to be able to take a step back and do this, then ask a friend or colleague to read it with a critical eye. Remember Hemingway’s advice: ‘Prose is architecture, not interior decoration.’ Clarity is key.”
How often should a PhD candidate meet with their supervisor?
Since the PhD supervisor provides a range of support and advice – including on research techniques, planning and submission – regular formal supervisions are essential, as is establishing a line of contact such as email if the candidate needs help or advice outside arranged times. The frequency varies according to university, discipline and individual scholars.
Once a week is ideal, says Dr Brabazon. She also advocates a two-hour initial meeting to establish the foundations of the candidate-supervisor relationship .
The University of Edinburgh guide to writing a thesis suggests that creating a timetable of supervisor meetings right at the beginning of the research process will allow candidates to ensure that their work stays on track throughout. The meetings are also the place to get regular feedback on draft chapters.
“A clear structure and a solid framework are vital for research,” writes Dr Godwin on THE Campus . Use your supervisor to establish this and provide a realistic view of what can be achieved. “It is vital to help students identify the true scientific merit, the practical significance of their work and its value to society.”
How to proofread your dissertation (what to look for)
Proofreading is the final step before printing and submission. Give yourself time to ensure that your work is the best it can be . Don’t leave proofreading to the last minute; ideally, break it up into a few close-reading sessions. Find a quiet place without distractions. A checklist can help ensure that all aspects are covered.
Proofing is often helped by a change of format – so it can be easier to read a printout rather than working off the screen – or by reading sections out of order. Fresh eyes are better at spotting typographical errors and inconsistencies, so leave time between writing and proofreading. Check with your university’s policies before asking another person to proofread your thesis for you.
As well as close details such as spelling and grammar, check that all sections are complete, all required elements are included , and nothing is repeated or redundant. Don’t forget to check headings and subheadings. Does the text flow from one section to another? Is the structure clear? Is the work a coherent whole with a clear line throughout?
Ensure consistency in, for example, UK v US spellings, capitalisation, format, numbers (digits or words, commas, units of measurement), contractions, italics and hyphenation. Spellchecks and online plagiarism checkers are also your friend.

How do you manage your time to complete a PhD dissertation?
Treat your PhD like a full-time job, that is, with an eight-hour working day. Within that, you’ll need to plan your time in a way that gives a sense of progress . Setbacks and periods where it feels as if you are treading water are all but inevitable, so keeping track of small wins is important, writes A Happy PhD blogger Luis P. Prieto.
Be specific with your goals – use the SMART acronym (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and timely).
And it’s never too soon to start writing – even if early drafts are overwritten and discarded.
“ Write little and write often . Many of us make the mistake of taking to writing as one would take to a sprint, in other words, with relatively short bursts of intense activity. Whilst this can prove productive, generally speaking it is not sustainable…In addition to sustaining your activity, writing little bits on a frequent basis ensures that you progress with your thinking. The comfort of remaining in abstract thought is common; writing forces us to concretise our thinking,” says Christian Gilliam, AHSS researcher developer at the University of Cambridge ’s Centre for Teaching and Learning.
Make time to write. “If you are more alert early in the day, find times that suit you in the morning; if you are a ‘night person’, block out some writing sessions in the evenings,” advises NUI Galway’s Dermot Burns, a lecturer in English and creative arts. Set targets, keep daily notes of experiment details that you will need in your thesis, don’t confuse writing with editing or revising – and always back up your work.
What work-life balance tips should I follow to complete my dissertation?
During your PhD programme, you may have opportunities to take part in professional development activities, such as teaching, attending academic conferences and publishing your work. Your research may include residencies, field trips or archive visits. This will require time-management skills as well as prioritising where you devote your energy and factoring in rest and relaxation. Organise your routine to suit your needs , and plan for steady and regular progress.
How to deal with setbacks while writing a thesis or dissertation
Have a contingency plan for delays or roadblocks such as unexpected results.
Accept that writing is messy, first drafts are imperfect, and writer’s block is inevitable, says Dr Burns. His tips for breaking it include relaxation to free your mind from clutter, writing a plan and drawing a mind map of key points for clarity. He also advises feedback, reflection and revision: “Progressing from a rough version of your thoughts to a superior and workable text takes time, effort, different perspectives and some expertise.”
“Academia can be a relentlessly brutal merry-go-round of rejection, rebuttal and failure,” writes Lorraine Hope , professor of applied cognitive psychology at the University of Portsmouth, on THE Campus. Resilience is important. Ensure that you and your supervisor have a relationship that supports open, frank, judgement-free communication.
If you found this interesting and want advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the THE Campus newsletter .
Authoring a PhD Thesis: How to Plan, Draft, Write and Finish a Doctoral Dissertation (2003), by Patrick Dunleavy
Writing Your Dissertation in Fifteen Minutes a Day: A Guide to Starting, Revising, and Finishing Your Doctoral Thesis (1998), by Joan Balker
Challenges in Writing Your Dissertation: Coping with the Emotional, Interpersonal, and Spiritual Struggles (2015), by Noelle Sterne
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn?
Global perspectives: navigating challenges in higher education across borders, how to help young women see themselves as coders, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, authentic assessment in higher education and the role of digital creative technologies, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site
How to write a PhD in a hundred steps (or more)
A workingmumscholar's journey through her phd and beyond, concluding the thesis.
I am co-supervising a PhD student who is handing in her thesis for examination in November. She is currently revising her whole thesis, working towards the conclusion (and finally, the introduction). Conclusions can be tricky things to write – pulling something as big as a PhD dissertation together into a final, clear chapter is not easy. It is both an intellectual and an emotional challenge, as conclusion-writing comes towards the very end of the process, and you are so tired, and probably feeling like there are no more coherent words or sentences in your brain. This post reflects a little on what a thesis conclusion is for, with some thoughts on how to construct one that does justice to your meisterwerk .

