Making educational experiences better for everyone.
Immersive learning for 25 languages
Marketplace for millions of educator-created resources
Fast, easy, reliable language certification
Fun educational games for kids
Comprehensive K-12 personalized learning
Trusted tutors for 300+ subjects
35,000+ worksheets, games, and lesson plans
Adaptive learning for English vocabulary

Daily Routines – Past Tense
List of Daily Routines in the Past Simple Tense in English
(You can hear the pronunciation of each daily routine in the video)
- I turned off my alarm
- I took a shower / I had a shower
- I got dressed
- I combed my hair
- I made breakfast
- I ate breakfast / I had breakfast
- I brushed my teeth
- I went to work
- I started work at 9
- I answered emails
- I ate lunch / I had lunch
- I worked on my computer
- I finished work at 5
- I went home
- I arrived home
- I fed the dog
- I cooked dinner
- I ate dinner / I had dinner
- I watched TV
- I read a book
- I went to bed
- I fell asleep
Daily routines for School
- I went to school
- I had classes
- I finished school at 3
- I did my homework
Notice how in this lesson all of these phrases are in the past simple tense and have I (first person singular) as the subject.
Practice Exercises
Video practice: At the end of the video there is a practice exercise where a cartoon of a daily routine appears on the screen. There are also three phrases in the past tense next to the cartoon and you must choose which phrase best describes that activity. The answer will appear after 5 seconds (approximately).
Summary Chart

- 980k Followers
- 217k Followers
- 126k Followers
English Course
Past tense in english.
- Past Simple Tense in English
- ED Spelling Rules
- Daily Routines - Past Tense
- Object Pronouns in English
- Say vs. Tell - Said vs. Told
- 101 Irregular Verbs - Past Tense in English
Pin It on Pinterest
- Anatomy & Physiology
- Astrophysics
- Earth Science
- Environmental Science
- Organic Chemistry
- Precalculus
- Trigonometry
- English Grammar
- U.S. History
- World History
... and beyond
- Socratic Meta
- Featured Answers

Is, "I did do my homework" correct?
http://www.ToLearnEnglish.com - Resources to learn/teach English (courses, games, grammar, daily page...) For ESL/EFL learners/teachers.
|
|
|
|

Mastering the Past Tense of Do: Your Ultimate Guide to Fluent English
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: September 14, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Learning English grammar can be a challenging task, especially when it comes to understanding the past tense of irregular verbs. One of the most commonly used verbs in English is “do”, and its past tense can be tricky for non-native speakers to grasp. In this article, we will explore the different forms of the past tense of do and provide examples to help you understand how to use them correctly.
Understanding the correct usage of these different forms of the past tense of “do” is essential for effective communication in English. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into each form and provide examples to help you master this important grammatical concept. So, let’s get started!
Past Tense of Do – Image

Understanding the Verb ‘Do’
In English grammar, the past tense refers to the form of a verb that indicates that an action took place in the past.
The verb ‘do’ is one of the most frequently used verbs in the English language. It is used to form questions, negatives, and to emphasize the main verb in a sentence. Understanding the correct usage of the past tense of ‘do’ is essential for effective communication in English.
Simple Past Tense of ‘Do’
The simple past tense of ‘do’ is ‘did’. It is used to talk about completed actions in the past. For example:
- I did my homework yesterday.
- She did not come to the party last night.
- Did you watch the movie last weekend?
Past Continuous Tense of ‘Do’
The past continuous tense of ‘do’ is ‘was/were doing’. It is used to talk about actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past. For example:
- I was doing my homework when my friend called me.
- They were not doing anything when I arrived.
- What were you doing at 5 o’clock yesterday?
Past Perfect Tense of ‘Do’
The past perfect tense of ‘do’ is ‘had done’. It is used to talk about actions that were completed before another action in the past. For example:
- I had done my homework before I went to bed.
- She had not done her laundry when she ran out of clean clothes.
- Had you done your research before the presentation?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense of ‘Do’
The past perfect continuous tense of ‘do’ is ‘had been doing’. It is used to talk about actions that had been in progress for a period of time before another action in the past. For example:
- I had been doing my homework for two hours before I took a break.
- They had not been doing anything productive for weeks before the deadline.
- Had you been doing your exercises regularly before the injury?
In conclusion, understanding the past tense of ‘do’ is crucial for effective communication in English. Practice using the different tenses in various contexts to improve your fluency.
The Past Tense of Do
Form and Usage
In English grammar, the past tense of ‘do’ is ‘did’. ‘Did’ is used to express an action that occurred in the past. The verb ‘do’ is an irregular verb, which means that it does not follow the regular pattern of adding ‘-ed’ to the base form to form the past tense.
To form the past tense of ‘do’, we use ‘did’ as an auxiliary verb followed by the base form of the main verb. For example, “I did my homework” or “He did not eat breakfast this morning”.
Examples in Sentences
Here are some examples of ‘did’ in sentences:
- She did not like the movie.
- They did their best to finish the project on time.
- Did you finish your work before leaving the office?
- He did not want to go to the party.
It is important to note that ‘did’ is used in both affirmative and negative sentences, as well as questions. In questions, ‘did’ is placed at the beginning of the sentence followed by the subject and the base form of the main verb.
Knowing the past tense of ‘do’ is essential for anyone learning English grammar. By using ‘did’ correctly, you can accurately express actions that occurred in the past. Practice using ‘did’ in sentences and questions to improve your understanding of this important verb tense.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
When it comes to using the past tense of “do,” there are a few common mistakes and misconceptions that English learners often encounter. In this section, we’ll explore some of these common issues and provide tips on how to avoid them.
Using “did” Too Much
One common mistake that English learners make when using the past tense of “do” is using “did” too much. While “did” is the correct past tense form of “do,” it’s important to vary your language and use other forms of the past tense as well. For example, instead of always saying “did you do your homework?” try saying “have you finished your homework?” or “completed your homework?”
Forgetting the Auxiliary Verb
Another common mistake is forgetting to use the auxiliary verb “did” in questions and negatives. In English, we use “did” to form questions and negatives in the past tense. For example, instead of saying “you do your homework?” say “did you do your homework?” or instead of saying “I not do my homework,” say “I didn’t do my homework.”
Confusing “Done” and “Did”
A common misconception is that “done” is the past tense of “do.” While “done” is a form of the verb “do,” it’s actually the past participle form, not the past tense form. The past participle is used in perfect tenses, such as “I have done my homework.” The past tense form is “did,” as in “I did my homework yesterday.”
By avoiding these common mistakes and misconceptions, you can improve your use of the past tense of “do” and communicate more effectively in English.
Exercises and Practice
To reinforce your understanding of the past tense of do, we have created several interactive exercises that you can try out. These exercises are designed to help you practice using the past tense of do in different contexts and sentence structures.
Fill in the Blank : In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a blank space where the past tense of do should be. You will need to select the correct form of the past tense of do to complete the sentence.
Example: Yesterday, I __________ my homework before dinner.
Sentence Scramble : In this exercise, you will be given a scrambled sentence that contains the past tense of do. You will need to unscramble the sentence to make it grammatically correct.
Example: Yesterday, homework I did my.
Multiple Choice : In this exercise, you will be given a sentence with a missing word. You will need to select the correct form of the past tense of do from a list of options.
Example: She __________ her laundry last night. a) do b) did c) does d) doing
We hope these exercises and worksheets will help you master the past tense of do. Keep practicing and you’ll be using it like a pro in no time!
Summary and Conclusion
In this article, we have covered the past tense of “do” in English grammar. We started with an overview of the verb “do” and its various forms in the present tense, before moving on to its past tense forms.
We learned that the past tense of “do” is “did,” and that it is used to talk about actions or events that occurred in the past. We also discussed the different ways in which “did” can be used, including as an auxiliary verb to form questions and negatives.
To help you better understand the past tense of “do,” we provided numerous examples throughout the article. We also included exercises for you to practice using “did” in context.
Overall, mastering the past tense of “do” is an important step in improving your English grammar skills. With practice and persistence, you can become more confident in using this verb tense correctly in your writing and speaking.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the past tense form of the verb ‘do’?
The past tense form of the verb ‘do’ is ‘did’. For example, “Yesterday, I did my homework.”
Can the past tense be used with the verb ‘do’?
Yes, the past tense form of ‘do’ (‘did’) can be used in sentences where the action has already happened in the past. For example, “Did you do your homework?”
What are the different verb forms (V1, V2, V3) for the verb ‘do’?
The different verb forms for ‘do’ are:
- V1 (base form): do
- V2 (past tense): did
- V3 (past participle): done
How is the verb ‘do’ used for emphasis?
The verb ‘do’ can be used for emphasis by adding it before a verb in a sentence. For example, “I do love chocolate!”
The past tense form of the verb 'do' is 'did'. For example, \"Yesterday, I did my homework.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Can the past tense be used with the verb 'do'?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Yes, the past tense form of 'do' ('did') can be used in sentences where the action has already happened in the past. For example, \"He did his best to help me.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What is the correct past tense for the verb 'learn'?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The correct past tense for the verb 'learn' is 'learned' in American English and 'learnt' in British English. For example, \"I learned a lot from that experience.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are the different verb forms (V1, V2, V3) for the verb 'do'?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The different verb forms for 'do' are:
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How is the verb 'do' used for emphasis?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
The verb 'do' can be used for emphasis by adding it before a verb in a sentence. For example, \"I do love chocolate!\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some examples of using 'do' and 'does' in the present tense?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
- Do: \"Do you like pizza?\"
- Does: \"He does his homework every day.\"
- Recent Posts
- Plural of Species: Rules and Examples - November 8, 2023
- 50th Birthday Wishes to Boost Your English Vocabulary and Writing Skills - October 28, 2023
- Plural of Synopsis: Mastering English Grammar Made Easy! - October 23, 2023
Related posts:
- Agreed Upon: Past Tense of Agree
- Biting into the Past: Learning the Past Tense of Bite
- Past Tense of Burn: Mastering Your English Grammar
- Mastering English Grammar: The Correct Past Tense of Clean Explained
Voice speed
Text translation, source text, translation results, document translation, drag and drop.

