NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12

CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech
April 25, 2019 by Veerendra
CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English . Here we have given CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech.
1. There are two different ways in which we can report the words of a speaker : (a) Direct Speech or Direct Narration. (b) Indirect Speech or Indirect Narration.
2. (a) Direct Speech contains the actual words of the speaker ; as— Sarla said, “My father has a roaring business in Mumbai.” He said to me, “I am feeling unwell today.” In these sentences, actual words of the speaker are given within inverted commas without any change.
(b) Indirect Speech gives the substance of the speaker’s actual words and not the exact words spoken by him or her ; as— Sarla said that her father had a roaring business in Mumbai. He told me that he was feeling unwell that day.
3. The actual words of the speaker, given within ‘inverted commas’ are called the Reported Speech. In the same way, the Verb which introduces the Reported Speech is called the Reporting Verb. In the sentence above ‘said’ is the Reporting Verb and ‘My father has a roaring business in Mumbai’ is the Reported Speech. Reporting Verb and Reported Speech. Look at the following sentences : Radha says, “I shall finish my home-work today.” Sushma said to Pushpa, “Show me your dolls.” The verbs ‘says and said’ in the above sentences are ‘Reporting Verbs’. The exact words of the speaker given within the inverted commas are ‘Reported Speech’.
4. Here are some distinctive points regarding the Direct Speech and Indirect Speech : In the Direct Speech 1. The Reported Speech is put within Reported (Inverted) Commas. 2. The Reported Speech and the Reporting Verb are separated by a Comma. 3. The first word of the Reported Speech begins with a capital letter.
Transformation of Direct Speech into Indirect Speech
I. Rules for the Change of Tense
| Rule I. If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future Tense, the Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech does not change. |
Examples 1 Direct: Rajesh says, “She has brought lame to her family.” Indirect: Rajesh says that she has brought fame to her family. 2. Direct: ohit has said, “I cannot displease my friend.” Indirect: Rohit has said that he cannot displease his friend. 3. Direct: I shall say, “I went to Agra on Monday.” Indirect: I shall say that I went to Agra on Monday. 4. Direct: She will say, “I have sent him a present.” Indirect: She will say that she has sent him a present.
| Rule II. If the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the tense of the verb in the Reported Speech must be changed into the corresponding Past Tense. |
Examples 1. Direct: I said, “I am speaking the truth.” Indirect: I said that I was speaking the truth. 2. Direct : The teacher said, “Boys fail because they do not study regularly.” Indirect: The teacher said that boys failed because they did not study regularly.
Exception to Rule II (i) If there is a Universal Truth or Habitual fact in the Reported Speech, the Tense of the verb is never changed ; as— 1. Direct: He said, “Face is the index of mind.” Indirect: He said that face is the index of mind. 2. Direct: The teacher said. “The earth rotates round its axis.” Indirect: The teacher said that the earth rotates round its axis. 3. Direct: Horatius said, “Death comes sooner or later.” Indirect: Horatius said that death comes sooner or later.
(ii) The Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech does not change if the reported speech states a past historical fact ; as— 1. Direct: He said, “India became free on 15th August, 1947.” Indirect: He said that India became free on 15th August, 1947. 2. Direct: She said. “Her father lived at Lahore for ten years.” Indirect: She said that her father lived at Lahore for ten years.
(iii) If two such actions are given in the Reported Speech which take place at the same time, the Past Indefinite or Continuous Tense does not change. Direct: He said, “Mohan was singing a song while Gopal was playing on a flute.” Indirect: He said that Mohan was singing a song while Gopal was playing on a flute. Examples 1. Direct: She said, “I am a top-class singer.” Indirect: She said that she was a top-class singer. 2. Direct: We said, “He is writing a poem.” Indirect: We said that he was writing a poem. 3. Direct: He said, “It may rain tonight.” Indirect: He said that it might rain that night. 4. Direct: He said, “A devil ever remains a devil.” Indirect: He said that a devil ever remains a devil.
The future tense of the reported speech is changed as under : Future Indefinite—would/should Future Continuous—would/should be Future Perfect—would/should have Future Perfect Continuous—would/should have been
Examples 1. Direct: You said, “He is a very good athlete.” Indirect: You said that he was a very good athlete. 2. Direct: I said, “I have finished my work.” Indirect: I said that I had finished my work. 3. Direct: He said, “Her parents will pay a visit to Delhi.” Indirect: He said that her parents would pay a visit to Delhi.
Interrogative Sentences Conversion of Interrogative Sentences A From Direct Into Indirect
| 1. The Reporting Verb is changed, into ‘ask, enquire, inquire or demand etc. 2. No conjunction is used to introduce the Reported Speech if the question begins with (an interrogative) word ; such as—what, who, whose, which, when, where, why, how, whom etc. 3. If or whether is used to introduce the Reported Speech if the reported speech has no question word. 4. Change the questions into statements. Put full stop in place of mark of interrogation (?). |
Examples (a) Questions beginning with a Helping Verb 1. Direct: He said to her, “Shall I accompany you to Agra ?” Indirect: He asked her if he would (should) accompany her to Agra. 2. Direct: She said to him, “Had I been absenting myself from school for a month ?” Indirect: She asked him if she had been absenting herself from school for a month. 3. Direct: He said to us, “Has she been spinning since yesterday ?” Indirect: He asked us if she had been spinning since the previous day. 4. Direct: They said to you, “Shall we be going on picnic tomorrow ?” Indirect: They asked you if they would be going on picnic the next day. 5. Direct: I said to her, “Will you have ironed your clothes ?” Indirect: I asked her if she would have ironed her clothes.
(b) Sentences having ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ 1. Direct: “Are there any more files ?” He asked. “Yes, sir,” said the peon. Indirect: He asked the peon if there were any more files. The peon replied respectfully in affirmative. 2. Direct: The teacher said to Lila. “Did you break the window pane ?” “No, sir.” said Lila, “I did not.” Indirect: The teacher asked Lila if she had broken the window pane. Lila replied respect¬fully and refused it (to have done it). 3. Direct: “If you find my answers satisfactory, will you give me five rupees ?” said the astrologer. “No.” replied the customer. Indirect: The astrologer asked the customer whether he would give him five rupees if he found his answers satisfactory. The customer replied in negative. 4. Direct: I said to him. “Do you want to go to Chandigarh ?” He said, “No, sir.” Indirect: I asked him if he wanted to go to Chandigarh and respectfully he replied in negative. 5. Direct: He said to me, “Does Mohan still play ?” I said, “Yes, sir.” Indirect: He asked me if Mohan still played and I replied in positive.
(c) Questions beginning with Interrogative Words 1. Direct: He said to me. “Whom does she want to contact ?” Indirect: He asked me whom she wanted to contact. 2. Direct: They said to her, “Whose house are you purchasing ?” Indirect: They asked her whose house she was purchasing. 3. Direct: You said to him “Why are you making mischief ?” Indirect: You asked him why he was making mischief. 4. Direct: They said to us, “How have you solved this sum ?” Indirect: They asked us how we had solved that sum. 5. Direct: We said to them, “Who has misguided you ?” Indirect: We asked them who had misguided them.
(d) Questions beginning with modal auxiliaries 1. Direct: I said to him, “May Sunita come in to discuss with you something ?” Indirect: I asked him if Sunita might come in to discuss with him something. 2. Direct: The traveller said to me, “Can you tell me the way to the nearest inn ?” Indirect: The traveller asked me if I could tell him the way to the nearest inn. 3. Direct: He said to me. “Must I leave for Mumbai tomorrow ?” Indirect: He asked me if he had to leave for Mumbai the next day. 4. Direct: I said to her, “Could you give me your notes ?” Indirect: I asked her if she could give me her notes. 5. Direct: I said to him, “Need I go to him ?” Indirect: I asked him if I had to go to him.
Exercise 1 (Solved)
Convert the following sentences into Indirect Speech : 1. He said to her. “Do you want to go home ?” 2. He said to you. “Where are you going ?“ 3. I said to him, “What brings you here ?” 4. You said to us, “How do you solve this sum ?” 5. She said to me, “How are you getting on with your studies ?” 6. I said to my friend, “Have you been to England ?”
Convert the following sentences into Indirect Speech : 1. She said to me, “Who taught you English ?” 2. He said to his mother, “Why did you not wash my school dress ?” 3. The mother said to the child, “Did you have your breakfast ?” 4. Anil said to his sister, “How did you fare in the interview ?” 5. The policeman asked me, “Had the thief stolen your watch ?” Answers: I. 1. He asked her if she wanted to go home. 2. He asked you where you were going. 3. I asked him what brought him there. 4. You asked us how we solved that sum. 5. She asked me how I was getting on with my studies. 6. I asked my friend if he had been to England.
II. 1. She asked me who had taught me English. 2. He asked his mother why tehe had not washed his school dress. 3. The mother asked the child if he had his breakfast. 4. Anil asked his sister how she had fared in the interview. 5. The policeman asked me if the thief had stolen my watch.
Exercise 2 (Solved)
Change the following into indirect speech : 1. He said to me, “I have often told you not to play with me.” 2. They wrote, “It is time we thought about settling this matter.” 3. The teacher promised. “If you come to school tomorrow, I will explain it.” 4. “What do you want ?” he said to her. 5. He said, “How’s your father ?” 6. “Don’t you know the way home ?” asked I. 7. “Do you really come from China ?” said the prince. 8. “Sit down, boys,” said the teacher. 9. “Run away, children,” said the mother. Answers: 1. He told me that he had often told me not to play with him. 2. They wrote that it was time they thought about settling the matter. 3. The teacher promised to me that he would explain it if I went to school the following day. 4. He asked her what she wanted. 5. He enquired about my father. 6. I asked if he did not know the way home. 7. The Prince asked him if he really came from China. 8. The teacher asked the boys to sit down. 9. The mother asked the children to run away.
Exercise 3 (Solved)
The following passage has not been edited. There is an error in each line. Write the error along with the correction. Do not forget to underline the error. Her mother said that you must go straight to (a) your grandmother. There was a wolf (b) _______ in the wood through which she are (c) _______ going. But if she keep the road, he (d) _______ will not do any harm. The mother (e) _______ asked her to do as she tells her. (f) _______ Answers: (a) you—she (b) your—her (c) are—was (d) keep—kept (e) will—would (f) tells—had told
Exercise 4 (For Practice)
Police told Maninder that he is entitled (a) _______ to have a solicitor present. He denies (b) _______ that he knows anyone by the name of (c) _______ Surinder. Maninder confirmed that he has been (d) _______ in the vicinity of the factory last Monday. (e) _______ However, he said that he is visiting his mother. (f) _______ He maintains that he is innocent. (g) _______
Exercise 5 (For Practice)
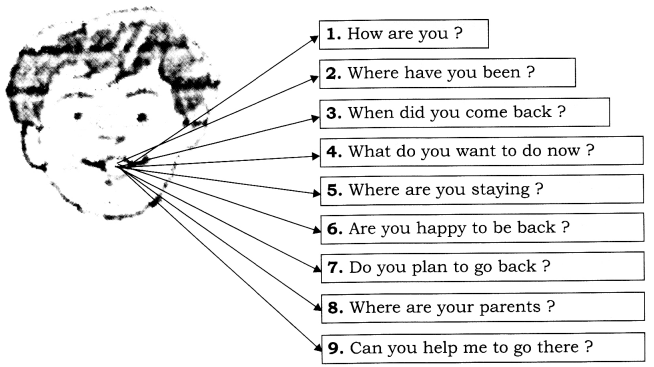
Exercise 6 (For Practice)
Each of the pair of sentences given below is a dialogue between a man and a woman. Change each pair into one simple sentence. Complete the answers. The first one has been done as an example. Question 1. “Shall we get married ?” “Yes, let us.” Answer: They decided to get married.
Question 2. “Please help me”. “O.K.” Answer: She agreed
Question 3. “May I help you ?” “No, thanks.” Answer: He offered
Question 4. “Let’s meet after the class.” “O.K. fine.” Answer: They arranged
Question 5. “What’s your name ?” “I won’t tell you”. Answer: She refused
Question 6. “I have stood first.” “Congratulations”. Answer: She congratulated
Multiple Choice Questions Exercise 1
Read the dialogues given below and then complete the report by choosing the correct options from the ones given below the dialogue : 1. Judge: Why don’t you speak the truth ? Witness: I have spoken only the truth. Judge: Were you really present at the scene ? Witness: Yes, sir.
The judge asked the witness (a) ……… the truth. The witness replied that (b) ……….. only the truth. At this the judge asked (c) ………….. at the scene. The witness replied in positive. (a) (i)why don’t you speak (ii) why didn’t he speak (iii) why you didn’t speak (iv) why he did not speak
(b) (i) he had spoken (ii) I have spoken (iii) I had spoken (iv) he has spoken
(c) (i) if you are really present (ii) that you were really present (iii) if he was really present (iv) that he was really present
2. Mother: What is the matter ? Son: Grandfather has shot a policeman. Mother: Why ? Son: He was a deserter. Mother asked the son (a) ………… The son replied (b) …………. a policeman. The mother demanded (c) ………… To this the son replied that he was a deserter. (a) (i) that what is the matter (ii) what is the matter (iii) what the matter was (iv) if what was the matter
(b) (i) that the grandfather has shot (ii) that Grandfather had shot (iii) if grandfather had shot (iv) why Grandfather had shot
(c) (i) why (ii) why Grandfather has shot (iii) that why grandfather had shot (iv) why Grandfather had shot
3. Merchant: How much have you collected ? Accountant: Twenty thousand in cash and the balance on paper. Merchant: Where have you deposited the cash ? The Merchant asked the accountant (a) …………. collected. The accountant replied (b) …………. and the balance on paper. Then the merchant wanted to know (c) …………. . (a) (i) how much you have (ii) how much have you (iii) how much had he (iv) how much he had
(b)(i) that I have collected twenty thousand in cash (ii) that he has collected twenty thousand in cash (iii) that he had collected twenty thousand in cash (iv) he had collected twenty thousand in cash
(c)(i) where have you deposited the cash (ii) where he had deposited the cash (iii) where had he deposited the cash (iv) where the cash had been deposited
4. Son: How are you feeling now? Father: Much better, son. Son: Are you taking the medicines regularly? Father: Yes, my dear. The son asked his father (a) …………. then. The father replied that (b) …………. much better. The son further asked (c) …………. the medicines regularly. The father replied in affirmative. (a) (i) that how he was feeling (ii) how he was feeling (iii) how you are feeling (iv) how was he feeling
(b) (i) I am feeling (ii) I was feeling (iii) he is feeling (iv) he was feeling
(c) (i) if you are taking (ii) if he is taking (iii) that he was taking (iv) if he was taking
5. Ram: Do you shave every day? Mohan: Yes. Don’t you? Ram: No. I shave only once a week Ram asked Mohan (a) …………. everyday. Mohan replied in positive and asked (b) …………. the same. Ram agreed that he didn’t and said (c) …………. only once a week. (a) (i) do you shave (ii) did he shave (iii) if he shaved (iv) that if he shaved
(b) (i) don’t you (ii) you don’t (iii) if you don’t (iv) if he didn’t
(c) (i) I shave (ii) that he shaved (iii) if he shaved (iv) if I shaved
6. Sue: What is it dear? Johnsy: The leaves. Sue: Are you counting the leaves? Johnsy: Yes. Sue asked Johnsy (a) …………. Johnsy replied that (b) …………. Sue further asked (c) …………. the leaves. Johnsy replied in positive. (a) (i) what it is (ii) what is it (iii) what is was (iv) what was it
(b) (i) that it was the leaves (ii) it is leaves (iii) that it are leaves (iv) that it had leaves
(c) (i) are you counting (ii) that she was counting (iii) was she counting (iv) if she was counting Answers: 1. (a) (iv) why he did not speak (b) (i) he had spoken (c)(iii) if he was really present 2. (a) (iii) what the matter was (b)(ii) that Grandfather had shot (c) (iv) why Grandfather had shot 3. (a) (iv) how much he had (b) (iii) that he had collected twenty thousand in cash (c) (ii) where he had deposited the cash 4. (a) (ii) how he was feeling (b) (iv) he was feeling (c) (iv) if he was taking 5. (a) (iii) if he shaved (b) (iv) if he didn’t (c) (ii) that he shaved 6. (a) (iii) what is was (b)(i) that it was the leaves (c) (iv) if she was counting
We hope the CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect) Exercise with Answer
Reported Speech – Reported speech refers to recording the speaker’s speech, whether it is done directly by recording the speaker’s words or indirectly by recording the speaker’s words but changing them.