To begin with, let’s think a bit about what conclusions are for in a piece of written work. In undergraduate studies, students are typically taught that conclusions are summaries . You restate the thesis, or main claim, of your paper, reiterate what each paragraph has said that contributes to that argument, and then bring it all together with a firm final sentence or two that says something about the relevance of the paper, or argument. There should be no new information, just a summing up of what has already been said. Sometimes you are allowed recommendations, depending on the discipline. It makes sense, then, that we progress into postgraduate studies believing that we are writing summaries whenever we conclude (a paper, or a journal article, or a thesis). I have seen many conclusions like this in postgraduate, postdoctoral and early career writing. But, unfortunately, at these levels conclusions that merely summarise a paper the reader has just read are not adequate, or suitable . A shift is needed.
As Pat Thomson usefully argues in this post about writing a thesis conclusion, the conclusion to a thesis (or journal article) is not a summary of the whole . The summary part of a thesis conclusion should ideally be quite brief, and used rather as a springboard to the real work of the conclusion: using the preceding writing and research to show how the study has addressed the research questions, and in so doing, how it has made a valid, and useful, contribution to knowledge .
A strong conclusion shows your readers what your research means within the context of the field you have referenced in your ‘literature review’, and how in answering your research questions you have been able to speak back to this body of research in which you have located your own study. It answers your research questions, succinctly and clearly, so that your readers understand the overall claims of your study, the focus of your argument, the basis upon which you have advanced your argument, and the significance, meaning or value of that argument to your (their) field. It discusses – argues – for the place of your research within your field, and the contribution it is making.

There are a few ways in which you can approach writing such a conclusion (and Pat’s post above is very helpful here). There are also a few guidelines to consider in writing this vital part of your thesis.
To begin with, you do need to bring your reader up to speed with the thesis thus far . Examiners and other readers are unlikely to read your whole PhD in one go, so ending each chapter with a brief summary, and starting the next one with a short section that connects the present chapter to the previous one is a good idea for creating coherent connections between chapters, and is helpful for your readers. Thus, you should begin your conclusion with an overview, or brief summary, of the argument thus far.
Then, consider your research questions : what did you set out to do in this project or study? Your research questions could make useful sub-headings here, at least in a first draft, to help you organise your thoughts. Starting here, you can begin to pull out the answers you have found (in the ‘analysis chapter/s’) so that you can discuss the implications of your findings, their relevance in relation to your overall argument, and the way in which what you have found relates to the body of research to which you have connected your study. No new information : just an analytical discussion of selected aspects of your findings that are useful for answering your research questions, and further consolidating your argument.
Perhaps you have recommendations , on the basis of your findings and their implications for practice, and/or further research. You could include a section on these, discussing a step further the possible implications of your research in relation to your field. Something else that may be relevant to include here could be limitations to the size or scope of your findings: are there any that your readers need to know about, so that they don’t expect your study to have done something other than what it has done? Don’t just list all the things you could have done but didn’t do: think carefully about pertinent limitations that may represent counter-arguments you could defend or mitigate against.
At the end of the end, consider your argument again : what has your thesis claimed and to what end? Try to end your thesis with a paragraph that reiterates not just what your thesis has argued, but WHY this argument has relevance, or import, for your readers. What do you hope the outcome of your research will be? Why are you so passionate about it, and why do you think others should care too? Read a few thesis conclusions to get a sense of different ways of doing this, and check out Pat Thomson’s posts on conclusion writing , too. Then write a draft and share it with your supervisor for feedback.
It’s worth really taking your time and not rushing this chapter, even as it comes at the end when you are tired, and really just want to be done. End on the highest note you can: you owe yourself that much after all your hard work getting there.
Share this:
I am at exactly this point with my thesis so your very helpful suggestions couldn’t have been better timed. Pretty sure I would have most of the mistakes mentioned otherwise, so many thanks!
I’m so pleased that this is helpful – good luck with the conclusion and submission 🙂
You have a great blog! I didn’t reall of the posts, but all the titles of the posts seem to apply to me right now! I’m trying to finish up my PhD, which means, a lot of writing. This is very helpful!
Thanks for the comment, and all the best with the final push!
Timely. Half way through writing mine!
Swapped university with a few years to run on my candidature, got really sick and was struggling. Employed in aviation so COVID-19 has been great fun!
This summary is very timely!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