Website translation
Enter a URL
Image translation

Chapter 3: Simple Present
Daily Habits & Routines

Learning Goals
At the end of this chapter you should be able to:
- Add -s for the third person singular verb
- Write yes/no questions and short answers
- Write information questions using wh- question words
- Add the plural marker -s ,-es, and -ies to verbs and nouns
Recognize and use
- the simple present in the affirmative and negative
- adverbs of frequency

Activity 3.1: Conversation
Directions: Ask your partner or group the following questions about your morning routines. A “routine” is a habit you usually do or a series of actions you do regularly.
- What do you do before school?
- Do you ever wake up late? Do you usually wake up early?
- Do you drink coffee or tea in the morning?
- Do you do your homework in the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening, or at night?
- How long does it take for you to get ready in the morning?
- How long does it take you to get to campus? Do you live close or far from campus?
- How do you get to campus? Drive? Bike? Bus? Walk? Carpool? Dropped-off?

Directions: Read this story out loud with a partner. One person reads a paragraph, then the other person reads the next paragraph. When you are finished, read the story again. This time, read the paragraphs, you did not read.
Yuri & Palani
Hi! My name is Yuri. I am from Ukraine. I am a student at Clackamas Community College. I have a roommate. His name is Palani. He is from Laos. We live together, but we are very different.
I wake up early at 6:00 am. Palani pushes the snooze button on his alarm clock many times, so he wakes up very late. He gets up at 7:30 am. I take a shower in the morning, but Palani takes a shower at night. I take a shower at 6:15 am. He takes a shower at 9:00 pm. I eat breakfast at home, but Palani doesn’t eat breakfast. I make coffee, and I eat cereal for breakfast. I bike to school, but Palani drives to school. I am never late. I leave at 7:30 am. Palani leaves at 7:50 am. I arrive at school early, but Palani arrives late. I arrive at school at 7:45 am. Palani arrives at 8:05 am. Palani sometimes arrives late because he can’t find parking. We are friends, so I always save him a seat next to me. We sit with Jacques and Ana. They arrive early too. Class begins at 8:00 am.
How often do you arrive late to class? Are you similar to me, or are you more similar to Palani?
Activity 3.2: Comprehension
Directions: Please write the answers to the questions in complete sentences.
1. What is the name of the man who is talking?
___________________________________________________________________
2. What is the name of his roommate?
3. What is Yuri comparing?
4. Who wakes up early? Who wakes up late?
5. What time does class begin?
6. Who arrives late? Who arrives on time?
7. How about you? Are you an early riser or a late riser?
8. What time does Yuri wake up? What time does Palani wake up?
Activity 3.3: Noticing
Part 1 Directions: Look at the story about Yuri and Palani. Choose (by underlining or otherwise markin g) the verbs you find. Don’t choose the BE verb. We are not studying that verb in this chapter.
Part 2 Directions: Complete the table with the verb forms that agree with each subject.
| Verb | Subject | Form |
|---|---|---|
| 1. wake up | I | |
| He/Palani | ||
| 2. take | I | |
| He/Palani | ||
| 3. leave | I | |
| He/Palani | ||
| 4. arrive | I | |
| He/Palani |
Activity 3.4: Try It Out!
Directions: Write the correct simple present tense form of the verb (in parentheses) on the line.
1. I (wake up)_________________________ at 6:00 am.
2. He (wake up)_________________________ at 7:30 am.
3. You (eat)_________________________ breakfast on the bus.
4. They (take)_________________________ a shower before bed.
5. He (take)_________________________ a shower in the morning.
6. We (go) _________________________ to a restaurant for lunch.
7. She (have)_________________________ cereal for breakfast.
8. His class at Oregon City (begin)_________________________ at 9:00 am.
9. My classes at Harmony (begin)_________________________ at 6:00 pm.
10. She (wash) _________________________ the dishes in the morning.

Uses of the Simple Present
The simple present is used for talking about routines, habits, and repeated activities in the present time. We use the simple present to talk about facts, which are always true. Time expressions (e.g., every day, in the summer ) and adverbs of frequency (e.g., never, sometimes, always ) signal the simple present tense.
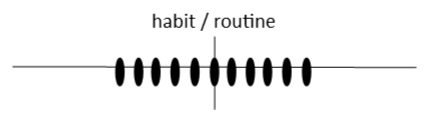
What is a routine? Something you do every morning, every week, every year.
- I brush my teeth two times a day.
- You go to the gym three times a week.
- He makes breakfast for my children every morning.
- She starts work at 7:00 am.
- They do laundry every Saturday.
What is a habit? Something you do regularly.
- My husband reads in bed before he goes to sleep.
- My cat wakes me up on Saturdays because he is hungry.
What is a repeated action? Action that we do more than once.
- I shop at Winco (not every week, but I like to go there).
- She wears shorts in the summer.
What is a fact? Something that is always true.
- The moon revolves around the earth.
- She has two children.
- Vegetables are healthy.
- Water boils at 212 degrees Fahrenheit.
Forms of the Simple Present
Affirmative statements in the simple present.
You must add an -s to the verb with the subjects he , she , and it .
subject + verb
| Subject | Verb |
|---|---|
| I You We They | walk. |
| He She It | walks. |
Activity 3.5: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of the verbs in parentheses.
1. Yuri (wake up)______________ at 6:00 am.
2. Palani (drive)______________ to school.