For example Shyam said, “Taj Mahal was built by Shahjahan.” Shyam said is the reporting verb. “Taj Mahal was built by Shahjahan.” is the reported speech.

Direct Speech
It refers to reporting the exact words spoken by the speaker. There is no change in the verb or the sentence.
Rules of Direct Speech
- Speech should be opened with quotations or inverted commas.
- The word said is used to connect two sentences.
- Reporting clause should be used at the end of the sentence.
- At the end of the sentence full stop should be placed.
Let us look at some examples
- Neha said, “Roger Federer has won the match against Rafael Nadal.”
- Shivani says, “I am having my lunch.”
Indirect Speech
It is the speech that tells what someone has said but it does not explain the actual words spoken by the person. It just conveys the basic narration of what is being said to the third person.
Rules of Indirect Speech
- Past tense is used when the situation is uncertain.
- The present tense of the sentence is changed to the past tense in indirect speech.
- Universal facts tense remains the same.
- The use of the word “that” connects the reported verb and reported speech.
- Gargi said that she enjoyed watching the movie Avatar.
- Shiva says that he is eating an apple.
Changing direct speech into reported speech
Change of Pronouns

Change in Tenses

Change of Adverbs of Place and Adverbs of Time

Change of Modal Verbs
Let us look at some examples using comic strips-

Exercise on Reported Speech (Practice Questions)
Convert the following sentences into reported speech.
- Mohini said to her mother, “The ladies have been making pickles for 10 years.”
- The teacher said to us, “Water boils at 100°C.”
- Mr Gupta said, “All the flights are delayed due to heavy rains.”
- Radhika asked me, “When are you leaving?”
- She said, “He likes Mughlai food.”
- He said, “Her dress is ready.”
- Dronacharya said to Arjun, “Shoot the fish’s eye.”
- He said to her, “You are an understanding person.”
- The teacher said to Shelly, “Why are you laughing?”
- Rashi told him, “Your bag is new.”
- Meera said, “I’m reading a comic.”
- The old man said to the sailor, “The sea will be rough according to the weather forecast.”
- My father said to me, “Please wait here till I return.”
- Rita told her, “Your friend likes you.”
- “Call the ambulance,” said the woman.
- The chef said to the helper, “Chop the vegetables quickly.”
- Robert said to me, “I shall do my homework.”
- The student said to the librarian, “Please allow me to go to the library.”
- Grandma said to Kishore, “Avoid drinking chilled water as it will further harm your sore throat.”
- He said to her, “Go there.”
- Mohini told her mother that the ladies had been making pickle for 10 years.
- The teacher told us that water boils at 100°C.
- Mr Gupta said that all the flights were delayed due to heavy rains.
- Radhika asked me when I was leaving.
- She said that he liked Mughlai food.
- He said that her dress was ready.
- Dronacharya ordered Arjun to shoot the fish’s eye.
- He told her that she was an understanding person.
- The teacher asked Shelly why she was laughing.
- Rashi told him that his bag was new.
- Mera said that she was reading a comic.
- The old man informed the sailor that the sea would be rough according to the weather forecast.
- My father requested me to wait there till he returned.
- Rita told her that her friend liked her.
- The woman urged to call the ambulance.
- The chef ordered the helper to chop the vegetables quickly.
- Robert said to me that he would do his homework.
- The student requested the librarian to allow him to go to the library.
- Grandma advised Kishore to avoid drinking chilled water as it would further harm his sore throat.
- He ordered her to go there.
Convert the dialogue in the comic strip into indirect speech-

Answers –

B Convert the following paragraph into reported speech.
- Mother said to Rahul, ”Drive slow”. He replied, “I always drive slow.” Handing over a packed lunch she said, “Keep me updated about your whereabouts.” Raghav hugged her goodbye and took off for Manali.
Ans. Mother said to Rahul to drive slow. He replied that he always drives slow. Mother gave him a packed lunch and asked him to keep her updated about his whereabouts. Raghav hugged her goodbye and took off for Manali.
- “Do you want to know something cool?” Preeti asked Rama. Rama said, “Why not.” Preeti said, “Did you know “strengths” is the longest word in the English language with one vowel?” Rama seemed surprised. Preeti said, “According to the Guinness Book of World Records, “strengths” is the longest word in the English language with one vowel. The word contains nine letters, eight of them being consonants.”
Ans Preeti asked Rama if she wanted to know something cool. Rama replied that why not. Preeti asked her whether she knew that “strengths” is the longest word in the English language with one vowel. Rama seemed surprised. Preeti said that according to the Guinness Book of World Records, “strengths” is the longest word in the English language with one vowel. The word contains nine letters, eight of them being consonants.
- She said, “You should eat your vegetables.” Raghav replied, “I don’t like brinjal, I want to have fries.” His mother said, “If you’ll have your vegetables throughout the week, then I will treat you with fries on the weekend.”
Ans She said to Raghav that he should eat his vegetables. Raghav replied that he did not like brinjal, he wanted to have fries. His mother told him that if he’d have his vegetables throughout the week then she would treat him with fries on the weekend.
- Robert asked Paul, “Are you a potterhead?” Paul excitedly replied, “Yes, a big one!” Robert asked, “Did you know actor Daniel Radcliffe went through nearly 70 wands and 160 pairs of glasses during the making of the Harry Potter films?” Paul was amazed to know this.
Ans Robert asked Paul whether he was a potterhead. Paul excitedly replied that he was a big one. Robert asked whether he knew that actor Daniel Radcliffe went through nearly 70 wands and 160 pairs of glasses during the making of the Harry Potter films. Paul was amazed to know this.
- Vinay said, “Good afternoon, sir! May I come in?” His boss replied, “Yes Vinay, please come in.” Vinay said, “Actually, I wanted to speak to you about something, so do let me know when you are free!” his boss said, ”Yes, Vinay please have a seat. What do you have to say, please do tell me!”
Ans Vinay wished good afternoon to his boss and asked whether he could come in. His boss said yes and requested him to go in. Vinay said that he actually wanted to speak to him about something so could he please let him know when he was free. His boss replied yes and asked him to have a seat and to tell him what he had to say.
- Tenses for class 8 Students| Types of Tenses with Examples
- Determiners for Class 8 Rules, Exercises
- Modals for Class 8 use, examples, exercises
- Class 8 Subject Verb Agreement, Examples, Exercise
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Birthday Wishes in Hindi
- Anniversary Wishes in Hindi
- Father’s Day Quotes and Messages
- Father’s Day quotes in Hindi
- International Yoga Day Slogans, Quotes and Sayings
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय योग दिवस Slogans, Quotes and Sayings
- Good Morning Messages in Hindi
- Good Night Messages in Hindi | शुभ रात्रि संदेश
- Wedding Wishes in Hindi
English Writing Skills
English Grammar Examples
All English Grammar Topics, Exercises, examples, MCQ Tests
Analytical Paragraph Writing | Format, Examples, Samples
Report Writing Format | How to Report Writing Examples, Topics, Samples and Types
Letter to Editor Class 10 to 12, Topics, Sample and Example
Informal Letter Format, Topics, Examples
Article Writing Format, Topics and Examples
Classified advertisement writing examples
Letter to the Principal, Format, Samples
Story Writing , Format, Topics, Examples
Job Application with Biodata, Format, Topics, Examples
Leave Application Format for Office, School and Sample
Leave Application for Marriage, Format, Sample, and Examples
Speech Writing format, examples for Class 11, 12
Invitation writing tips for class 12
Report writing tips for class 12
10 Important Things to DO to score more in Debate writing question
Let us revise Reported Speech in 9 Quick Steps
Job Application Writing Tips for Class 12 English
Tips to ace the question on Analytical Paragraph writing in Class 10
English Grammar
Active and Passive Voice Definition, Rules, Exercise, and Example Sentences
Countable and Uncountable Nouns Meaning, Definition, Difference and Examples
Direct and Indirect Speech, Format, Rules, Exercise, and Examples
Determiners Definition, Types, Exercise and Examples
All About Tenses | Tenses Examples, Types of Tenses in English Grammar
English Vocabulary for Bank PO Exams – Synonyms MCQ Videos
Noun Definition, Types, Exercise with Examples in Hindi and English
What is a Verb? Definition, Types of Verbs, Exercise and Verbs Examples in Hindi and English
What is a Preposition? Definition, Types, Exercise, and Examples in Hindi and English
Subject Verb Agreement Rules and Examples
Modals Definition | Modals Exercise, List of Modals with Examples
Master Tenses in English Grammar – The Easy Way
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
| Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said) |
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
| I | He, she |
| Me | Him, her |
| We | They |
| Us | Them |
| You | He, she, they |
| You | Him, her, them |
| My | His, her |
| Mine | His, hers |
| Our | Their |
| Ours | Theirs |
| Your | His, her, their |
| Yours | His, hers, theirs |
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Now | Then |
| Today | That day |
| Tomorrow | The next day / The following day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tonight | That night |
| Last week | The week before |
| Next week | The week after |
| Last month | The previous month |
| Next month | The following month |
| Last year | The previous year |
| Next year | The following year |
| Ago | Before |
| Thus | So |
| Simple Present Example: Preethi said, “I cook pasta.” | Simple Past Example: Preethi said that she cooked pasta. |
| Present Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I am cooking pasta.” | Past Continuous Example: Preethi said that she was cooking pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Present Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I have been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Simple Past Example: Preethi said, “I cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I was cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Past Perfect Example: Preethi said, “I had cooked pasta.” | Past Perfect (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had cooked pasta. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Example: Preethi said, “I had been cooking pasta.” | Past Perfect Continuous (No change) Example: Preethi said that she had been cooking pasta. |
| Will | Would |
| May | Might |
| Can | Could |
| Shall | Should |
| Has/Have | Had |
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Learn Insta
RD Sharma Solutions , RS Aggarwal Solutions and NCERT Solutions
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8 CBSE With Answers
July 29, 2021 by Prasanna