UCL Centre for Languages & International Education (CLIE)
Writing your PhD Thesis Results and Discussion

Writing your PhD Thesis Workshops
Information on workshops for UCL PhD students and researchers who are writing up their thesis methods section.
We offer two 'Writing your PhD workshops':
Writing your PhD Thesis Methods / Methodology
Workshop overview.
This workshop is for PhD students and researchers who are writing up their thesis methods section. This workshop is particularly suitable for those PhD students with little experience of writing research in English.
* This workshop is not suitable for students embarking on the first stages of their PhD.
Workshop aims
The workshop will review essential elements of the methodology chapter and is delivered by UCL lecturers who specialise in teaching academic literacies. Participants will work with the lecturer and peers, using authentic examples and their own work to identify how to structure this chapter, how to describe the research method effectively and understand the language and style used in writing up this section.
Workshop content
During the workshop, areas to be covered may include:
- Research method
- Participants/Materials
- Data analysis
- Reflexivity
By the end of this workshop you will be able to:
- understand how to plan this section of your PhD
- analyse the structure of information in methodology chapters of a PhD thesis
- develop your writing skills through peer review and free writing
Workshop dates and times
How to register.
Registration for this course is managed by UCL Doctoral Skills using inkpath. If you have not previously registered with inkpath, you will need to follow the ‘Use Single Sign-On’ button.
Register now for Writing your PhD Thesis Methods / Methodology
The workshop will review essential elements of the results and discussion chapter(s) and is delivered by UCL lecturers who specialise in teaching academic literacies. Participants will work with the lecturer and peers, using authentic examples and their own work to identify how to structure these chapters, how to describe results effectively and understand the language and style used in writing up these sections.
- Degree of commentary or analysis
- Organisation and content of commentary/analysis
- Caution/Hedging
- Dealing with unexpected outcomes
- Discussion strategies
- Argument across disciplines
By the end of the workshop you will be able to:
- understand how to plan this (these) section(s) of your PhD
- understand how to explain your findings clearly and effectively in writing
- to develop your writing skills through peer review and free writing
Register now for Writing your PhD Thesis Results and Discussion
Information for both workshops
Course feedback / staff-student consultative exercise.
All students on Part-time English courses have the opportunity to give general feedback on their course to senior representatives of CLIE.
Academic support
If you have any questions about your course, please feel free to ask your tutor. Alternatively, contact the Course Coordinator, Mrs Daphne Thomas: [email protected] .
Rights and responsibilities
CLIE seeks to ensure that all students have a positive experience in respect of courses taken here, and fully adheres to the broader rights and responsibilities policies of UCL .
As part of our responsibility, our courses will follow a logical structure consistent with delivering the content and skills practise that we advertise, but with the freedom for teachers to respond (e.g. via needs analysis at the beginning of the course) to further relevant areas of particular interest to each student group.
Problems and complaints
If you are unhappy about any aspect of your course we would advise you in the first instance to speak to a member of staff at CLIE to see if the problem can be easily resolved within the department. For further details of our formal complaints procedure, please email the Part-time Course Coordinator or administration team at [email protected] .
UCL Academic Communication Centre
Academic Communication support is available for Master's and undergraduate students through the UCL Academic Communication Centre .
Useful links
The Self-Access Centre : online academic English resources, including videos, books, lectures and a language laboratory.
International Student Support : key information and advice on how best to prepare, settle in and enjoy life in the UK.
+44 (0)20 8138 7872
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 21 August 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 25 October 2022.