4. Yuri (make)______________ coffee.
5. I (cook)______________ breakfast.
6. She (eat)______________ cereal.
7. Palani (take)______________ a shower in the evening.
8. They (carpool)______________ together.
9. She (ask)______________ for a pencil.
10. Yuri and Palani (attend) ______________ Clackamas Community College.
11. We (attend) ______________ Clackamas Community College.
12. I (take)______________ a shower in the morning.
13. He (make)______________ and (drink)______________ coffee every morning.
14. She never (arrive)______________ late.
15. Class (begin)______________ at 11:30 am.
16. He usually (find)______________ parking easily.
17. Palani (live)______________ with Yuri.
18. They (brush) ______________ their hair in the morning.
19. We (brush)______________ our teeth twice a day.
20. My cats (sleep)______________ all day.
Activity 3.6: Listening
Directions: Read the paragraph. Then, listen to your instructor read the paragraph. Listen for the verbs and write them on the line. Listen closely for the correct form of the verb.
Ana and Pedro’s Morning Routine
Ana and Pedro (1)__________ at 6:00 am. Ana (2)__________ coffee. Her brother, Pedro, (3)__________breakfast. She (4)__________a shower at 6:30 am. Her brother (5)__________ a shower at 7:00 am. They (6)__________ and (7)__________ their teeth. Ana (8)__________ the cat. Ana (9)__________ her hair and (10)__________ makeup. Pedro (11)__________ his hair. Ana’s book bag (12)__________ready. Pedro (13)__________ his books in his backpack. Ana (14)__________lunches. Class (15)__________ at 9:00 am. Ana and Pedro (16)__________ the house at 8:30 am. They (17)__________ at school at 8:45 am. Ana (18)__________ out books from the college library before class. She always (19)__________ good books to read. Ana and Pedro (20)__________ to class at 8:55 am. Their first class (21)__________ at 10:50 am.
Activity 3.7: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Interview your partner.
1. Where do you live?
2. What time do you wake up?
3. When do you eat breakfast?
4. What do you eat for breakfast?
5. How do you get to school (walk, bus, car, etc.)?
6. What time do you go to school?
7. What time do you get home?
8. When do you go to bed?
Part 2 Directions: Write 8 sentences about your own daily routine using the same questions.
1. ________________________________________________________________
2. ________________________________________________________________
3. ________________________________________________________________
4. ________________________________________________________________
5. ________________________________________________________________
6. ________________________________________________________________
7. ________________________________________________________________
8. ________________________________________________________________
Part 3 Directions: Share and compare your daily activities. Read your sentences to your partner. Your partner reads to you. See if you have the same (or different) daily activities.
Part 4 Directions: Your instructor will give you a Venn Diagram to complete. Write sentences about yourself where it says You. Write sentences about your partner where it says Partner. If you and your partner have any activities that are the same, write them where it says both.

Adverbs of Frequency with the Simple Present
Adverbs of frequency (AoF) let us talk about how often we do something.
How often do you come to class? I always come to class!
How often do you shop at Fred’s? I often shop at Fred’s.
Study the chart below to learn the meanings of the following adverbs.
| Adverb | Frequency |
|---|---|
| always | 100% |
| usually | 70-90% |
| often | 50-60% |
| sometimes | 30-40% |
| seldom/rarely | 10-20% |
| never | 0% |
Adverbs of Frequency (AoF) with the BE Verb
With the BE verb, the AoFs are added between BE and the rest of the sentence. You will see in the next section that this is different with other verbs.
subject + BE + AoF + rest of sentence
| Subject | BE | AoF | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | am | never | late. |
| He She It | is | always | on time. |
| You We They | are | sometimes | early. |
Activity 3.8: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Put the correct form of the BE verb followed by the AoF on the line.
1. I (be/always) _____________________________________ late.
2. He (be/never) _____________________________________ on time.
3. She (be/often) _____________________________________ busy on Saturday.
4. It (be/never) _____________________________________ cold in August.
5. You (be/usually) _____________________________________ cold in the morning.
6. We (be/never) _____________________________________ hungry in the morning.
7. They (be/seldom) _____________________________________ tired at 9:00 pm.
8. You (be/rarely) _____________________________________ late for school.
9. He (be/sometimes) _____________________________________ tired after work.
10. It (be/usually) _____________________________________ sunny in Los Angeles.
Activity 3.9: Fill-in-the-Blank
1. Class (usually)___________________________ interesting.
2. They (often)___________________________ busy.
3. I (always)___________________________ friendly.
4. You (never)___________________________ hungry after lunch.
5. She (always)___________________________ hungry at 3:00 pm.
6. He (rarely)___________________________ on time for class.
7. They (sometimes)___________________________ confused in class.
8. You (often)___________________________ sleepy.
Adverbs of Frequency with Other Verbs

But, what if we want to say how often we do some activity? In that case, we don’t use the BE verb. We use another verb, like eat, sleep, cook, drive, or talk.
Instead of adding the AoF after the verb, like we did with the BE verb, we add it before the verb. We do this because we are saying how often the activity of the verb happens.
subject + AoF + verb + rest of sentence
| Subject | AoF | Verb | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | always | eat | breakfast. |
| He She It | usually | does | his own laundry. |
| You We They | never | walk | to school. |
We use the AoF to talk about how often or how frequently something happens.
How often do you eat breakfast? I always eat breakfast.
In the sentence above, we are saying how often we eat breakfast (always).
How often does he cook dinner? He usually cooks dinner.
In the sentence above, we are saying how often he cooks dinner. (usually).
How often do they walk to school? They never walk to school.
In the sentence above, we are saying how often they walk to school (never).
Activity 3.10: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the Adverb of frequency (AoF) and the verb in the correct form on the line.
When we use any verb except the BE verb, the AoF goes before the verb.
1. I (never/eat) ___________________ breakfast.
2. You (often/do) ___________________ laundry on Saturdays.
3. He (usually/swim) ___________________ on weekends.
4. She (never/sing) ___________________ karaoke.
5. It (rarely/rain) ___________________ in July.
6. They (seldom/watch) ___________________ movies.
7. We (always/do) ___________________ our homework.
8. She (sometimes/make)___________________ the bed.
Activity 3.11: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Put the AoF and the verb in the correct order.
Ana and Pedro (wake up) _______________________________ at 6:00 am.
Our class (start) _________________________________________ at 6:00 pm.
The college (cancel) ________________________ classes because of snow.
The teacher (give) ____________________________________ us homework.
Vegetarians (eat) ________________________________________ vegetables.
The students (sleep) ____________________________________ during class.
7. sometimes
Ana (make) _________________________________________ lunch for Pedro.
Students (speak) ____________________________________ English in class.
Activity 3.12: Classmate Interview
| How often do you… | always | usually | often | sometimes | seldom / rarely | never |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wake up before 7:00 am? | ||||||
| eat breakfast? | ||||||
| fall asleep before 11:00 pm? | ||||||
| drive to work? | ||||||
| do laundry on the weekend? | ||||||
| eat dinner before 6:00 pm? | ||||||
| sleep in on Sundays? | ||||||
| go grocery shopping on the weekdays? | ||||||
| come to class on time? | ||||||
| do your homework before class? |
Part 2 Directions: Choose 5 of the questions (and answers) from Part 1. On your own lined paper, use the answers to write sentences about your classmate’s activities. Remember to use adverbs of frequency. Turn this in to your teacher. Write your name, the date, and Activity 3.12 on the top of your paper.
Activity 3.13: Game
Directions: The purpose of this game is to practice using adverbs of frequency. Your teacher will give you some AoF game cards (often, sometimes, never).
- Stand up and find a partner.
- Ask your partner a question. Begin the sentence “How often…”
- The partner answers the question using an AoF.
- If your partner answers your question using the AoF that you have in your hand, give your partner the card.
- If your partner answers using an AoF that you don’t have, then change to another student and try again.
- You can only ask two questions before you need to change partners.
- You can only talk to the same person after you have talked with all your other classmates.
- Talk to as many partners as you can. When you have no more cards, sit down.
The goal of the game is to give away all of your cards.
Student 1: How often do you eat french fries for breakfast?
Student 2: I never eat french fries for breakfast.
(Student 1 gives the card saying “never” to Student 2)
Student 1: How often do you do your homework?
Student 2: I usually do my homework.
(Student 1 doesn’t have a ”usually” card. Student 1 changes partners and tries again.)
Ideas for Questions: How often do you…
wash your hair?
eat at a restaurant?
call your brother?
walk to school?
Pronunciation and Spelling: Adding -s and -es
We add -s and -es for two reasons:
1. The word is a noun, and we are making it plural.
2. The word is a verb, and it agrees with the subject (he, she, or it–3rd person singular)
Pronunciation
In English the same letters can have different sounds. For example, the letter “c” can sound like /k/ in cat , but it can also sound like /s/ in ice .
For words that end in -s or -es, there are three different sounds: /s/, /z/, and /ɪz/. We can predict how the -s or -es ending will sound by the last sound of the word before we add the -s or -es ending.
| If the word ends with these sounds: | This is the sound made by adding -s or -es: | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| /f/ /k/ /p/ /θ/ or /t/ | → /s/ | laughs, drinks, sleeps, births, writes, gets |
| /b/ /d/ /g/ /l/ /m/ /n/ /ŋ/ /r/ /v/ /ð/ and all vowel sounds | → /z/ | grabs, rides, hugs, comes, runs, sings, lives, sees, goes, plays, buys, studies |
| /ʤ/ /z/ /ks/ /s/ /tʃ/ or /ʃ/ | → /ɪz/ | changes, quizzes, fixes, kisses, uses, teaches, pushes |
/θ/=th as in bath /ð/=th as in that /ʤ/=j as in judge /tʃ/=ch as in church /ʃ/=sh as in wash