When we want to tell somebody else what another person said, we can use either direct speech and reported speech.
When we use direct speech, we use the same words but use quotation marks, For example: Scott said, “I am coming to work. I will be late because there is a lot of traffic now.”
When we use reported speech, we usually change the verbs, specific times, and pronouns. For example: Scott said that he was coming to work. He said that he would be late because there was a lot of traffic at that time.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8 CBSE With Answers Pdf
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English will help you to write better answers in your Class 10 exams. Because the Solutions are solved by subject matter experts.
Fundamentals: The art of reporting the words of a speaker is called Narration. It is of two types:-
- Direct Speech: We quote the actual words of the speaker in inverted commas: He said to me, “I am playing.”
- Indirect Speech: We quote the words or speech of the speaker in our own words, without inverted commas: He told me that he was playing.
In narration a sentence has two parts:-
- Reporting verb: He said to me,
- Reported speech: “I am playing.”
Rules of Changing Pronouns
- The pronoun of First Person is changed according to the subject of Reported speech.
- The pronoun of Second Person is changed according to Object
- The pronoun of Third Person is not changed at all. (The formula to change pronoun is 123/SON.) SON: S – subject, O – object, N – no change
Persons: There are three types of persons:-
- First Person (I, we, my, me, our)
- Second Person (You, your)
- Third Person (He, she, it, his, they, them etc.)
Part-I (Assertive Sentences in Present or Future)
Rules 1. If Reporting Verb is in Present or Future Tense the tense of Reported speech is not changed. 2. (” “) inverted commas are replaced with the conjunction ‘that’. 3. Say to is replaced with tell, says to with tells and said to with told.
- The boys say, “We have learnt the lesson”. The boys say that they have learnt the lesson.
- Reena will say, “I am going to America”. Reena will say that she is going to America.
- The servant says to me, “The manager will come in the evening”. The servant tells me that the manager will come in the evening.
- He has said to them, “You were playing cricket yesterday.” He has told them that they were playing cricket yesterday.
Part-II (Assertive Sentences in Past)
Rules:- 1. ‘said to’ is changed into ‘told’. 2. Use conjunction ‘that’ to connect 3. If Reporting Verb is in Past Tense the tense of the Reported Speech is changed according to the rules given below: –
- Present Indefinite changes to Past Indefinite
- Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous
- Present Perfect changes to Past Perfect
- Present Perfect.Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Indefinite changes to Past Perfect
- Past Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous
- Will/Shall changes to Would/Should
- Can changes to Could
- May changes to Might
In Reported Speech words showing nearness changes into words showing distance:-
- This becomes That
- These becomes Those
- Now becomes Then
- Today becomes That day
- Tonight becomes That night
- Yesterday becomes The previous day
- Last night becomes The previous night
- The next day becomes The following day
- Here becomes There
- Ago becomes Before
- He said, “I am going to college today.” He said that he was going to college that day.
- Sunny said to me, “You will get good marks in this test.” Sunny told me that I would get good marks in that test.
- She said to her mother, “My teacher awarded me yesterday.” She told her mother that her teacher had awarded her the previous day.
- Rajani said to her friends, “You were shopping in the market.” Rajani told her friends that they had been shopping in the market.
- I said, “Ritu, you will learn very fast.” I told Ritu that she would learn very fast.
- “I may go to London next month,” he said. He told that he might go to London the following month.
Note: If Reported Speech has an explanation of Universal Truth, Habitual Fact or Historical Fact its Tense is not changed at all. Examples:-
- He said, “The earth moves round the sun.” He.said that the earth moves round the sun.
- She said to me, “Mohan plays with left hand.” She told me that Mohan plays with left hand.
- The teacher said to the students, “India became independent in 1947.” The teacher told the students that India became independent in 1947.
Part-III (Interrogative Sentences) Rules: 1. In Interrogative sentences said or said to of reporting verb are replaced with asked or enquired. 2. If the interrogative (question) begins with Helping Verb or Modal (is, am, are, do, does, was, were, has, have, had, will, shall, would, can, could, should, may, might, must, etc.) the inverted commas (” “) are replaced with the conjunction if or whether. 3. If the interrogative (question) begins with WH-family (Why, what, which, when, whose, who, whom, how, etc.) the inverted commas (” “) are not replaced with any conjunction at all. 4. If there are no interrogatives (questions) in indirect speech we place helping verb or modal after the subject.
- The teacher said to us, “Have you completed your home work?” The teacher asked us if we had completed our home work.
- He said to me, “Did you finish your work yesterday?” He asked me if I had finished my work the previous day.
- Rocky said, “Meena, do you want to go to Shimla?” Rocky asked Meena if she wanted to go to Shimla.
- I said to him, “Will you return tomorrow?” I asked him if he would return the next day.
- Ravi said to him, “What have you learnt?” Ravi asked him what he had learnt.
- She said, “Which train will go to Jaipur?” She enquired which train would go to Jaipur.
Interrogative Sentences in present or future:
- She says to them, “Have you taken the money?” She asks them if they have taken the money.
- He will say to me, “What can I do for you?” He will ask me what he can do for me.
Part-IV (Imperative Sentences) Rules: 1. In Imperative sentences said to is replaced with ordered, commanded, advised, suggested, proposed, persuaded, warned, etc. 2. Inverted commas (” “) are replaced with ‘to’. The first form of verb is applied after ‘to’. 3. In Negative sentences ‘said’ to is replaced with ‘forbade’ or ‘do’ is replaced with ‘not’.
- She said to me, “Work hard”. She advised me to work hard.
- I said to my friend, “Please give me your car for two hours.” I requested my friend to give me his car for two hours.
- She said to Meena, “Do not make a noise”. She forbade Meena to make a noise. (or She ordered Meena not to make a noise.)
- The general said to the soldiers, “March forward.” The general commanded the soldiers to march forward.
- Ramesh said to him, “Let me do my home work.” Ramesh requested him to let him do his home work.
- The manager said to the peon, “Let the visitors come in.” The manager ordered the peon to let the visitors come in.
- He said to me, “Let us go on picnic this Sunday”. He proposed/suggested me that we should go on a picnic that Sunday. (or He proposed me to go on a picnic that Sunday.
- He said, “Thank you, doctor.” He thanked the doctor.
- Dinkar said to me, “Beware of such politicians.” Dinkar warned me against such politicians.
PART-V (Exclamatory Sentences)
Rules: 1. Use conjunction ‘that’ to connect the speech with reporting verb. 2. Change tenses according to the rules learnt in PART-II. 3. ‘Said’ is mostly changed into ‘exclaimed’ (sometimes ‘applauded saying’) 4. Replace ‘what’ or ‘how’ with ‘very’ (sometimes ‘big’ or ‘great’). 5. Replace exclamatory words as follows: AH!, Alas!…. with sorrow; Aha!, Ha!, Hurrah! ….with joy; Oh with surprise; Pooh! ….with contempt; Sorry! with regret, Bravo! with applauded saying.
- The child said, “What a bitter medicine!” The child exclaimed that the medicine was very bitter.
- He said, “How big the train is!” He exclaimed that the train was very big.
- Vikas said, “Alas! I have lost my wallet.” Vikas exclaimed with sorrow that he had lost his wallet.
- Rajani said to her friend, “Pooh! You have cheated me.” Rajani exclaimed with contempt that her friend had cheated her.
- The captain said to the players, “Bravo! You played well today.” The captain applauded his players saying that they had played well that day.
PART-VI (Optative Sentences)
Rules: 1. Such sentences indicate greeting & wishes (good morning, good noon, good day, would that, etc.), and prayer (may, may God). Therefore ‘said’ is mostly replaced with ‘wished’ or ‘prayed’. 2. In case of good bye, farewell, good night (when parting company) ‘said’ is replaced with ‘bade’. Examples:-
- He said, “Good morning uncle!” He wished his uncle good morning.
- Ranjita said, “Good bye friends!” Ranjita bade her friends good bye.
- My grandmother said to me, “May you live long.” My grandmother prayed me that I might live long.
- Montu said, “Would that I were a minister!” Montu wished that he had been a minister.
Indirect Speech of two or more sentences:
- She said to me, “I am going to the market. Do you want to go?” She told me that she was going to the market and asked if I wanted to go.
- The manager said to the clerk, “You may leave now. Don’t forget to keep these files in the file cabinet.” The manager told the clerk that he might leave then and ordered not to forget to keep those files in the file cabinet.
- The doctor said to the patient, “Why didn’t you come yesterday. You have a high fever.” The doctor asked the patient why he hadn’t come the previous day as he had a high fever was high.
- I said to Rocky, “Don’t abuse others. It is a bad habit. How will you feel if others abuse you?” I advised Rocky not to abuse others because it is a bad habit and asked how he would feel if others abused him.
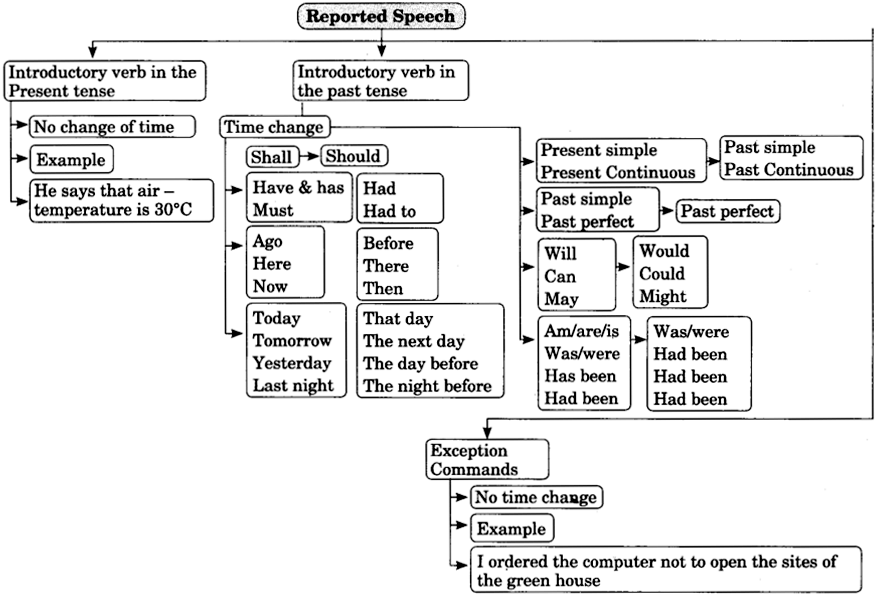
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 8 CBSE
Question 1. Fill in the blanks (i) She looks pretty sick. I think she _____________ go to a doctor. (a) should (b) can Answer: (a) should
(ii) You’ve been driving all day. You _____________ be exhausted! (a) should (b) must Answer: (b) must
(iii) You _____________ smoke so much. It’s bad for your health. (a) can’t (b) shouldn’t Answer: (b) shouldn’t
(iv) Hey I’m lost _____________ you help me? (a) can (b) should Answer: (a) can
(v) You have such a beautiful voice. You _____________ sing for us! (a) should (b) can Answer: (a) should
(vi) I know he speaks five languages, but _____________ he speak Arabic? (a) should (b) can Answer: (b) can
(vii) That looks very expensive. It _____________ have cost a fortune! (a) should (b) must Answer: (b) must
(viii) I _____________ believe that you failed your test! (a) can’t (b) shouldn’t Answer: (a) can’t
(ix) I’m on my way. I _____________ be there in about 10 minutes. (a) should (b) can Answer: (a) should
(x) I _____________ afford that. (a) can’t (b) shouldn’t Answer: (a) can’t
Question 2. Complete the sentences. (i) Jacob: “I work in an office.” Jacob told me (that) _____________ worked in an office.
(ii) Ryan and Lucas: “We play football.” Ryan and Lucas told me (that) _____________ played football.
(iii) Victoria: “I like my cat.” Victoria told me (that) _____________ liked _____________ cat.
(iv) Henry: “Can you see me?” Henry asked me if _____________ could see
(v) Julian: “I will have to borrow your pencil.” Julian told me (that) _____________ would have to borrow
(vi) Melanie: “My father is Jamaican.” Melanie told me (that) _____________ father is Jamaican.
(vii) Emma and Doris: “Can we use your camera?” Emma and Doris asked me if _____________ could use _____________ camera.
(viii) Leah: “How is your journey?” Leah’ asked me how _____________ journey was.
(ix) Isabella and Ella: “We love our pets.” Isabella and Ella told me (that) _____________ loved _____________ pencil.
(x) Grandmother: “Please bring me a cup of my tea.” Grandmother told me to bring _____________ a cup of _____________ tea. Answer: (i) he (ii) they (iii) she, her (iv) I, him (v) he, my (vi) her (vii) they, my (viii) my (ix) they, their (x) her, her.
Question 3. Change the direct speech into reported speech. Choose the past simple of ‘ask’, ‘say’, or ‘tell: (i) “Don’t do it!” She _____________
(ii) “I’m leaving tomorrow” She _____________
(iii) “Please get me a cup of tea” She _____________
(iv) “She got married last year” She _____________
(v) “Be quick!” She _____________
(vi) “Could you explain number four, please?” She _____________
(vii) “Where do you live?” She _____________
(viii) “We went to the cinema and then to a Chinese restaurant” She _____________
(ix) “I’ll come and help you at twelve” She _____________
(x) “What are you doing tomorrow?” She _____________ Answer: When I used ‘said’ you can also use ‘told me’) (i) She told me to do it. (ii) She said (that) she was learning tomorrow. (the next day). (iii) She asked me to get her a cup of tea. (iv) She said (that) she got married last year. (v) She told me to be quick. (vi) She asked me to explain number four. (vii) She asked me where I lived. (viii) She said (that) they went (had been) to the cinema and then to a Chinese restaurant. (ix) She said (that) she would come and help me at twelve. (x) she asked me what I was doing tomorrow (the day after).
Reported Speech Practice Examples Exercises for Class 8 CBSE
Question 1. Change the direct speech into reported speech. Choose the past simple of ‘ask’, ‘say, or “tell: (i) “Don’t go!”. She _____________
(ii) “Do you work in London?” She _____________
(iii) “Could you tell me where the post office is?” She _____________
(iv) “Come here!” She _____________
(v) “I’ve never been to Wales” She _____________
(vi) “Have you ever seen ‘Lord of the Rings?” She _____________
(vii) “I don’t like mushroom” She _____________
(viii) “Don’t be silly!” She _____________
(ix) “Would you mind waiting a moment please?” She _____________
(x) “How often do you play sport?” She _____________
Question 2. Write here, that day, the day before, the next day, the week before, according to the sentences.
1. Anita (a week ago): “Tanya and I are going to a concert tomorrow.” You (today): Anita said she and Tanya were going to a concert ________ 2. Jyoti (two days ago): “I’ve only been in England since yesterday.” You (today): Jyoti said he had only been in England since ________ 3. Nitin (a week ago): “I’m meeting my friend at the airport later today.” You (today): Nitin said he was meeting his friend at the airport later ________ 4. Mohan (in the street): “I’ll see you at the coffee bar.” You (at the coffee bar): Mohan said he would see me ________ 5. Pawan (a month ago): “The festival was in the last week.” You (today): Pawan told me the festival had been ________
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8 CBSE With Answers
Reported speech is when we express or say things that have already been said by somebody else.
Looking for an easy way to Learning of new elementary english grammar and composition for class 8 answers, Solutions. You have to learn basic English Grammar topics like Tenses Verbs, Nouns, etc… In this article, we will review the best English Grammer Topics and compare them against each other.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8 CBSE With Answers Pdf
When we say things that have been said, we use two ways of expressing it. The first is direct speech when we express what the speaker said as it is and the second is indirect speech where we express what was said in our words.
How do we use reported speech?
| “I know quite a lot of people here.’ Robert said. | Present Simple | Simple Past | He said that he knew quite a lot of people there |
| ‘John is feeling much better ‘Paul said. | Present continuous | Past Continuous | He said that John was feeling much better. |
| ‘I enjoyed my holiday in the States’ David said. | Simple Past | Past Perfect | He said that he had enjoyed his holiday in the States. |
| ‘Jackie wasn’t feeling very well’ The teacher said. | Past Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | He said that Jackie had been feeling very well. |
| ‘They’ve seen the Eiffel Tower’ john Said | Present Perfect | Past Perfect | He said that they had seen the Eiffel Tower. |
| ‘I have been waiting for ages ‘My father said. | Present Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | He said that he had been waiting for ages. |