The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results .
It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review , and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion . It should not be a second results section .
There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your writing around these key elements:
- Summary: A brief recap of your key results
- Interpretations: What do your results mean?
- Implications: Why do your results matter?
- Limitations: What can’t your results tell us?
- Recommendations: Avenues for further studies or analyses
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What not to include in your discussion section, step 1: summarise your key findings, step 2: give your interpretations, step 3: discuss the implications, step 4: acknowledge the limitations, step 5: share your recommendations, discussion section example.
There are a few common mistakes to avoid when writing the discussion section of your paper.
- Don’t introduce new results: You should only discuss the data that you have already reported in your results section .
- Don’t make inflated claims: Avoid overinterpretation and speculation that isn’t directly supported by your data.
- Don’t undermine your research: The discussion of limitations should aim to strengthen your credibility, not emphasise weaknesses or failures.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarising your major findings. Don’t just repeat all the data you have already reported – aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research question . This should be no more than one paragraph.
Many students struggle with the differences between a discussion section and a results section . The crux of the matter is that your results sections should present your results, and your discussion section should subjectively evaluate them. Try not to blend elements of these two sections, in order to keep your paper sharp.
- The results indicate that …
- The study demonstrates a correlation between …
- This analysis supports the theory that …
- The data suggest that …
The meaning of your results may seem obvious to you, but it’s important to spell out their significance for your reader, showing exactly how they answer your research question.
The form of your interpretations will depend on the type of research, but some typical approaches to interpreting the data include:
- Identifying correlations , patterns, and relationships among the data
- Discussing whether the results met your expectations or supported your hypotheses
- Contextualising your findings within previous research and theory
- Explaining unexpected results and evaluating their significance
- Considering possible alternative explanations and making an argument for your position
You can organise your discussion around key themes, hypotheses, or research questions, following the same structure as your results section. Alternatively, you can also begin by highlighting the most significant or unexpected results.
- In line with the hypothesis …
- Contrary to the hypothesised association …
- The results contradict the claims of Smith (2007) that …
- The results might suggest that x . However, based on the findings of similar studies, a more plausible explanation is x .
As well as giving your own interpretations, make sure to relate your results back to the scholarly work that you surveyed in the literature review . The discussion should show how your findings fit with existing knowledge, what new insights they contribute, and what consequences they have for theory or practice.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support existing theories, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge existing theories, why do you think that is?
- Are there any practical implications?
Your overall aim is to show the reader exactly what your research has contributed, and why they should care.
- These results build on existing evidence of …
- The results do not fit with the theory that …
- The experiment provides a new insight into the relationship between …
- These results should be taken into account when considering how to …
- The data contribute a clearer understanding of …
- While previous research has focused on x , these results demonstrate that y .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Even the best research has its limitations. Acknowledging these is important to demonstrate your credibility. Limitations aren’t about listing your errors, but about providing an accurate picture of what can and cannot be concluded from your study.
Limitations might be due to your overall research design, specific methodological choices , or unanticipated obstacles that emerged during your research process.
Here are a few common possibilities:
- If your sample size was small or limited to a specific group of people, explain how generalisability is limited.
- If you encountered problems when gathering or analysing data, explain how these influenced the results.
- If there are potential confounding variables that you were unable to control, acknowledge the effect these may have had.
After noting the limitations, you can reiterate why the results are nonetheless valid for the purpose of answering your research question.
- The generalisability of the results is limited by …
- The reliability of these data is impacted by …
- Due to the lack of data on x , the results cannot confirm …
- The methodological choices were constrained by …
- It is beyond the scope of this study to …
Based on the discussion of your results, you can make recommendations for practical implementation or further research. Sometimes, the recommendations are saved for the conclusion .
Suggestions for further research can lead directly from the limitations. Don’t just state that more studies should be done – give concrete ideas for how future work can build on areas that your own research was unable to address.
- Further research is needed to establish …
- Future studies should take into account …
- Avenues for future research include …

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 8 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/discussion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a results section | tips & examples, research paper appendix | example & templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
Non-Credit Certificate Program in Medical Writing and Editing
Master the fundamentals and best practices of medical writing, editing, and communication.