Activity 3.14: Pronunciation
| Target Word | Ending Sound (Circle your choice) |
|---|---|
| 1. teaches | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 2. teachers | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 3. asks | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 4. kicks | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 5. does | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 6. reads | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 7. watches | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 8. begins | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 9. pushes | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 10. listens | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 11. She works at a hospital. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 12. He lives with his sister. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 13. He puts the book on the table. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 14. She goes to school four nights a week. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 15. He cooks for her in the evening. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 16. We need boxes to move house. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 17. The mom buys groceries after class. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 18. The mom buys groceries after class. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 19. I sweep up the leaves on the sidewalk. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
| 20. The boys play soccer in the park. | /s/ /z/ /ɪz/ |
Activity 3.15: Listening
Directions: Listen to the teacher say a list of words and then sentences. You will hear each word or sentence two times. Decide if the ending sound is /s/, /z/, or /ɪz/ and choose (by circling or otherwise marking) your choice.
1. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
2. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
3. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
4. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
5. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
6. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
7. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
8. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
9. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
10. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
11. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
12. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
13. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
14. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
15. /s/ /z/ /ɪz/
Activity 3.16: Listening & Speaking
Part 1 Directions: Identify which of the three ending sounds (/s/, /z/, or /ɪz/) is at the end of each of the target words. Write the sound symbol on the line.
/s/ /z/ /ɪz/
1. changes _____
2. crabs _____
3. dishes _____
4. touches _____
5. helps _____
6. books _____
7. pencils _____
8. sleeps _____
9. mixes _____
10. kisses _____
11. The students eat breakfast. _____
12. My sister walks her dog. _____
13. The dogs eat peanut butter. _____
14. The student catches the bus. _____
15. I have three cats. _____
16. Most teachers have pets. _____
17. She writes a book. _____
18. Natasha buys food. _____
19. Yuri wakes up on time. _____
20. She sees her daughter. _____
Part 2 Directions: With a partner, say the word or sentence. Your partner will point to the sound they hear.
If a word ends in /s/, /z/, /ch/, /sh/ or /x/ sound → add -es
Only add -es for the he/she/it form of the verb (third person singular).
watch → watches
wash → washes
kiss → kisses
I pass out papers. → She passes out papers.
I wash the dishes. → He washes the dishes.
Activity 3.17: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of the verb in parentheses on the lines.
1. (watch) I __________ TV in the morning, but she ________ TV at night.
2. (wash) They ________ dishes together after dinner. He ________ dishes on weekends.
3. (fix) My father and I _________ cars together. My husband ________ the bicycle.
4. (teach) They ________ their daughter Ukrainian. Eva ________ her son Amharic.
5. (brush) I ________ my teeth twice a day. He _______ three times a day.
6. (kiss) She _______ her husband in the morning. I ________ my children before bed.
7. (stretch) I always ________ before exercise. Viktor ________ after exercise.
8. (guess) I never ________ the answer, but Tatiana often ________ the answer.
9. (mix) She ________ Spanish and English. They _______ English and Ukranian.
10. (splash) The kids ______ in the bathtub. My daughter always ________, too.
11. (cash) I ______ my check at the bank. He _________ his check too.
12. (latch) I ________ my screen door. She ________ her screen door.
13. (notice) I always ________ mistakes. She never ________ mistakes when she writes.
14. (touch) He ________ the door. We ________ the window.
15. (brush) They ________ their hair once a day. He _________ his hair three times a day.
16. (pass) She ________ all her classes. They ________ their ESL classes.
17. (ask) I ________ for vegetarian food. Natasha ________ for Ukrainian food.
18. (ask) He ________ a question. We ________ to play a game.
19. (watch) She ________ Jackie Chan movies. They ________ Jet Li movies.
20. (dance) I ______ twice a week. He ________ once a week.
Activity 3.18: Listening
Directions: Read the story. Then listen to your teacher read the story. Listen for the missing words and write them on the line. Remember that the subject and the verb of a sentence have to agree. If they don’t agree, you should listen again. Some verbs end in -s and some verbs end in -es.
Viktor and Tatiana
Viktor and Tatiana (1)_________ married. They (2)_________ English at Clackamas Community College. They (3)_________ from Ukraine. Tatiana sometimes (4)_________ angry with Viktor because he doesn’t help around the house. Tatiana (5)_________ dinner and Viktor (6)_________ TV. Tatiana (7)_________ the house, and Viktor (8)_________ English.
Then Tatiana remembers that Viktor (9)_________ the car while she (10)_________ books. In the grocery store, he always (11)_________ the shopping cart. He (12)_________ for her when she is sick. He also (13)_________ the socks when they (14)_________ movies at home. On school nights, Viktor (15)_________ the dishes after Tatiana cooks. He (16)_________ her every day when they leave the house, and he (17)_________ her every night before they (18)_________ asleep. Then Tatiana isn’t angry anymore.
If a word ends in a consonant plus -y, change -y to i and add -es. If the word ends in a vowel plus -y, just add -s.
Consonant + -y
Change -y to i and add -es
cry → cries
study → studies
pay → pays
buy → buys
Activity 3.19: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of the verb on the line in the sentences below.
1. (study) I ___________ in the morning, but he ___________ at night.
2. (worry) He ___________ about money. I ___________ about him.
3. (cry) The cat ___________ when I leave. The babies ___________ all the time.
4. (play) She ___________ piano. We ___________ violin.
5. (pay) I ___________ for groceries with a credit card. Tatiana ___________ with cash.
6. (stay) He ___________ after class for help. They ___________ after class to talk.
7. (stay) She ___________ at a hotel. I ___________with my mom.
8. (worry) My husband ___________ about school. I ___________ about our health.
9. (enjoy) We ___________ playing board games. He ___________ online games.
10. (say) They ___________ they are busy Friday, but she ___________ Friday is ok.
11. (fly) A bird ___________ south in winter. Birds ___________ north for the summer.
12. (buy) They ___________ paper online. She ___________ supplies at the store..
13. (fly) He ___________ to Paris today. I ___________ to Denver tomorrow.
14. (study) We ___________ before vocabulary tests. She ___________ for grammar.
15. (pay) He ___________ for 2 classes. I ___________ for 3 classes.
16. (try) I ___________ to study 3 times a week. She ___________ to study every day.
Activity 3.20: Listening
Using infinitives with like, want, & need.
Some verbs can be combined with an infinitive (to + verb) to express a different meaning or opinion about the activity.
| Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|
| like + to ski (Infinitive) | This shows an activity that is pleasurable or fun. Example: I like to ski. |
| want + to go (Infinitive) | This shows an activity that I have a desire to do. Example: I want to go to a movie. |
| need + to finish (Infinitive) | This shows an activity that I have to do. Example: I need to finish my homework. |
Activity 3.21: Fill-in-the-Blank
Part 1 Directions: Complete the sentences by writing like, want, or need on the line.
1. I ___________ to pay my rent.
2. She ___________ to study for the test.
3. They ___________ to buy a diamond necklace.
4. You ___________ to have an expensive new car.
5. I ___________ to read a book before bed to help me sleep.
6. You ___________ to do your homework.
7. We ___________ to eat dessert first.
8. I ___________ to sleep until 10:00 am, but I __________ to get up because work starts at 7:00 am.
Negative Statements in the Simple Present
Negatives with the be verb, activity 3.22: writing.
Directions: Make these sentences negative by adding not after the verb.
1. She is a hairdresser.
2. He is busy today.
3. They are from Colombia.
4. He is a contractor.
5. It is sunny.
6. They are students.
7. He is a teacher.
8. The dog is in the garden.
Negatives with All Other Verbs
Using auxiliary verbs.
There are three auxiliary verbs in English: BE, DO, and HAVE. We will learn about BE and DO in this class. We will learn about using HAVE as an auxiliary in the next level. You have already seen the first of our three auxiliary verbs, BE, in Chapter 2. We combine the BE verb with the -ing form of the verb to create the present progressive (an action happening now).
When we make negative sentences with other verbs, we use the auxiliary verb, DO. It has two forms: do and does . The negative not comes after do or does and is followed by the base form of the main verb.
The base form is the infinitive without the to . Instead of “to sing” (infinitive), the base form is sing . Do not add -s to the base verb. Let’s look at an example sentence.
subj do/does neg. base verb rest of sentence
He does not sing in the shower.
- He is the subject
- Does is the auxiliary verb. Do/Does agrees with the subject (3rd person singular: add -es).
- Sing is the main verb in the base form. Do not add -s to the main verb.
subject + auxiliary DO + not + base form + rest of sentence
| Subject | Auxiliary DO | Negative | Base Form of Main Verb | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I You We They | do | not | drink | coffee after 5:00 pm. |
| He She It | does |
Negative Contractions
To make negative contractions, we contract the auxiliary verb and the negative.
| Subject | Auxiliary DO + not |
|---|---|
| I You We They | do not = don’t |
| He She It | does not = doesn’t |
Activity 3.23: Choose the Correct Form
Directions: Choose the correct form, and then write the contraction on the line. Remember that the auxiliary DO (do/does) has to agree with the subject.
1. The teacher do not / does not eat meat. ___________________
2. I am a homemaker. I do not / does not work outside my home. ___________________
3. She is a driver. She do not / does not work in an office. ___________________
4. He is a vegetarian. He do not / does not eat meat. ___________________
5. They do not / does not drink coffee in the evening. ___________________
6. Palani do not / does not like to wake up early. ___________________
7. Yuri do not / does not want to come to school late. ___________________
8. Yuri do not / does not press snooze on his alarm clock. ___________________
9. They do not / does not have the same habits. ___________________
10. It do not / does not look like a good book. ___________________
11. The students do not / does not do their homework. ___________________
12. He do not / does not get good grades on tests. ___________________
Activity 3.24: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Write the correct form of do or does on the line.
1. (do/sing) She ___________ not ___________ in public.
2. (do/write) They ___________ not ___________ on the wall.
3. (do/drive) He ___________ not ___________ for a job.
4. (do/ask) You ___________ not ___________ for a diamond ring.
5. (do/play) We ___________ not ___________ guitar.
6. (do/like) The dog ___________ not ___________ my cat.
7. (do/type) She ___________ not ___________ fast.
8. (do/read) He ___________ not ___________ online.
Activity 3.25: Writing
Directions: Make these sentences negative. Use full forms for numbers 1-5 and contractions for numbers 6-10.
1. I go to work at 3:00 pm.
2. She wants to eat Chinese food.
3. They have two children.
4. He has a dog and two cats.
5. You need to stand in line.
6. She finishes her homework.
7. I eat breakfast.
8. You drink coffee.
9. He drinks diet soda.
10. My car has red seats.
Activity 3.26: Interview
Part 1 Directions: Use the sentences below to interview your partner. Take notes on your own lined paper.
Student A: Tell me a food you don’t like.
Student B: I don’t like eggs.