| ‘Nobody had warned them about the storm’ He said. | Present Perfect | Past Perfect | He said that had warned about the storm. |
| ‘She had been reading all ‘Brenda said. | Past Perfect Continuous | Past Perfect Continuous | She said that she had been reading all day. |
Reporting Questions We use a special form when we report questions:
WH – Questions : Where is + Tom’s house? He asked where Tom’s house + was. Where does Tom live? He asked where Tom lived,
Yes/No Questions: Does Tom live in Miami? She asked if Tom lived in Miami. Is Tom happy? She asked if Tom was happy.
Say vs. Tell Say something June : “I love English.” June said (that) she loved English.
Tell someone something June: “I love English.” June told me (that) she loved English.
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech Must, might, could, would, should, and ought to stay the same in reported speech. We usually change may to might.
| They said, “we would apply for a visa” He said “I would start a business. She said, “I would appear in exam” | They said that they would apply for visa. He said that he would start a business. She said that she would appear in the exam. |
| She said, “she could play the piano” They said, “we couldn’t learn the lesson” He said, “I could run faster | She said that she could play a violin. They said they couldn’t learn the lesson. He said that he could run faster. |
| He said, “guest might come” She said, “it might rain” John said, “I might meet him” | He said that guest might come. She said that it might rain. John said that he might meet him. |
| He said, “I should avail the opportunity,” She said, “I should help a him” They said, “we said take the exam” | He said that he should avail the opportunity. She said that she should help him. They said that they should take the exam. |
| He said to me, “you ought to wait for him” She said, “I ought to learn method of study” They said, we ought to attend our classes” | He said to me that I ought to wait for him. She said that she ought to learn method of study. They said that they ought to attend their classes. |
Reported Requests There’s more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)?
For example:
- Direct speech: close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
All of these requests mean the same thing, so we don’t need to report every word when we tell another person about it. We simply use ‘ask me + to + infinitive’:
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Here are a few more examples:
| Direct Request | Reported Request |
| Please help me. | She asked me to help her. |
Reported Orders And finally, how about if someone doesn’t ask so politely? We can call this an ‘order’ in English, when someone tells you very directly to do something.
- Direct speech: Sit down! In fact, we make this into reported speech in the same way as a request. We just use ‘tell’ instead of ‘ask’:
| Go to bed! | He told the child to go to bed. |
| Don’t worry! | He told her not to worry. |
| Be on time! | He told me to be on time. |
| Don’t smoke! | He told us not to smoke. |
Changes in words showing proximity (time and place) Study the list given below to revise the changes in words showing the proximity of place and time when converting direct speech to indirect speech.
this becomes that these become those here becomes there now becomes then before becomes earlier/previously today becomes that day tomorrow becomes the next day yesterday becomes the previous day
Reported Speech Practice Exercises for Class 8 CBSE
A. Write the following sentences in indirect speech. The first one has been done for you.
1. He said, “I will meet you outside the post office at three tomorrow afternoon.” He said that he would meet me outside the post office at there the following afternoon .
2. The teacher told us, “The freezing point of water is 0°c.” _______________________________________ 3. “When I dropped the jug, it smashed to pieces,” my little brother says. _______________________________________ 4. The man said, “I have seen you somewhere before.” _______________________________________ 5. The mechanic said, “Your car was ready last night, but you did not come to get it.” _______________________________________ 7. He said, “I shall return your magazines tomorrow.” _______________________________________ 8. “My car broke down, and I had to walk two kilometers to get to a phone-booth,” the man said. _______________________________________ 9. “An English play is being held in the school hall now,” she told us. _______________________________________ 10. “The building burnt down many years before we moved here,” my father told me. _______________________________________
B. Write the following sentences into indirect speech.
1. “Don’t leave your bag out here, Tommy,” Kiren said. _______________________________________ 2. “Stand at attention!” the captain commanded his men. _______________________________________ 3. “Don’t touch it! Leave it alone!” I said _______________________________________ 4. “Please take me to the park, Father,” the little boy said. _______________________________________ 5. “Please tell me exactly what happened,” she said. _______________________________________ 6. “Speak up. I can’t hear you,” he said to the new boy. _______________________________________ 7. “Don’t shake the table while I am writing!” Pawan told his brother. _______________________________________ 8. “Please bring your own plates and spoons,” she told us. _______________________________________ 9. “Return to the ship immediately!” the officer ordered his men. _______________________________________ 10. “Open that drawer and bring me the scissors,” Deepak told his brother. _______________________________________
C. Write the following sentences in indirect speech.
1. “The Prince and Princess lived happily ever after,” the storyteller told the children. _______________________________________ 2. “Don’t push!” the conductor said to the passengers who were boarding the bus. _______________________________________ 3. “I’m sorry but I can’t join you for lunch,” he told his friend. _______________________________________ 4. “Do the exercises from pages sixty to sixty-two,” Miss Malhotra told the pupils. _______________________________________ 5. “Do you know how to operate a computer?” asked the personnel officer. _______________________________________ 6. “Help! Help! Help!” I heard someone shout. _______________________________________ 7. “Are you mad at me?” asked the elder sister. _______________________________________ 8. The cheerleaders shouted, “Hurray! Fight them! Show them all your might!” _______________________________________ 9. “Keep the change,” the rich man said to the waitress. _______________________________________ 10. I said to myself, “I will definitely beat him in the next event.” _______________________________________
D. Rewrite these sentences in direct speech. The first one has been done for you.
1. My mother asked me to buy a dozen eggs from the shop. “Can you buy me a dozen eggs from the shop?” asked my mother .
2. I told myself that I would finish painting the gate by that afternoon. _______________________________________ 3. The judge asked the defendant to speak louder. _______________________________________ 4. The engineer wanted the workers to complete the project by the following day. _______________________________________ 5. Anu reported to the police about her purse being snatched. _______________________________________
E. Use past tenses, present perfect or past perfect tenses to complete the sentences.
We _____________ in Bristol from January to March. (stay) Where is my wine? Someone _____________ my wine! (drink) When you _____________ you _____________ fast? (crash, drive) I’m sorry. Dad isn’t here. He _____________ our neighbour’s flat since the morning. (decorate) What a nice coat! Where _____________ you _____________ it? (buy) At 6 o’clock he _____________ there for three hours! (sit) I want to learn French. But I _____________ yet. (not start) We didn’t want to spend our holiday in Strobl because _____________ already _____________ there. (be) What _____________ ? You are so dirty! (do) Oh, no! I _____________ my way. What shall I do? (lose) Jim _____________ the dishes after dinner. The kitchen sink is full of plates. (not wash) She _____________ three clients since the morning. (contact) I couldn’t help you. I _____________ your problems. (not understand) Does he know about it? _____________ him yet? (tell) Bill admitted that he _____________ the catalogue to the agency. (not send) As soon as I _____________ the message, I _____________ my house (get, leave) While Maggie _____________ a new Jumper, Jill and I _____________ (knit, read) Here he is! He _____________ for me all the time, he _____________ for Ann! (not look, wait) _____________ you in your room at 5.30? Yes, I think I _____________ my suitcase. (be, pack) Nice to meet you! I _____________ uyou for 10 years. What _____________ you _____________ all this time? (not see, do) He _____________ but he’ll be back home today. The doctors ____________ to cure him. (die, manage) After we _____________ to the top of hill we had a great view of the bay. (elimb) The pigeon finally delivered the news after it _____________ for the whole day. (fly)
F. In the following sentences the speakers are all saying something different to what they told you before. Write replies to their statements as given in the example. Example:
- “I’m going out with Alisha.” But you said you weren’t going out with her .
1. “I haven’t finished my project.” I thought you said ________________ 2. “I’m better at tennis than golf.” But you told me ________________ 3. “I enjoy parties.” I remember you saying ________________ 4. “I’ve got a video recorder.” But you said yesterday ________________ 5. “I’m applying for the job.” I thought you told me ________________ 6. “I like Indian food more than Chinese.” But you said ________________ 7. “I prefer pop music to classical music.” You told me ________________
G. Change the following sentence to indirect speech.
1. Our teacher said, “Time is precious, so spend your free time in the best possible way.” ________________________________________________ 2. “Ugh! This toilet is so smelly,” Rita said. ________________________________________________ 3. Chetan said, “Please buy me a bar of chocolate.” ________________________________________________ 4. “Polish your boots,” the army officer said to his men. ________________________________________________ 5. “Get me a glass of water,” he said to her. ________________________________________________ 6. “What a beautiful car!” he remarked. ________________________________________________ 7. “Please spare me some money,” the beggar said. ________________________________________________ 8. “You must listen to me!” his mother cried. ________________________________________________ 9. “Pass me that salt, please,” the man said to her. ________________________________________________ 10. “Get out or I’ll call the police!” the lady said to him. ________________________________________________
H. Change the following to reported speech by completing the sentence.
1. She asked, “Have you been here before?” She asked me if _________________ 2. “Is your sister still asleep?” my mother asked. My mother asked _________________ 3. The policeman said, “Show me your license.” The policeman demanded _________________ 4. “Shall I open the windows for you?” he asked. He asked me whether _________________ He offered to _________________ 5. “Where will you be going for your holidays?” she asked. She wanted to know _________________ 6. “When will you be visiting the hospital? I want to come along,” she said. She wanted to know _________________ 7. “Is the ship leaving on Monday or Tuesday?” She inquired. She inquired whether _________________ 8. “What’s wrong with your cheek? Have you been fighting again?” my mother asked. My mother asked what _________________ 9. “Did you learn anything interesting at the seminar?” he inquired. He inquired _________________ 10. “The purpose of this project is to encourage teamwork and inculcate a sense of belonging,” he said. He said that _________________
I. Change these sentences from Direct to Indirect Speech. Example
- “Oh!” she cried in fright on seeing him.
- “Why did you suddenly appear like this?”
She exclaimed in fright when she saw him and asked him why he had suddenly appeared like that.
1. “I am sorry,” she said to me, “but my brother won’t be back until late tonight.” ___________________________________________________ 2. The guard reported, “I heard some shots and ran out into the compound to investigate.” ___________________________________________________ 3. “When will he be back?” Sheela said. “I have something important to tell him.” ___________________________________________________ 4. “Did you go to the circus that’s performing here?” Jatin asked me. “It was a wonderful show.” ___________________________________________________ 5. “Good morning!” she said when she saw me. “How are you today? I heard you had been quite ill.” ___________________________________________________ 6. “Come here at once!” he ordered the frightened boy. “If you don’t, I shall give you a beating.” ___________________________________________________ 7. “Don’t do too much heavy work now,” the doctor advised Mrs. Birla. “Get as much rest as possible.” ___________________________________________________ 8. “Please come,” he said. “I want to show you my new fish. My father bought it yesterday.” ___________________________________________________ 9. “Are you going out now? If you are, see that you are back by ten,” my mother said to! me. ___________________________________________________ 10. “Yes, please do so,” I answered her. “I will wait here until you return.” ___________________________________________________
- Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 16 Direct and Indirect Speech
Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 16 Direct and Indirect Speech. When we use the actual words of the speaker, we use Direct Speech but when we report what he said in our own words, we use Indirect Speech. The actual words of the speaker are called Reported Speech and the verb introducing the Reported Speech is called the Reporting Verb. What a person says can be written in direct or indirect speech whereas the mode of narration which we use to report others’ thoughts and speech is known as indirect or reported speech.
Grade 8 English Grammar Chapter 16 Direct and Indirect Speech
- Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 16 Revision Book
- Class 8 English Grammar Next Chapter
- Class 8 English Grammar Main Page
- Class 8 English NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 all Subjects Solutions
The intricacies of language and expression become evident when one dives into the fascinating realm of Direct and Indirect Speech. Platforms dedicated to NCERT Solutions, such as Tiwari Academy, provide valuable insights into this topic, ensuring students grasp its nuances as presented in Chapter 16 of Class 8 English Grammar.
Direct Speech : This form of expression captures the verbatim words of a speaker, preserving its original essence. Enclosed within quotation marks, it presents an authentic representation of what someone stated. For instance, She said, “I am going to the market.” Here, the speaker’s exact words “I am going to the market” exemplify Direct Speech.
Indirect (or Reported) Speech : In contrast, Indirect Speech relays the essence of what was spoken but paraphrases it, translating the speaker’s words into the reporter’s own linguistic style. Using our earlier example, the Indirect Speech would be: She said that she was going to the market. Notice the subtle shift in words and tenses.
| Class: 8 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 16 | Direct and Indirect Speech |
| Content: | Study Material and Notes |
| Academic Session: | 2024-25 |
Direct Speech
- The Reported Speech is put within Inverted Commas . (“ ”)
- The First word of the Reported Speech begins with a capital Letter.
- The Reported Speech is separated by a comma (,) from the Reporting Verb.
Download App for Class 8