Upcoming Events

Freelancing in Medical Writing and Editing
Apr 9, 2024 • Online

How to Land Your First Job in Editing
Apr 29, 2024 • Online
At a Glance
The University of Chicago’s non-credit certificate in Medical Writing and Editing uses the AMA Manual of Style as the foundation for mastering the fundamentals and best practices of medical writing, editing, and communication.
Developed for professionals with backgrounds in science or writing, the online medical writing certificate program with synchronous course sessions has a comprehensive curriculum focused on creating medical communicators with strong writing, editing, data reporting, and analytic skills. Student have the opportunity to boost their skills quickly in nine months to one year, part-time.
Designed For
Designed for both professionals with a background in science who want to acquire writing skills, and those with a background in writing or an English degree who want to understand medical terminology.
Learn from Industry Experts
Our program instructors have worked with and for a wide range of leading organizations, including the American Medical Association, WebMD, the Mayo Clinic, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, and the Journal of Graduate Medical Education.

Want to Learn More?
View our comprehensive curriculum, taught by seasoned medical writers and editors.
Grow Your Network
Current students and alumni have access to networking events and webinars hosted by our Student Advisory Board and our Professional Development team, who also fund an alumni scholarship program.
Join a Thriving Field in Medical Writing
Driven by the expansion of scientific and technical products, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a faster growth rate in the employment of technical writers than that in other fields.
Potential Job Titles for Medical Writers and Editors
- Content Specialist
- Medical Writer/Editor
- Regulatory Writer/Editor
- Technical Editor
Average salaries for Medical Writers and Editors
According to Glassdoor, the salaries of both medical writers and editors average around $97,000.
Focus Areas
- Specialization Track in Freelancing
Offered by The University of Chicago's Professional Education
Ready to Take Your Next Step?
Of interest.
- Non-Credit Certificate Program in Regulatory Writing
Gain in-demand medical writing skills that will help elevate your career in healthcare or medical...
Inescapable Ethics