2. Tell me a movie you don’t like.
3. Tell me a place you don’t like.
4. Tell me a sport you don’t like.
5. Tell me a color you don’t like.
6. Tell me a singer or band you don’t like.
7. Tell me a type of music you don’t like.
8. Tell me a book you don’t like.
Part 2 Directions: Now, write 5 sentences about your partner. Use your notes to help you. Write your partner’s answers in FULL sentences.
Yes/No Questions & Short Answers
Yes/No questions mean that the answer to the question is either yes or no . These questions don’t use wh- question words. Remember, when we use an auxiliary verb, the main verb is in the base form. The auxiliary verb goes before the subject and the main verb goes after the subject.
auxiliary DO + subject + base verb + rest of sentence
| Auxiliary DO | Subject | Base Form of Main Verb | Rest of Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Do | I you we they | eat | breakfast? |
| Does | he she it |
Short Answers
Short answers are quick answers to yes/no questions. Remember that if the question uses the BE verb, use the BE verb in your answer. If the auxiliary DO is used in the question, then use DO in the answer.
Do you have cats? Yes, I do.
Are you a teacher? Yes, I am.
| Affirmative | Negative | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes, | I you we they | do. | No, | I you we they | do not. OR don’t. |
| he she it | does. | he she it | does not. OR doesn’t. | ||
Do you drink coffee in the morning? Yes, I do.
Does he drink coffee in the morning? No, he doesn’t.
Activity 3.27: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Complete the questions with the missing auxiliary verb and subject.
A: Does she wake up early?
B: No, she doesn’t.
1. A:___________________ do her homework every day?
B: Yes, she does.
2. A:___________________ wash the dishes after dinner?
B: Yes, he does.
3. A:___________________ eat dinner together?
B: Yes, they do.
4. A:___________________ work late every day?
5. A:___________________ drive to school?
6. A:___________________ study vocabulary?
B: Yes, I do.
7. A:___________________ eat lunch at home?
B: No, we don’t.
8. A:___________________ ask questions?
9. A:___________________ practice English at the grocery store?
10. A:___________________ do laundry on Saturdays?
Activity 3.28: Game
Information questions in the simple present.
We have seen several lists of wh- question words in previous chapters. Here is a bigger list. You can practice making questions with the new words and review the ones you have seen in Chapters 1 and 2.
| Wh- Question Word | Asks about... | Example Question |
|---|---|---|
| Who | a person | Who is your teacher? |
| What | information | What is your name? |
| Where | location | Where are you from? |
| When What time | Time *(specific and general) | When is your birthday? What time is your class? |
| Why | a reason | Why are you late? |
| How | directions, process, or means | How do you get home? |
| How many | a number | How many children do you have? |
| How often | frequency | How often do you drink coffee? |
| How much | an amount or money | How much is our textbook? |
| What kind | one from a group | What kind of fruit do you like? |
* What time asks about specific time. When asks about general time.
What time does class start? Class starts at 9:00 am.
When is your birthday? My birthday is in August.
We form information questions (sometimes called wh- questions) the same as yes/no questions. Add the question word (who, what, where, when, what time, etcetera) to the beginning of the question.
wh- + auxiliary DO + subject + main verb
| Wh- Question Word | Auxiliary DO | Subject | Base Form Main Verb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Who What Where When What time Why How How many How often How much | do | I you we they | see? eat? drive? write? |
| does | he she it |
Activity 3.29: Choose the Correct Form
Directions: Choose the correct question word.
1. Who/What is your teacher? My teacher is Susan.
2. Where/What is your address? My address is 19 Molalla Ave, Oregon City.
3. Where/When do you wake up? I wake up at 7:30 am.
4. Why/Who do you have an umbrella? Because it’s raining.
5. How/Where do you take ESL? I take ESL classes at CCC.
6. When/What do you work? I work at 5:00 pm.
7. Why/How do you get to school? I take the bus.
8. What/How do you cook hotdogs? I boil them, but some people grill them.
9. How much/How often milk do you want? I want 1 cup.
10. How many/Why cookies do you want? I want 2 dozen.
Activity 3.30: Fill-in-the-Blank
Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct question word.
1. A:___________ do you go to work?
B: I go to work at 5:00 am.
2. A:___________ is he wearing a sweater?
B: He’s cold.
3. A:___________ do you study vocabulary?
B: I use vocabulary cards.
4. A:___________ are they from?
B: They’re from Italy.
5. A:___________ are you doing?
B: I’m doing my homework.
6. A:___________ often do you sleep in?
B: I sleep in on Saturdays.
7. A:___________ time does class start?
B: Class starts at 6:00 pm.
8. A:___________ do you study?
B: I study at the library.
9. A:___________ is your favorite actor?
B: My favorite actor is Brad Pitt.
10. A:___________ many classes do you take?
B: I take three classes each term.
Activity 3.31: Interview
Directions: Your instructor will give you a worksheet that you can use to interview a classmate.
- Match the wh- question word with the question. You can only use a word one time.
- When you finish matching you will have 10 questions and 10 answers. Choose 5 questions to ask your classmate.
- Write the answers to the 5 questions below.
1. ___________________________________________________________________
2. ___________________________________________________________________
3. ___________________________________________________________________
4. ___________________________________________________________________
5. ___________________________________________________________________
Activity 3.32: Error Correction
Directions: There are 10 mistakes in the paragraph below. Find the mistakes with the simple present, adverbs of frequency, negative sentences, or -s / -es endings and correct them.
My name is Jacques. I lives next to Yuri and Palani. I am a student at CCC also. I arrive always early to class. My brother drive me to school. I do not drives. I eat lunch with my friends. We eat often at Ana and Pedro’s house. I doesn’t cook. After class, always I study in the library. I finishes my homework in the afternoon. I study with my friend. My friend Palani finish his homework at night. I live with my family. My mother cook dinner for the family. She wash the dishes after dinner. I dry them.