In the realm of English grammar, two crucial terms stand out: Reported Speech : This refers to the actual words or the content of what the speaker articulated. It becomes the crux of our conversion from direct to indirect speech. Reporting Verb : The verb, often ‘said’ or ‘told’, which introduces the Reported Speech, playing a pivotal role in setting the context for the narration.
Indirect Speech
- Inverted Commas (“ ”) are not used in Reported Speech. It is generally introduced by the Conjunction if., that, what, why, etc.
- The comma separating the Reporting Verb from the Reported Speech is removed.
- The Tense of the Reporting Verb is never changed.
- The Question Mark (?) and the Mark of Exclamation (!) are not used.
- The Interrogative, the Imperative and the Exclamatory sentences are put as statements.
| Kind of Sentences | Direct | Indirect |
|---|---|---|
| Assertive | say, says, | said, said to |
| Imperative | said, said to | asked, advised, ordered, requested etc. |
| Exclamatory | said, said to | excaliamed with joy/sorrow etc. |
| Interrogative | said, said to | asked, enquired, demanded of |
| Optative | said, said to | wished/prayed |
Change of the Tense
While changing Direct Speech into indirect Speech, the rule of Sequence of Tenses is followed. If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future Tense, the tense of the verb in the Reported Speech is not changed at all.
| Direct | Indirect |
|---|---|
| You say, “She is a nurse.” | You say that she is a nurse. |
| I say, “Mohan is a good boy.” | I say that Mohan is a good boy. |
| I say to Sham, “Ram is a student”. | I tell Sham that Ram is a student. |
| He says to me, “The peon rings the bell.” | He tells me that the peon rings the bell. |
| I shall say to him, “She will go to school.” | I shall tell him that she will go to school. |
| I shall say, “Rita is a doctor.” | I shall say that Rita is a doctor. |
If the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the Tense of the Reported Speech will change.
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| He said, “Reena combs her hair.” | He said that Reena combed her hair. |
| She said, “He is going to school.” | She said that he was going to school. |
| I said, “I am taking tea.” | I said that I was taking tea. |
| You said, “They are laughing.” | You said that they were laughing. |
| He said, “They were laughing.” | He said that they had been laughing. |
If the Reported Speech expresses some Universal Truth, Factual Truth, Habitual Fact, Custom, Proverb, Natural Fact, Historical Fact and Scientific Fact, the tense of the verb in the Reported Speech is not changed into the Past, but remains exactly.
The dynamic shift between Direct and Indirect Speech offers versatility in communication. While Direct Speech provides immediacy and emotional resonance by capturing the exact words, Indirect Speech offers flexibility, allowing the narrator to frame the information in a manner that aligns with the broader narrative.
Students diving into this chapter, with resources like those available at Tiwari Academy, will benefit from numerous examples and exercises. These are designed to instill confidence in them to switch between Direct and Indirect modes of speech seamlessly, enriching their expressive capabilities and bolstering their command over English communication.
| Direct | Indirect |
|---|---|
| Mother said, “The dogs bark at the strangers.” | Mother said that the dogs bark at (Habits) the strangers. |
| He said, “The Hindus burn their dead.” | He said that the Hindus burn their dead. |
| He said, “Sea water tastes saltish.” | He said that sea water tastes saltish. |