Essential Courses on Medical Copyediting

From Freelancer to Founder
- Non-Credit Certificate Program in Editing
- Learning the Business of Freelance Medical Writing and Editing
- Request info
- Majors & Degrees
- Prospective Students
- Current Undergraduate Students
- Current Graduate Students
- Online Students
- Alumni and Friends
- Faculty and Staff
USM Center for Writers Hosting Writing Camp: Young Authors Academy in July
Mon, 04/08/2024 - 11:55am | By: Ivonne Kawas
The Center for Writers at The University of Southern Mississippi (USM), housed in the School of Humanities, will host the Young Authors Academy (YAA) — a creative writing summer camp —July 8-12 for young teens ages 9-13. The camp will be held from 1 p.m.- 5 p.m. on the Hattiesburg Campus.
YAA provides a space for campers who want to practice creative writing in a nurturing and collaborative environment. Participants gain confidence in their own writing, as they are introduced to fiction, poetry, and a process designed to diversify writing skills.
“Our goal is to offer young writers the opportunity to create many poems and stories, as well as a productive writing process that they can continue when camp is over,” said Dr. Rachael Fowler, assistant teaching professor of English. “At the YAA, they’ll find an outlet to experiment with creativity, express themselves in new ways, and support each other as they share their voices and words. We look forward to providing new writing experiences to our many returning campers and all newcomers.”
Experienced camp counselors, who are published writers in USM’s Creative Writing program, will lead participants through many activities: writing prompts, walking field trips on campus, practice reading their own work to others, and guidance for providing supportive feedback to fellow writers. This year’s interactive field trips include sites such as the Archaeology Lab, the Theatre and Dance Building, and the Gallery of Art and Design
Camp participants get to showcase the work they produce at a reception and public reading—open to family and friends—and get a printed anthology of their writing to take home.
The summer camp costs $200. Register or contact Dr. Rachael Fowler, the camp coordinator, via email.
Categories: Arts and Sciences
Recent News Articles
Usm statement regarding incident on hattiesburg campus, usm celebrates its graduate students with week of activities.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The PhD Discussion Chapter: What It Is & How To Write It. Sep 11, 2023. Your PhD discussion chapter is your thesis's intellectual epicenter. Think of it as the scholarly equivalent of a courtroom closing argument, where you summarise the evidence and make your case. Perhaps that's why it's so tricky - the skills you need in your ...
Step 1: Restate your research problem and research questions. The first step in writing up your discussion chapter is to remind your reader of your research problem, as well as your research aim (s) and research questions. If you have hypotheses, you can also briefly mention these.
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example. Other interesting articles.
2. Determine a clear structure. The first step in organizing a perfect discussion chapter for a PhD thesis is to divide them into separate sections that move from a particular result to implications. However, depending on your PhD thesis topics, you may utilize the followings: Analyze and summarize your main findings.
If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you're writing to meet their expectations. Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader.
Here are some examples of how to present the summary of your findings; "The data suggests that", "The results confirm that", "The analysis indicates that", "The research shows a relationship between", etc. 2. Interpretations of Results. Your audience will expect you to provide meanings of the results, although they might seem ...
So, in a nutshell, the discussion and conclusion chapters of your PhD dissertation are all about making sense of your research and thinking about what it means for the big picture. The discussion chapter digs into the details of your findings and how you got them. The conclusion chapter zooms out to look at the broader implications and what ...
The Discussion chapter brings an opportunity to write an academic argument that contains a detailed critical evaluation and analysis of your research findings. This chapter addresses the purpose and critical nature of the discussion, contains a guide to selecting key results to discuss, and details how best to structure the discussion with ...
Crafting the Discussion Chapter: A Step-by-Step Guide. Now that you've grasped the essence of the discussion chapter and its essential elements let's delve into structuring this pivotal chapter. In a broad sense, you can break down this chapter into six key components, which serve as sequential steps in the chapter-writing journey.
Learn exactly how to write a clear and compelling discussion chapter or section for your dissertation, thesis or research project. We explain how to craft th...
What's Included: Discussion Template. This template covers all the core components required in the discussion/analysis chapter of a typical dissertation or thesis, including: The purpose of each section is explained in plain language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. The template also includes practical ...
Andrea Bingham. One of the most difficult parts of writing an article based on your research is the discussion section. My PhD students struggle with it, but established researchers have difficulty with it as well because the discussion section is where you have to put your money where your mouth is, so to speak.
Planning, structuring and writing your dissertation discussion chapter is relatively straightforward and simple. That does not mean it's EASY, but when you h...
Yet, with little guidance available on how to think about and write an integrated discussion, graduate students may miss the opportunity to engage in this higher-order thinking and critical reflections. In this paper, we offer a practical four-step approach with templates for writing an integrated discussion for article-based theses.
The reporting and discussion thesis chapters deal with the central part of the thesis. This is where you present the data that forms the basis of your investigation, shaped by the way you have interpreted it and developed your argument or theories about it. In other words, you tell your readers the research story that has emerged from your ...
The helpful Manchester Academic Phrase Bank 'discussing the findings' section, gives you some sentences that you can use as the 'steps' for each move. Try some of these sentence starters to get you going: Restate Results: "The current study found that …". "The results of this study show/indicate that …".
Here are some points to consider while your discussion in thesis writing: Example of Recommendations. You are almost done, the last step is to provide a brief summary of a section. It is not the same as a conclusion for whole research. However, you need to briefly outline key points from the dissertation discussion.
Writing the discussion section of a PhD dissertation. The discussion section of your PhD dissertation is one of the final sections in a long line of work representative of years of your life. While most students hasten through this part because it seems like regurgitation—boring, too—it is quite important. ...
A PhD thesis (or dissertation) is typically 60,000 to 120,000 words ( 100 to 300 pages in length) organised into chapters, divisions and subdivisions (with roughly 10,000 words per chapter) - from introduction (with clear aims and objectives) to conclusion. The structure of a dissertation will vary depending on discipline (humanities, social ...
To begin with, you do need to bring your reader up to speed with the thesis thus far. Examiners and other readers are unlikely to read your whole PhD in one go, so ending each chapter with a brief summary, and starting the next one with a short section that connects the present chapter to the previous one is a good idea for creating coherent ...
Writing your PhD Thesis Results and Discussion; Writing your PhD Thesis Methods / Methodology. Workshop overview. This workshop is for PhD students and researchers who are writing up their thesis methods section. This workshop is particularly suitable for those PhD students with little experience of writing research in English.
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarise your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example.
The University of Chicago's non-credit certificate in Medical Writing and Editing uses the. AMA Manual of Style. as the foundation for mastering the fundamentals and best practices of medical writing, editing, and communication. Developed for professionals with backgrounds in science or writing, the online medical writing certificate program ...
The Center for Writers at The University of Southern Mississippi (USM), housed in the School of Humanities, will host the Young Authors Academy (YAA) — a creative writing summer camp —July 8-12 for young teens ages 9-13. The camp will be held from 1 p.m.- 5 p.m. on the Hattiesburg Campus.