Activity 3.33: Writing
Directions: Rewrite these sentences to include the adverb of frequency (AoF) in parentheses.
1. (usually) We eat dinner outside in summer.
2. (always) I wear slippers in the house.
3. (never) My family wakes up early.
4. (sometimes) My friends and I watch movies on Fridays.
5. (rarely) We eat uncooked food.
6. (often) They are late to class.
7. (never) I finish my homework on the computer.
8. (seldom) She takes her dog to the dog park.
9. (usually) You are on time.
10. (rarely) She eats fast food.
11. (never) It snows in August.
12. (always) It rains in October.
13. (often) We have homework.
14. (never) They forget books at home.
Activity 3.34: Writing
Directions: Write the question on the line below. Use the answer for extra information. Some questions are wh-questions, and some are yes/no questions.
1. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I wake up at 8:00 am.
2. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: Yes, I do (I have a dog.)
3. A:_______________________________________________________________
B: My birthday is in August.
4. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: No, I don’t. (I don’t do my homework in the morning.)
5. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I take a shower in the morning.
6. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I arrive early for class.
7. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: He drives to school.
8. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: He washes the dishes every day.
9. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: Yes, I do. (I exercise 3 times a week.)
10. A: ______________________________________________________________
B: I eat fast food once a month.
Directions: Write a paragraph comparing your daily schedule with a partner’s daily schedule. Use the simple present tense, adverbs of frequency, and time expressions.
Pre-writing:
- Write 6 questions to ask your partner. Use 6 different wh-question words. There is a place to write each question in the chart that follows.
- Answer the 6 questions for yourself.
- Choose a partner, ask your questions, and then write down your partner’s answers.
| Question | My Answer | Partner’s Answer |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ||
| 2. | ||
| 3. | ||
| 4. | ||
| 5. | ||
| 6. |
- Use your own 8.5″ x 11″ lined paper. Do not use other paper sizes, please.
- Heading: Put your full name, the due date, and Ch. 3 Writing Assignment at the top of your paper. Your instructor will tell you where the heading goes (left or right side).
- Indent the first sentence, skip lines (double space), and leave a 1-inch margin on the sides and bottom.
Writing and Grammar:
- First sentence: begin writing by using this topic sentence: [Partner’s name] and I are classmates, but we are very different.
- In your sentences, write your answer and your partner’s answer.
- Use 3 adverbs of frequency.
- Write 2 negative sentences.
- Use full forms; do not use contractions.
- Use capital letters and punctuation correctly.
- Use the rubric below to check your work.
Model Paragraph:
My partner and I are classmates, but we are very different. I get up very early at 5:00am. My partner doesn’t get up early. She often gets up at 9:00am. I usually drink coffee in the morning, but my partner doesn’t like coffee. She likes tea instead. I have two children, so I am busy with them. My partner is married, but she doesn’t have any children. I leave for school at 8:30am. My partners never goes straight to school. She goes to her parents house first. She always helps them because they are very old. My parents are still young at age 50 and 55.
Assignment Rubric:
| Heading: Full Name, Due Date, Ch. 3 Writing Assignment | 1 point |
|---|---|
| Format: Indent, double space, margins | 1 point |
| Your paragraph has at least 10 sentences | 1 point |
| Every sentence has a subject and verb, & they agree | 1 point |
| There are 3 adverbs of frequency | 3 points |
| There are 2 negative sentences | 4 points |
| Correct use of spelling | 1 point |
| Correct use of capital letters | 1 point |
| Correct end punctuation | 1 point |
| Total | 14 points |
Self-Assessment
These were our goals at the beginning of Chapter 3:
At the end of this chapter you will be able to:
- Add -s , -es, and -ies to verbs and nouns
Directions: Choose yes if you think you achieved the goals or no in the table below if you think you did not achieve the goals. Then, write an example of the goal in the last column.
| I can… | I achieved this goal: | My example: |
|---|---|---|
| add -s for 3rd person singular | yes no | He walks. |
| write an affirmative sentence in the simple present | yes no | |
| write a negative sentence in the simple present | yes no | |
| write yes/no questions using the simple present | yes no | |
| answer yes/no questions using short answers | yes no | |
| make information questions using wh- question words | yes no | |
| use AoF with the simple present | yes no |
Explorations 1: Grammar for the Experienced Beginner Copyright © by Susan; Jen; and Kit is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Grammar - Past Simple vs. Past Continuous (Eleme ...
- Game Code: 31654
- English 16 Public ESL, Grammar, Elementary, A1, Past Simple vs. Past Continuous
- Play Study Slideshow Share Merit ESL Resources 184
Share Grammar - Past Simple vs. Past Continuous (Elementary)
Use Class PIN to share Baamboozle+ games with your students. Upgrade
Save to Folder
- I ____________________ (DO) all my homework last Monday. did
- Yesterday, I ____________________ (WAKE) up, I ____________________ (HAVE) a shower and I ____________________ (GO) to school. woke / had / went
- I ____________________ (WATCH) TV at 5 o'clock yesterday. was watching
- Sarah ____________________ (READ) a book and her friend ____________________ (READ) a magazine. was reading / was reading
- They ____________________ (NOT GO) to the zoo last weekend. didn't go
- They ____________________ (NOT GO) to the zoo yesterday at 10 o'clock. weren't going
- ____________________ you ____________________ (PLAY) computer games last weekend? Did - play
- ____________________ you ____________________ (PLAY) computer games yesterday at 7 o'clock? Were - playing
- A. What ____________________ you ____________________ (DO) this morning at 10 o'clock? --- B. I ____________________ (DO) my homework. were - doing / was doing
- They ____________________ (HAVE) dinner in that new restaurant last night. had
- He ____________________ (NOT SLEEP) at 7 o'clock yesterday. wasn't sleeping
- ____________________ you ____________________ (SEE) him this morning? Did - see
- They ____________________ (COOK) at 7pm yesterday. were cooking
- ____________________ you ____________________ (LIKE) that film? Did - like
- She ____________________ (NOT TAKE) the bus to work this morning. She ____________________ (GO) on foot. didn't take / went
- We ____________________ (NOT GO) to the cinema last weekend. didn't go
Sign up for a trial to unlock features.
- Rules/Help/FAQ Help/FAQ
- Members Current visitors
- Interface Language
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
- English Only
forgot/forgotten my homework
- Thread starter KonradBade
- Start date Feb 21, 2011
Senior Member
- Feb 21, 2011
Hey, which one is more natural in BE and AE? at school your teacher is checking the homework: [1] Oh, I've done my homework... but,... I've forgotten it home! [2] Oh, I've done my homework... but,... I forgot it home! [3] Oh, I did my homework... but,... I forgot it home! [4] Oh, I did my homework... but, ... I've forgotten it home! To the first part: Is it more important that you did it (present perfect) or that you know when you did it e.g. the day before (simple past)...? I think it's more important that you did it at any time before now. Second part: Is it more important that you forgot it this morning? (simple past) or is it the result: you can't show it now!? I think it's the result, not the action, that really matters in this situation! Therefore, I would choose [1] Oh, I've done my homework... but,... I've forgotten it home! Am I right?
Your answer is fine. Many native speakers would choose the simple past. I did my homework but I forgot it. All four examples sound possible. People who are trying to be careful with their tenses might use the present perfect in these sentences, but anybody would understand if you used the simple past for everything. Both the "doing" and the "forgetting" take place in the past. In this situation, those actions do have some relation to the present, so present-perfect versions are fine. Many native speakers choose the simplest tense that will convey their ideas. More often than not, those tenses will be the simple past and the present.
JulianStuart
[1] Oh, I've done my homework... but,... I've left it at home! [2] Oh, I've done my homework... but,... I left it at home! [3] Oh, I did my homework... but,... I left it at home! [4] Oh, I did my homework... but, ... I've left it at home! There are nuances available here, despite the very similar meanings of all of these. (Note the at before home). You can see why asking these kinds of questions without any real context is not helping you very much because there are few helpful guidances that will always apply in all possible contexts! 1 might be said to a friend on the bus to school. 2 might be said to the teacher at school. 3 might be part of a story told days later. 4 might be said to a friend on the bus to school emphasizing that I didn't do anyone else's homework. I changed forgotten because it's a separate issue of whether you have remembered yet and whether something is still forgotten. They are not good examples for the question you are asking.
Oh, that's very interesting. So "I forgot it at home" does not mean "I forgot to bring it - it's still at home"?! It means "I forgot to do it"? So you have to say "I left it at home", "I forgot to bring it" something like that? What do you think about the two sentences in post #3? I crossed "home" out there? Do they make sense / do they express what I was thinking of?!
I don't think I would just say "forgot it," I would say what I forgot to do. I did my homework last night, but I forgot to bring it to school (this morning). I did my homework and meant to bring it to school this morning, but I forgot to [bring it]. I did my homework, but I forgot it when I left the house (this morning). This kind of explanation is not necessary when what you forgot has already been mentioned. Teacher: Did you bring your homework? Student: Oh no, I forgot it! / Oh no, I forgot to! / Oh no, I forgot! If you forgot something else, then you must explain. Teacher: Did you bring your homework? Student: Oh, no, I forgot to do it! Please, can I bring it tomorrow? Student: Oh no, I forgot (all) about it! . . .
Hi, Konrad. "I forgot it home" and "I've forgotten it home" are not natural things to say in AmE, but I think I see what you mean: I left it at home and forgot to bring it to school. A natural way in AmE to say this is "I forgot and left it at home". Referring to JulianStuarts versions of the three sentences for simplicity's sake— If we make the reasonable assumption that first I did my homework (the first event) and then I left it at home (the second event), all four corrected sentences are equally applicable, and all four are equally natural when taken without context. Note 1: The difference between past simple and present perfect in these sentences has nothing to do with the importance of doing it or of knowing when you did it. Note 2: To me, all four apply equally well on the bus, after it has left my house, and at school, and all four apply equally well no matter who I am talking to. Note 3: I am assuming I have not had a chance to return home to retrieve my homework, but otherwise the time elapsed is irrelevant. The difference between past simple and present perfect has to do only with the time or times we choose as reference points. In sentence 1, we are looking back at both events from the present. Sentence 2 uses a shift in reference points, from looking back from the present at doing the homework to looking from a point in the past at leaving the finished homework at home. I interpret this shift to be stressing that my homework is complete (in the present), but when I left home (in the past) I forgot to bring it with me. Sentence 3 looks at the two events in chronological order, looking at them from a forward-moving reference point in the past. Sentence 4 shifts reference points from past to present. I interpret this shift as stressing that when I was meant to do my homework (in the past), I did it, no problem, but now (in the present) I find myself without it. EDIT: I am presupposing , in addition to the sequence of events, that the statement "My homework is complete" began to be true when I did my homework and continues to be true in the present and that the statement "I find myself without it" began to be true when I left it at home and continues to be true in the present. I am not imagining that any of the statements with present perfect implies either of these presuppositions. I interpret the changes in tense as changes in emphasis, the facts remaining the same for all four sentences.
KonradBade said: Oh, that's very interesting. So "I forgot it at home" does not mean "I forgot to bring it - it's still at home"?! It means "I forgot to do it"? So you have to say "I left it at home", "I forgot to bring it" something like that? What do you think about the two sentences in post #3? I crossed "home" out there? Do they make sense / do they express what I was thinking of?! Click to expand...
Participant
Can I add the fifth option? Oh, I had done my homework...but I forgot it at home (emphasizing that my work was done before I forgot it at home). How is that? Thank you.
Participant said: Can I add the fifth option? Oh, I had done my homework...but I forgot it at home (emphasizing that my work was done before I forgot it at home). How is that? Thank you. Click to expand...
sound shift
Fabulist said: Forgot in AE is past tense; forgotten is the past participle, used with auxiliary verbs to make the perfect tenses: have forgotten, had forgotten. Non-AE uses "forgot" in place of AE "forgotten." Click to expand...
- Feb 22, 2011
The particular usage "forgot my <something> at <location" has been discussed at length in several previous threads. I forgot / left my bag in a taxi I forgot it at home
Forero said: EDIT: I am presupposing , in addition to the sequence of events, that the statement "My homework is complete" began to be true when I did my homework and continues to be true in the present and that the statement "I find myself without it" began to be true when I left it at home and continues to be true in the present. I am not imagining that any of the statements with present perfect implies either of these presuppositions. I interpret the changes in tense as changes in emphasis, the facts remaining the same for all four sentences. Click to expand...
I have done my homework. How can you "undo" your homework? That is the conundrum I left unaddressed! So whether the sentence refers to the state of the homework as of now or some time in the past isn't something that makes sense to try to distinguish - in isolation . I think I need a brief reminder of what the question actually is that we are trying to answer. One question that we can answer with a "NO" is "Are there rules about nuances of meaning to determine selection of past and present perfect that can be laid down for sentences with no context ?"
But it emphasise the result (it's done now) in contrast to "I did my homework" that is more about the action, the fact that you did it at some point in the past. am I right about that?
KonradBade said: But it emphasise s the result (it's done now) in contrast to "I did my homework" and that is more about the action, the fact that you did it at some point in the past. A m I right about that? Click to expand...
The distinction is clear in this example: "I've always done my homework on time" implies I still do ( present perfect) homework while "I always did my homework on time" implies I don't do homework any more - homework is a thing of the past . However, "I just did my homework" and "I've just done my homework" don't have that distinction.
JulianStuart said: The distinction is clear in this example: "I've always done my homework on time" implies I still do ( present perfect) homework while "I always did my homework on time" implies I don't do homework any more - homework is a thing of the past . However, "I just did my homework" and "I've just done my homework" don't have that distinction. Click to expand...