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education


Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
| Simple present “I to go home.” | Simple past She said she to go home. |
| Present continuous “I a good book.” | Past continuous She said she a good book. |
| Simple past “I pasta for dinner last night.” | Past perfect She said she pasta for dinner the night before. |
| Present perfect “I just cleaning my room.” “My mother never to Japan.” | Past perfect She said she just cleaning her room. She said her mother never to Japan. |
| Can/can’t “I meet with you next Monday.” “Sorry, I talk now; I’m at work.” | Could/couldn’t She said she meet with me next Monday. She said she talk at the moment because she was at work. |
| Will/won’t “I pick him up from the airport.” “I tell anyone your secret.” | Would/wouldn’t She said she pick him up from the airport. She said she tell anyone my secret. |
| Should “You apologize.” | Should She said I apologize. |
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to Backshift in Reported Speech
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Relative Clauses + Exercises

Advanced English Prepositions Quiz

Hi, I’m Shayna. I create courses helping English as a Second Language learners become more fluent in just a few minutes a day – so they can speak English naturally and confidently in work and daily life.

Direct and Indirect Speech Class 8 - Download Free PDF with Solutions
In simple terms, we can understand direct speech as the precise words that a speaker or writer uses. The spoken words are enclosed in inverted commas in a direct speech. On the other hand, indirect speech entails summarising another person’s words using our own language. In indirect speech, we do not write someone else’s precise words, and we do not use inverted commas. Learning direct and indirect speech in Class 8 is an integral part of their overall grammar syllabus, and having a firm grasp on the topic is essential to score good marks in exams.
In today’s day and age, solely sticking to NCERT textbooks and exercises is not enough. Some extra hand holding goes a long way, and students need some ancillary academic support in the form of revision notes, sample tests, etc. Teachers and parents should go the extra mile to provide children with additional study material from credible sources.
English Grammar for Class 8 Direct and Indirect Speech Download Free PDF
Today we will study an exciting topic “Reported speech”. Reported speech refers to how we have interpreted the words of the speaker.

Definition of Reported Speech
In simple terms, Reported speech refers to reporting the speech of the speaker i.e. whether conveying directly the words of the speaker or indirectly conveying after altering the words of the speaker. For good understanding and idea clarity, practice questions and solved examples are provided throughout the article. Let's start our journey on this pretty topic.

The Convey of Speech
Parts of reported speech in a sentence
Reported verb
Reported speech,
For example, Ram said to me,” he wants to eat pizza”.
Here in the sentence, Ram said to me is the reporting verb,
And the sentence in inverted commas “he wants to eat pizza” is the reported speech.
The reported verb refers to the simple sentence at the starting of the sentence and reported speech refers to the sentence in inverted commas that defines someone else.
Reporting Verb
The part of the sentence which is not in the inverted commas is called the reported verb.
When we change a direct speech into indirect speech then there are 3 types/ forms of changes that take place.
Change of person
Change of tense and
Change of other parts of speech
For example, Priya said to the class,” keep quiet teacher is coming”.
Here in the sentence, Priya said to the class is the reporting verb.
Reporting Speech
The part of the sentence which is under inverted commas is called reporting speech.
The second part of the sentence refers to some other person, universal facts, imaginary parts, historical facts, happening events, etc.
For example, Shyam said,” taj mahal was built by Shahjahan”
Here the sentence “taj mahal was built by Shahjahan” is the reported speech.
Basically, there are two types of speech.
Direct speech
Indirect speech
Direct Speech

It refers to reporting the exact words spoken by the speaker. There is no change in the verb or the sentence.
For example, Ram said to Riya, “go to school”
Priya asked Ram, “where is her bag”
Ratan enquired Raman,” why was he not picking up her call”.
Rules of Direct Speech
Speech should be opened with quotations or inverted commas.
The word said is used to connect two sentences.
Reporting clause should be used at the end of the sentence.
At the end of the sentence full stop should be placed.
Indirect Speech

It is the speech that tells what someone has said but it does not explain the actual words spoken by the person. It just conveys the basic narration of what is being said to the third person.
For example, Ram asked Riya to go to school.
Priya asked Ram where was her bag.
Ratan enquired Raman why was he not picking up her call.
Rules of Indirect Speech
Past tense is used when the situation is uncertain
The present tense of the sentence is changed to the past tense in indirect speech.
Universal facts tense remains the same.
The use of the word “that” connects the reported verb and reported speech.
Difference Between Direct Speech and Indirect Speech
Basic | Direct speech | Indirect speech |
Definition | Direct speech basically refers to what someone has said i.e. the actual words and we also use quotation marks in this. | In indirect speech we don't use quotation marks rather we use the conjunction “that”. |
Examples | She said, “ she must go”. She has written three letters to her friends. | She said she had to go. |
Difficult Words Meaning
Word | Meaning |
Narration | The act or process of narrating |
conjunction | A word used for joining other words |
Quotation | A phrase or speech being constantly repeated. |
Practice Question
Rewrite the following sentence converting from direct speech to indirect speech.
He asked me “ what is your mother’s name”.
Riya said to the shopkeeper, “ what is the price of the item?”
Ram said, “How is the weather”.
Commander said to militarians, “practice well”.
Honey told his mother, “I am not feeling well”.
The Doctor said, “Health is your wealth”.
Traffic police said, “Don't rush”.
He asked me what my mother's name is.
Riya asked the shopkeeper what the price of the items was.
Ram asked how the weather was.
Commander ordered militarians to practice well.
Honey told he mother that he was not feeling well.
The Doctor advised that health is wealth.
Traffic police asked the public not to rush.
Importance of Learning Direct and Reported Speech Class 8
Having a firm grasp on direct and reported speech in Class 8 is integral to building the foundation of English grammar for young minds.
Knowing when and how to use direct and indirect speech can help students form grammatically correct sentences.
The essay writing and answer composition skills of young minds improve significantly when they know the nitty-gritty of direct and indirect speech.
Learning the rules of changing speech from direct to indirect enables students to summarise texts more aptly.
Lastly, indirect and direct speech introduces young students to the fundamentals of quoting, which is an aspect of grammar that they will need for years on end.
Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech for Class 8 Students
Riya said, “I am going on a long vacation.” – Direct Speech
Riya said that she was going on a long vacation. – Indirect Speech
The stranger asked me, “Where is your house?” – Direct Speech
The stranger asked me where my house was. – Indirect Speech
Rina asked Steve if he had overheard her conversation. – Indirect Speech
Rina asked Steve, “Did you overhear my conversation?” – Direct Speech
The direct and indirect speech exercises for Class 8 with answers PDF should include simple and relatable examples like the ones stated above.
Interesting Facts about Direct and Indirect Speech for Class 8 Students
While changing a sentence from direct to indirect speech, we use the conjunction ‘that.’
Likewise, while changing a sentence from direct to reported speech, the tense of the verb is changed from present to past.
Direct speech helps in defining the character of a person.
The prolonged use of direct speech in an essay can slow its pace. However, the use of indirect speech smoothens the pace of a writeup.
If the reported speech expresses some universal truth, then we do not have to change the tense of the sentence.
All direct and indirect worksheets with answers in Class 8 ought to be an amalgamation of examples, definitions, and interesting facts to make learning more interesting for young minds.
Important Topics of Direct and Indirect Speech Class 8
The 17th Chapter of the Class 8 NCERT grammar book is on direct and indirect speech. Below are the topics students will learn from this chapter.
Understanding direct speech
Understanding indirect speech
Rules for changing direct speech into indirect speech
Exceptions to rules
Therefore, all direct and indirect speech exercises for Class 8 with answers PDF should encompass the following topics.
Learn English Grammar Direct and Indirect Speech with PDFs
Meticulously designed by the subject matter experts of Vedantu, the English grammar PDFs for Class 8 students on direct and indirect speech are the one-stop destination for all young minds keen on expanding their horizons. The PDFs include reported speech exercises for Class 8 CBSE with answers , tips and tricks to learn grammar faster, sample question papers, etc.
The PDFs of Vedantu are downloadable from the comfort of your homes.
They are free.
The content is regularly updated by Vedantu’s subject matter experts.
The PDFs contain more than 50 examples of direct and indirect speech exercises.
So, do not wait any longer and download Vedantu’s PDFs now to watch your child reach new academic zeniths.

FAQs on English Grammar Direct and Indirect Speech Class 8
1. What is direct narration?
When we quote the exact words of the speaker, then it is direct narration.
2. What is the indirect speech of the sentence – Rima said, “The sun rises in the east.”
Rima said that the sun rises in the east.
3. When should I use direct speech in a sentence?
The ideal time to use direct speech is when you want to precisely quote the words of some other person. Direct speech can help break the monotony in an essay and make it more interesting to readers.
Reported Speech Class 8 Worksheet
Reported Speech Class 8 Worksheet: Hello Students, welcome to Net Explanations. In this page we have posted Reported Speech Class 8 English Grammar Worksheet Extra Questions Answers. For more CBSE Board Class 8 Grammar Worksheet you can check this page.
Reported Speech Class 8 English Grammar Worksheet – Change Sentences into Indirect Speech
2.) He said to me, ” My name is Ram”.
4.) The girl said, ” A bot stole my purse.”
8.) She said, “I do not know English.”
14.) Fauji Baba said, ” My son loves me very much”.
4.) Radha said to Hari, “ Where is my book?”
5.) You said to her, “ what is your name?”
9.) Ram said to her, “How do you cook rice?”
12.) Hari said to me, “ where do you live?”
Answer Sheet –
4.) The girl said that a boy had stolen her purse.
5.) Dadaji told me that I was a lazy boy.
2.) He asked if he could sleep.
6.) Gopal asked Seema when could come to her.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, locating places on the earth class 6 mcq questions answers, kerala scert class 8 english a shipwrecked sailor question answer, west bengal board class 4 maths chapter 12 solutions দাদুর বাড়ি যাই, telangana scert class 5 maths chapter 14 factors and multiples solution.