Quality Point(s): 1094
Answer: 278
- English (US)
"I did it first thing in the morning this morning. " Hi, is the sentence above ok?
- Report copyright infringement

Quality Point(s): 51028
Answer: 11179
Yes, it is natural. When you say this sentence, you need to pause before saying... this morning. We do it to keep from confusing someone and to emphasize that I did it at that time.
Was this answer helpful?
- Why did you respond with "Hmm..."?
- Your feedback will not be shown to other users.
You're welcome.

Quality Point(s): 7744
Answer: 2180
@u-1 Your sentence does not sound natural to me, and it’s better to avoid repeating words like “morning” twice in a short sentence. To me, the natural and common sentence with the same meaning is: ✅ I did it first thing this morning.
@u-1 it very natural to use “in the morning” interchangeably with “this morning”. it’s not natural to say “in the morning this morning” with or without a pause. by the way, if you want to create a pause in a sentence, there are various punctuations you can use such as a comma, colon, semi-colon, em dash, parentheses, or ellipses..
- What is the difference between is it ok for you? and is it ok with you? ?
- What is the difference between speak and speaks ?
- What is the difference between sorry for bothering you and sorry to bother you ?
- What is the difference between i'm down for it and i'm up for it ?
- How do you say this in English (US)? 準備できたものから送ってください
- 亚洲大片精品永久免费看网站高清完整版
- 亚洲精品国产永久无损音乐_亚洲精品国产永久无损音乐大全影视
- 91丨国产丨精品入口高清美剧网
- 亚洲永久精品国产无损音乐_亚洲永久精品国产无损音乐星空影视
- 左手影院~永久入口高清在线观看版片
- to exasperate, is it common? do you use it? how do you use it ?
- criminal case and criminal record and record what's the difference? do you have a criminal case?...
- 1. if someone frustrates me, can I say - "I don't know what to do with you anymore" or "I'm at my...
- acquistion and purchase - what's the difference? please provide examples
- What's up guys! Is written "Oh my God" or "Oh my god" I think writting "Oh my God" is more common...
- When to use might and when to use will?
- In the following sentence: - Is "manufacturer" not a division of "a company". - Who is import...
- There are nouns that don't need an article in certain situations, like the "school" in "go to sch...
- what does (smash) mean? I'm gonna punish my opponent I'm gonna (smash) him?
- hey! I'm looking for a girl to practice Speaking with! so if you wanna help pls lmk! also if you...
- How do you say this in Japanese? therapy session
- I put away everything on the floor. Does this sound natural?
The Language Level symbol shows a user's proficiency in the languages they're interested in. Setting your Language Level helps other users provide you with answers that aren't too complex or too simple.
Has difficulty understanding even short answers in this language.
Can ask simple questions and can understand simple answers.
Can ask all types of general questions and can understand longer answers.
Can understand long, complex answers.
Show your appreciation in a way that likes and stamps can't.
By sending a gift to someone, they will be more likely to answer your questions again!
If you post a question after sending a gift to someone, your question will be displayed in a special section on that person’s feed.
Ask native speakers questions for free

Solve your problems more easily with the app!
- Find the answer you're looking for from 45 million answers logged!
- Enjoy the auto-translate feature when searching for answers!
- It’s FREE!!
- "I did it first thing i...
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Statement from President Joe Biden on the Death of Yahya Sinwar
Early this morning, Israeli authorities informed my national security team that a mission they conducted in Gaza likely killed Hamas leader Yahya Sinwar. DNA tests have now confirmed that Sinwar is dead. This is a good day for Israel, for the United States, and for the world.
As the leader of the terrorist group Hamas, Sinwar was responsible for the deaths of thousands of Israelis, Palestinians, Americans, and citizens from over 30 countries. He was the mastermind of the October 7th massacres, rapes, and kidnappings. It was on his orders that Hamas terrorists invaded Israel to intentionally – and with unspeakable savagery – kill and massacre civilians, a Holocaust survivor, children in front of their parents, and parents in front of their children.
Over 1,200 people were killed on that day, the deadliest day for Jews since the Holocaust, including 46 Americans. More than 250 were taken hostage, with 101 still missing. That number includes seven Americans, four of whom are believed to still be alive and held by Hamas terrorists. Sinwar is the man most responsible for this, and for so much of what followed.
Shortly after the October 7 massacres, I directed Special Operations personnel and our intelligence professionals to work side-by-side with their Israeli counterparts to help locate and track Sinwar and other Hamas leaders hiding in Gaza.
With our intelligence help, the IDF relentlessly pursued Hamas’s leaders, flushing them out of their hiding places and forcing them onto the run. There has rarely been a military campaign like this, with Hamas leaders living and moving through hundreds of miles of tunnels, organized in multiple stories underground, determined to protect themselves with no care for the civilians suffering above ground. Today, however, proves once again that no terrorists anywhere in the world can escape justice, no matter how long it takes.
To my Israeli friends, this is no doubt a day of relief and reminiscence, similar to the scenes witnessed throughout the United States after President Obama ordered the raid to kill Osama Bin Laden in 2011.
Israel has had every right to eliminate the leadership and military structure of Hamas. Hamas is no longer capable of carrying out another October 7.
I will be speaking soon with Prime Minister Netanyahu and other Israeli leaders to congratulate them, to discuss the pathway for bringing the hostages home to their families, and for ending this war once and for all, which has caused so much devastation to innocent people.
There is now the opportunity for a “day after” in Gaza without Hamas in power, and for a political settlement that provides a better future for Israelis and Palestinians alike. Yahya Sinwar was an insurmountable obstacle to achieving all of those goals. That obstacle no longer exists. But much work remains before us.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Translate I did my homework this morning. See Spanish-English translations with audio pronunciations, examples, and word-by-word explanations. ... Word-by-word. i. yo. do. hacer. my. mi. homework. la tarea. this. este. esta. morning. la mañana. Examples. Random Word. Roll the dice and learn a new word now! Get a Word. Want to Learn Spanish ...
Use Grammarly's free sentence checker to ensure your writing is clear, compelling, and easy to read. Just enter your text where it says "check my sentences" to check for run-on sentences, tone, clarity, and more. Step 1: Add your text, and Grammarly will underline any issues. Step 2: Hover over the underlines to see suggestions.
You wouldn't say "I have done my homework yesterday," you would need to say "I did my homework yesterday." I think those both sound natural. I think the timeline of 'this morning' allows for either verb tense to be used, because it is both in the past and also not long ago, it's still today.
Synonym for I did my homework When you use I have done something it means specifically you've done it reacently in the past. just using plain past tense means it could be at anytime in the past. English (US) French (France) German Italian Japanese Korean Polish Portuguese (Brazil) Portuguese (Portugal) Russian Simplified Chinese (China) Spanish ...
Daily routines for School. I went to school. I had classes. I ate lunch / I had lunch. I finished school at 3. I went home. I did my homework. Notice how in this lesson all of these phrases are in the past simple tense and have I (first person singular) as the subject.
I did do my homework seems correct. Native expression. I make my bed I do my drill every morning. I occasionally make a mistake. I do hope this time I did not make any mistake. We make an experiment in this issue now. All is common native styles. I did do my homework seems correct.
Present simple or Present continuous? Put the verbs into the correct tense (present simple OR present continuous): The train always _____(1: leave) on time.
A common misconception is that "done" is the past tense of "do.". While "done" is a form of the verb "do," it's actually the past participle form, not the past tense form. The past participle is used in perfect tenses, such as "I have done my homework.". The past tense form is "did," as in "I did my homework ...
I'm done my homework is notable enough in dialects of parts of Canada and the USA to have its own entry in the Yale Grammatical Diversity Project. I personally would say I've done my homework , and in more formal written English I would expect to see either I have done my homework or I did my homework , perhaps with finished or completed ...
do the shopping: I'll do the shopping after work. do the ironing: Lee is doing the ironing right now. do housework: She does the housework at the weekends. BUT make your bed: I make my bed every morning. Good or bad actions: do well: He did well in his exams. do badly: I did badly in the race. do something, nothing, etc.: They did something ...
Google's service, offered free of charge, instantly translates words, phrases, and web pages between English and over 100 other languages.
I arrive always early to class. My brother drive me to school. I do not drives. I eat lunch with my friends. We eat often at Ana and Pedro's house. I doesn't cook. After class, always I study in the library. I finishes my homework in the afternoon. I study with my friend. My friend Palani finish his homework at night. I live with my family.
She _____ (NOT TAKE) the bus to work this morning. She _____ (GO) on foot.
I don't think I would just say "forgot it," I would say what I forgot to do. I did my homework last night, but I forgot to bring it to school (this morning). I did my homework and meant to bring it to school this morning, but I forgot to [bring it]. I did my homework, but I forgot it when I left the house (this morning). This kind of explanation is not necessary when what you forgot has ...
They visited a farm two weeks ago. Jenny and Peggy didn't help their brother. The children were not at home last weekend. When did you design this wonderful skirt? My mother didn't crash into the van. The boys took off the mudguards of their bicycles. Did you phone your aunt last week? He didn't drink milk at school.
Synonym for Did you finish your homework? @farriaran89 'Did you finish your homework' is referring to yesterday, a few days ago, or even this morning, if it is now afternoon or evening, example: Did you finish your homework this morning ? 'Have you finished your homework' is usually said in general, but always referring to the day in which you are asking the question.
A: Do you ever watch action movies? B: No, never. Well, I watched an action movie a few years ago, so I guess should say _____.
Yes, it is natural. When you say this sentence, you need to pause before saying... this morning. We do it to keep from confusing someone and to emphasize that I did it at that time. |You're welcome. |@u-1 Your sentence does not sound natural to me, and it's better to avoid repeating words like "morning" twice in a short sentence. To me, the natural and common sentence with the same ...
Early this morning, Israeli authorities informed my national security team that a mission they conducted in Gaza likely killed Hamas leader Yahya Sinwar. DNA tests have now confirmed that Sinwar ...