Narration Change Class 8 Rules with Examples and Exercises

Discover the narration change class 8 rules with examples and exercises and learn how to change from Direct speech to Indirect Speech . Class 8 Narration rules with examples and exercises have been arranged in the following with our comprehensive guide, complete with examples and exercises.
Narration Change Class 8
Narration Change means to change the speech of the speaker either from Direct to Indirect or from Indirect to Direct . When we quote the actual words of the speaker, it is called Direct Narration. But when someone narrates the speaker’s speech indirectly keeping the meaning the same, it is called Indirect Narration. For examples,
- Direct: Debi says, “I pray to God.”
- Indirect: Devi says that she prays to God.
We sometimes need to change the speaker’s actual words indirectly keeping the meaning the same or vice versa. This needs to change Direct Narration to Indirect Narration or Indirect to Direct. In order that we must know some rules to keep meaning the same.
People also search
| Narration Change Class 8 | |
Rules of Narration Change Class 8
The following Narration Change Rules must be observed carefully.
Rule 1: Change of Tense
1. If the reporting verb is in the Present or Future tense (e.g. say , will say ) there is no change in the tense of the verb in the Indirect Speech . For Example,
- Direct: Sabita says ( present ), ” I can do ( present ) the sum.”
- Indirect: Sabita says ( present ) that she can do ( present ) the sum.
- They will say ( Future ), “He could drive ( Past ) the car”
- They will say ( Future ) that he could drive ( Past ) the car.
2. If the Reporting verb is in the Past Tense , the tense of the verb in the reported speech or indirect speech must be generally changed.
Present Tense in the direct becomes Past Tense .
- Direct: He said, “I write a letter.”
- Indirect: He said that he wrote a letter
Past Tense becomes Past Perfect or remains Unchanged
- Direct: Ruby said, “I bought a pen yesterday.”
- Indirect: Ruby said that he had bought a pen the previous day.
Present Continuous becomes Past Continuous
- Direct: He said, “I am going to church.”
- Indirect: He said that he was going to church.
Past Continuous becomes Past Perfect Continuous
- Direct: Mohan said I was playing cricket
- Indirect: Mohan said that he had been playing cricket
Present Perfect becomes Past Perfect
- Direct: Kunal said, “I have done my homework.”
- Indirect: Kunal said that he had done his homework.
Present Perfect Continuous becomes Past Perfect Continuous
- Direct: Anita said I have been reading a novel
- Indirect: Anita said that she had been reading a novel
“ will ” and “ shall ” becomes ‘ would’ “ May ”, becomes “ might ” “ Can ”, becomes “ Could” “ Must ” becomes “ must ” or “ had to”
Rule 2: Change of Pronouns
The First Person Pronouns in the “ reported speech ” or “ Quoted Speech ” are put into the same person as “ the subject of the reporting Verb.”
- He said, “ I worked hard.”
- He said that he had worked hard.
The Second Person Pronouns in the “ reported speech ” or “ Quoted Speech ” are put into the same person as “ the indirect object of the reporting Verb.”
- I said to her , “ You are idle in your office.”
- I told her that she was idle in her office.
The Third Person Pronouns in the “ reported speech ” or “ Quoted Speech ” remain in the “Third Person.”
- I said, “ He will not wait for his friend.”
- I said that he would not wait for his friend.
Narration Change Class 8 Rules for Assertive Sentence:
1. No comma (, ) after the Reporting verb in Indirect Speech.
2. The full stop ( . ) at the end of the sentence in indirect speech.
3. Reporting verbs in Direct Speech (say/said/say to you / said to me) will be changed into (say/said/tell you / told me) in Indirect Speech.
4. Connective ‘that’ is to add between Reporting Verb and Direct Speech in Indirect Narration.
Examples of Narration Change Class 8 Assertive Sentences
Direct Speech: He said to me, “You are ill”
| ( ) | ( ) | ||
| He | said to | me | “You are ill” |
Indirect Speech: He told me that I was ill.
| ( ) | ( ) | |||
| He | told | me | that | I was ill. |
Assertive Sentence Workout Examples
Change the mode of Narration of the following sentences.
1. He says, “I shall help the poor.” Ans: He says that he will help the poor.
2. You will say, “I do not take tea.” Ans: You will say that you do not take tea.”
3. They said, “We are not afraid.” Ans: They said that they were not afraid.
4. She said, “I am working in the garden.” Ans: She said that she was working in the garden.
5. You said to me, “I have sold a bicycle.” Ans: You told me that you had sold a bicycle.
6. I said to Mitali, “You misunderstand me.” Ans: I told Mitali that she misunderstood me.
Q 7 . We said to them, “We will help you.” Ans: We told them that we would help them.
Q 8. Reba said to Rajib, “You are working very sincerely.” Ans: Reba told Rajib that he was working very sincerely.
Assertive Sentences Exercises & Answers
1. Sima told me that she had given me a pen the previous day. Ans: Sima said to me, “I gave you a pen yesterday.”
2. They said that they were happy then. Ans: They said. “We are happy now.”
3. The teacher said that man is mortal. Ans: The teacher said, “Man is mortal.”
4. He said that he walks in the morning every day. Ans: He said, “I walk in the morning every day.”
5. Mantu said that Iron is a very useful metal. Ans: Mantu said. “Iron is a very useful metal.”
Narration Change Class 8 Rules for Interrogative Sentence:
3. Reporting verbs in Direct Speech ( say / said / say to you / said to me ) will be changed into ( ask / asked / ask you / asked me ) in Indirect Speech. Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech may also be ‘ enquire of ’, or ‘ want to know ’.
4. Connective ‘ if/whether ’ is to add between Reporting Verb and Direct Speech in Indirect Narration, if the interrogative sentence is not introduced with interrogative pronouns – who, what , whom , when , why, whose , where , how, etc.
In Indirect speech, the interrogative sentence will turn into an Assertive Sentence. That means the subject will follow the verbs.
Examples of Narration Change Class 8 Interrogative Sentences
Direct Speech: The boy said to me, ‘Will you help me?” Direct Speech: He said to me, “How old are you?”
| ( ) | ( ) | ||
| The boy The man | said to said to | me me | ‘Will you help me?” “How old are you?” |
Indirect Speech: The boy asked me if I would help him. Indirect Speech: The man asked me how old I was.
| ( ) | ( ) | |||
| The boy The man | asked asked | me me | if how | I would help him. old I was. |
Interrogative Sentence Workout Examples
1. Mother said to my sister, “Will you entertain our guest?” Ans: Mother asked my sister if she would entertain their guests.
2. The teacher said to the boy, “Have you prepared your lesson?” Ans: The teacher asked the boy if he had prepared his lessons.
3. Mobarak said to Latif, “Did you go there yesterday?” Ans: Mobarak enquired of Latif whether he had gone there the previous day.
4. Hema said to Bina, “Are you ill today?” Ans: Hema asked Bina if she was ill that day.
5. Jyoti said to Moti, “are you weeping?” Ans: Jyoti asked Moti if she was weeping.
6. Debu said to Apu, “Have you closed the front door before you leave the house? Ans: Debu asked Apu if he had closed the front door before he left the house.
7. Geeta said to Sumita, “Can you solve this problem?” Ans: Geeta asked Sumita if she could solve the problem.
8. Haren said to Baren, “When have you come here?’ Ans: Haren asked Baren when he had gone there.
Interrogative Sentences Exercises & Answers
1. Dwijen asked Swapan how old he was. Ans: Dwijen said to Swapan,”How old are you?”
2. Rupa asked Nipa whom she had spoken with the night before. Ans: Rupa said to Nipa, “Whom did you speak with the last night?”
3. You enquired of me what I wanted from you. Ans: You said to me, “What do you want from me?”
4. Sipra asked us how long she would wait for our friends to come there. Ans: Sipra said to us, “How long shall I wait for your friends to come here?”
5. The boy asked me where I lived. Ans: The boy said to me, “Where do you live?”
6. The teacher asked whose book that was. Ans: The teacher said, “Whose book is this?”
7. The man asked her whom she wanted to see. Ans: The man said to her, “Whom do you want to see?”
Narration Change Class 8 Rules for Imperative Sentence:
1. In Indirect Speech, the reporting verb becomes order , request , advise , ask , tell , etc. according to the sense.
2. Infinitive, “to” is used before the main verb in Indirect Speech.
3. In the case of the Negative Imperative, ‘not’ is used before the Infinitive in the Indirect Speech. The verb ‘forbid’, ‘prohibit’, etc may be used and in that case ‘not’ is not used before the Infinitive.
4. The expressions like ‘Sir’ and ‘please’ i n Direct Speech are omitted in Indirect Speech and reporting verbs ‘request’ , ‘entreat’ etc., and adverbs ‘kindly’ , ‘politely’ , ‘respectfully’ etc, may be used in their place to express the sense.
An imperative Sentence beginning with ‘Let’
1. ‘Let’ with ‘us’ express ‘ suggestion’, or ‘proposal’ – reporting verb in Indirect Speech will be ‘suggest’, ‘propose’; ‘Let’ changed to ‘should’ and placed after subject; connective ‘that’ is used.
2. ‘Let’ with ‘me’, ‘him’, and ‘her’ not express ‘ suggestion’, or ‘proposal’ – reporting verb in Indirect Speech will be ‘request’ or ‘wish’ according to sense; ‘ Let ’ changed to ‘ may/may be allowed to ‘ – Present Tense; might /might be allowed to – Past Tense’ and placed after subject; connective ‘that’ is used.
Examples of Narration Change Class 8 Imperative Sentences
Direct Speech: The teacher said to the pupils, “Respect your superiors.” Direct Speech: You said to her, “Don’t insult me.”
Direct Speech: My friend said to me, “Let us go for a picnic.” Direct Speech: The girl said to her mother, “Let me take some rest for a while.”
| The teacher You My friend The girl | said to said to said to said to | the pupils her me her mother | “Respect your superiors.” “Don’t insult me.” “Let me take some rest for a while.” “Let us go for a picnic.” |
Indirect Speech: The teacher advised the pupils to respect their superiors. Indirect Speech: You told her not to insult you.
Indirect Speech: My friend suggested that they should go for a picnic. Indirect Speech: The girl requested her mother that she might be allowed to take some rest for a while.
| The teacher | advised | the pupils | to (infinitive) | respect their superiors. |
| You | told | her | ( ) to (infinitive) | insult you. |
| My friend | suggested | me (can be omitted) | that | they should go for a picnic. |
| The girl | requested | her mother | that | she / take some rest for a while. |
Imperative Sentences Workout Examples
Change the Narration of the following sentences.
1. The general said to the soldiers, “March forward.” Ans: The general ordered the soldiers to march forward.
2. The boy said to his friend, “Give your brother this information.” Ans: The boy told his friend to give his brother that information.
3. He said to me, “Follow me.” Ans: He asked (told) me to follow him.
4. You said to her, “Do not insult me in this way.” Ans: You forbade her to insult you in that way. Ans: You told her not to insult you in that way.
5. The student said to the teacher, “Please explain the law of Gravitation once again. Ans: The student requested the teacher to explain the law of Gravitation once again.
6. The master said to the servant, “Act up to my instruction. Ans: The master ordered the servant to act up to his instruction.
Imperative Sentences Exercises and Answers
7. The preceptor said to the disciple, “Lead a peaceful and truthful life. Ans: The preceptor advised the disciple to lead a peaceful and truthful life.
8. Father said to me, “Take care of your health and mind your lessons. Ans: Father advised me to take care of my health and to mind my lessons.
9. The Convict said to the Bishop, “Give me food and drink. Ans: The convict told the Bishop to give him food and drink.
10. The teacher said to the pupils, “Do not smoke. Ans: The teacher forbade the pupils to smoke. Ans: The teacher advised the pupils not to smoke.
11. The old man said to the traffic police, “Please show me the way to the hospital.” Ans: The old man requested the traffic police to show him the way to the hospital.
12. The prisoner said to the police officer on duty, “Sir, allow the inmates of my family to meet me. Ans: The prisoner politely requested the police officer on duty to allow the inmates of his family to meet him.
13. The teacher said, “Sit down, boys.” Ans: The teacher told the boys to sit down.
Imperative Sentence Examples with “Let”.
1. The boys said, “let us take a trip to Digha.’ Ans: The boys proposed or suggested that they should take a trip To Digha.
2. The girl says to her friends, “Let us arrange a picnic on Sunday.’’ Ans: The girl proposed or suggested to her friends that they should arrange a picnic on Sunday.
3. My friend said to us, “Let us avail ourselves of this unique opportunity.’’ Ans: My friend proposed (suggested) to us that we should avail ourselves of that unique opportunity.
4. Phatik said to his playmates, “Let us roll the log.” Ans: Phatik proposed (suggested) to his playmates that they should not the log.
5. He said to me, “Let me take off the lid of the kettle.” Ans: He proposed to me that he should take off the lid of the kettle.
6. The boy requests that he may be allowed to (or may) enjoy the Television Programme then. Ans: The boy says, “Let me enjoy the Television Programme now.”
7. The girl requested her mother that she might (or might be allowed to) take a rest for a while. Ans: The girl said to her mother, “Let me take a rest for a while.”
8. He said that he might ( might be allowed to) select the poem for recitation. Ans: He said, “Let me select the poem for recitation.”
9. The old man said that he might (or might be allowed to) die in peace. Ans: The old man said, “Let me die in peace.”
10. You requested that you might be allowed to (or might) try. Ans: You said, “Let me try.”
Narration Change Class 8 Rules for Optative Sentence:
1. In Indirect Speech, the reporting verb becomes wish , pray , desire.
2. Connective ‘that’ is introduced.
Optative Sentences Examples of Narration Change Class 8
Direct Speech: He said to me, ‘May you be happy.”
| He | said to | me | ‘May you be happy.” |
Indirect Speech: He wished that I might be happy.
| He | wished | me | I might be happy. |
Optative Sentences Workout Examples
1. Mother said, ‘May you be happy.’ Ans: Mother wished that I might be happy.
2. He said to you, ‘May God bless you.’ A ns: He prayed that God might bless you.
3. She said, ‘Had I been there!’ Ans: She wished that she had been there.
4. He said to me, ‘May you succeed.’ Ans: He wished that I might succeed.
5. They said, ‘Long live the leader.’ Ans: They prayed that the leader might live long.
6. He said to me, ‘May your mother recover soon.’ Ans: He wished that my mother might recover soon.
7. The monk said, ‘May peace prevail.’ Ans: The monk hoped that peace would prevail.
8. The boy said, ‘Had I the wings of a bird.’ Ans: The boy wished that he could have the wings of a bird.
Optative Sentences Exercise and Answers
1. The poor man said, ‘If only I had a hundred rupees.’ Ans: The poor man longed for a hundred rupees.
2. Mother said, ‘May the child the cured of cough and cold.’ Ans: Mother prayed that the child might be cured of cough and cold.
3. The people in Great Britain said, “May the departed soul of Diana rest in peace.’ Ans: The people in Great Britain prayed that the departed soul of Diana might rest in peace.
4. He said to me, “Wish you a happy retired life.” Ans: He wished that I might have a happy retired life.
5. You said to her, “May Heaven’s choicest blessings be showered on your wedded life.” Ans: You wished her that Heaven’s choicest blessings might be showered on her wedded life.
6. I said to him, “May Mother Teresa bless us.’ Ans: The people prayed that Mother Teresa might bless them.
7. They said to her, “May you come round soon.’ Ans: They wished that she might come round soon.
8. She said, “Oh, could I sing like a cuckoo.” Ans: She wished that she could sing like a cuckoo.
Class 8 Narration Change Rules for Exclamatory Sentences:
1. In reporting Exclamatory Sentences, the reporting verb according to sense in the Indirect Speech is introduced by some verb like ‘exclaim in (with) joy,’ ‘exclaim in (with) sorrow’, ‘exclaim in (with) wonder, ‘exclaim in (with) anger,’ ‘exclaim in (with) despair, ‘exclaim in (with) shame, may be used.
2. Where the nature of exclamation is not clear, the reporting verb ‘cry out’ or ‘exclaim’ only may be used.
3. The exclamation form is changed into Assertive Form with the linker ‘that’.
4. Exclamatory Sentence beginning with ‘what’ or ‘how’ becomes ‘great’ or ‘very’ according to sense, usually ‘great’ is used before a Noun and ‘very’ before an Adjective.
5. Note of exclamation ( ! ) turns into a full stop ( . ) in the Indirect Speech.
Examples of Narration Change Class 8 Exclamatory Sentences
Direct Speech: She said, “Alas! I am undone.”
| He | said | “Alas! I am undone.” |
Indirect: She exclaimed with/in sorrow that she was undone.
| He | exclaimed with/in sorrow | that | she was undone. |
Exclamatory Sentences Workout Examples
1. He said, “What a beautiful sight it is!” Ans: He exclaimed in (with) joy that it was a very beautiful sight
2. You said, “How happy we are here!” Ans: You exclaimed in (with) joy that you were very happy there.
3. She said, “Alas! I am undone.” Ans: She exclaimed in (with) sorrow that she was undone.
4. The boy said, “How big the snake is!” Ans: The boy exclaimed in (with) wonder that the snake was very big.
5. The boys said, “Hurrah! East Bengal has won the Asian cup.’ Ans: The boys exclaimed with (in) joy that East Bengal had won the Asain Cup.
6. He said to me, “What a loss you have done to me!” Ans: He cried out in anger that I had done a great loss to him
7. Sudeshna said, “How foolish she is !” Ans: Sudeshna cried out (exclaimed) in despair that she was very foolish.
8. The countrymen said, “Fie! What a treachery.” Ans: The countrymen exclaimed in shame that it was a great treachery.
9. The boy said, “Alas! I find no hope of recovery.” Ans: The boy exclaimed in despair that he found no hope of recovery.
10. He said, “By God, what a thrilling experience !” Ans: He swore by God that it was a very thrilling experience.
11. He said, “Good morning, my friend!” Ans: He wished good morning to his friends.
Exclamatory Sentences Exercises and Answers
1. The patriot said, “Goodbye, my countrymen!” Ans: The patriot bade goodbye to his countrymen.
2. He said to me, “Heartiest Bijoya Greetings!” Ans: He wished me the heartiest Bijoya Greetings.
3. They said, “Who knew that Mother Teresa would leave us so early!” Ans: They said that none knew that Mother Teresa would leave them so early.
4. The President said, “Thank you, my countrymen. Ans: The President thanked his countrymen.
5. You said to him, “Bravo! You have scaled over the wall.” Ans: You applauded him saying that he had scaled over the wall.
5. He said, ‘How nice it is!’ Ans: He exclaimed in joy that it was very nice.
6. She said, ‘Alas! I am ruined.’ Ans: She exclaimed in sorrow that she was ruined,
7. He said to his son, ‘Bravo! You have done well.’ Ans: He applauded his son, saying that he had done well.
8. How happy we were there !’ They said to each other. Ans: They wistfully / gloomily said to each other that they had been very happy there.
9. The supporters said, ‘Hurrah! we have won?’ Ans: The supporter exclaimed in joy that they had won.
10. The girl said, ‘How wonderful love is! Ans: The girl exclaimed in joy that love is wonderful.
Exclamatory Sentences Worksheet
1. The teacher said, ‘Bravo! Well done!’ Ans: The teacher applauded his students by saying that they had done well.
2. ‘Alas! I am undone’, said the woman. Ans: The woman cried out in sorrow that she was undone.
3. He said, ‘Goodbye, my friends! Ans: He bade his friends goodbye.
4. The old man said to the youth, ‘Fie! You are such a coward.’ Ans: The old man exclaimed that it was shameful for the youth to be such a coward.
5. ‘How dirty the house is!’ he observed. Ans: He exclaimed in irritation that the house was very dirty.
6. “Good God! I am saved’, said he. Ans: He exclaimed in the name of merciful God that he was saved.
7. The girl said, ‘What a fool I am!’ Ans: The girl exclaimed with grief that she was a great fool.
8. He said, ‘You cheat !’ Ans: He called me a cheat.
9. Our teacher said, ‘Congratulations! Ans: Our teacher congratulated us.
10. He said ‘Sorry, it was my mistake! Ans: He confessed that it was his mistake.
Related Posts:


45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Reported Speech /
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises For Class 8 [PDF Available]
- Updated on
- Jul 18, 2024

Direct and Indirect Speech for Class 8: This concept of direct and indirect speech is one of the most fundamental topics in English Vocabulary . Language is used to convey one’s thoughts and feelings, therefore, one must understand the importance of direct and indirect speech . Do you wish to improve your English learning skills? Then you have come to the right place. We have compiled this blog, especially for Class 8 students.
In this blog, you will get to learn about what direct and indirect speech for class 8 and how they should be used in sentences.
This Blog Includes:
What is direct speech, what is indirect speech, direct and indirect speech exercises for class 8 with answers pdf, direct and indirect speech exercise 1, direct and indirect speech exercise 2.
Direct Speech is a sentence where the speaker’s exact words are reproduced in speech marks (also known as quotation marks or inverted commas).
Here are some of the formulas of direct speech.
Simple Present Tense:
(Subject +Verb + Object),
Present continuous and Present Perfect Tense:
(Subject +is/am/are+Verb +ing+ Object) and
(Subject + has/have+Verb+Object) respectively.
- Marie said, “I’ll come back in 15 minutes.”
- Ram said, “You must give men another opportunity.”
- She said,” I wish I were that rich.”
- My mother said to me, “May you get well soon.”
- She said to me, “May you live long.”
Also Read: Reported Speech Rules with Tips and Exercises for Students
Indirect speech is when it tells you what someone said but does not use the person’s actual words.
Here are some formulas for indirect speech:
The Past Simple Tense did + V1 V2
Past Progressive Tense was /were + V4
Past Perfect Tense had + V3
- I told her I was not very happy at work.
- They told us they were going back to their village.
- She said she had been working out at the gym.
- He said that Julia would be late at work.
Also Read: Direct and Indirect Speech: Comprehensive Guide with Exercises
Now that we have talked about both direct and indirect speech. The students need to practice and test their knowledge. Moving ahead, we have compiled a few exercises on direct and indirect speech for Class 8 students. Have a look at them.
Convert the following sentences from direct to indirect speech.
- Direct: He said, “I am going to the park.”
- Direct: “I have completed my homework,” said Marie.
- Direct: “It’s raining outside,” she said.
- Direct: “We will visit the church tomorrow,” they told us.
- Direct: “I love waffles,” he exclaimed.
Check Your Answers:
- He said he was going to the park.
- Marie said she had completed her homework.
- She said that it was raining outside.
- They told us that they would visit the church tomorrow.
- He exclaimed that he loved waffles.
Also Read: Tenses Rules: Charts, Examples, Types [PDF Available]
Rewrite the following paragraph into indirect speech.
Direct: “I can’t come to the party,” Julia said. “I have a nail appointment. Andrew won’t be able to make it either. He’s stuck in traffic. But we hope you all have a fantastic time.”
Julia said that she couldn’t come to the party as she had a nail appointment. She also mentioned that Andrew wouldn’t be able to make it as he was stuck in traffic. However, they hoped that everyone would have a fantastic time.
The pdf for the Direct and Indirect speech exercises for class 8 with answers is given below which you can solve further.
Related Posts
Simply use the reporting verb, “say” or “said” in its correct tense. Make sure you remove the conjunctions such as “that”, “if”, “to” and “whether”. Lastly, insert quotation marks, question marks, exclamation and full stop.
For simple present tense, the formula is (Subject +V1st + Object). While the formula for Present continuous and Present perfect the formula can be (Subject +is/am/are+V1 +ing+ Object) and (Subject + has/have+V3+Object) respectively.
The clauses of direct speech are the reporting clause and the reported clause.
The reported speech class 8 exercises are based on direct and indirect speeches. You should learn them properly to solve them and get the answers right.
This was all about “Direct and Indirect speech exercises for class 8 [PDF Available]”. Hope you understand the concept and know how to proceed. You can also follow the Learn English page of Leverage Edu for more exciting and informative blogs related to grammar.
Malvika Chawla
Malvika is a content writer cum news freak who comes with a strong background in Journalism and has worked with renowned news websites such as News 9 and The Financial Express to name a few. When not writing, she can be found bringing life to the canvasses by painting on them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Reported Speech
Barbara Jaroszewicz
This is an activity to revise statements and questions in reported speech
Loading ad...
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF

Shane Montalvo
Lesson Plan for Grade 8: Direct and Reported Speech
Below, is my example of a semi-detailed lesson plan that I developed as an activity for one of my courses. I hope this lesson plan could help you in some ways. Padayon, future educat ors!
Lesson Plan 2 – Direct and Reported Speech
I. Objectives
At the end of the lesson, the students are expected to:
a. Identify direct and reported speech;
b. differentiate direct and reported speech; and,
c. create sentences using direct and reported speech.
II. Subject Matter Direct and Reported Speech
Reference/s
Konrad. (2016). Direct and indirect speech – What’s the difference?. Retrieved from: https://www.google.com/amp/s/www.eurocentres.com/blog/direct-and-indirect-speech-whats-the-difference%3fhs_amp=true
NA. (nd). Reported Speech: Indirect questions, direct commands. Retrieved from: https://www.zeepedia.com/read.php?reported_speech_indirect_questions_direct_commands_journalistic_writing&b=79&c=14
NA. (nd). What are direct and indirect speech?. Retrieved from: https://www.theschoolrun.com/what-are-direct-and-indirect-speech
- Apps for assessment
III. Procedure
A. Activity
The teacher will asked the students to discuss what they’ve learned about the last lesson that had been discussed.
2. Motivation
The teacher will post a picture on the board and then the students will be asked to observe the meaning behind those pictures.

B. Analysis
The students will be watching a short video that will be posted by the teacher. Then, they will be asked to reiterate the said information by the speaker in the video.
World’s Most Dangerous Food
C. Abstraction
Direct Speech – is a sentence in which the words that someone have been said are written exactly on the sentence. It is usually reproduced in speech marks or also known as quotation marks or inverted commas.
For example:
The policeman said, “All kids are safe.”
Anna said, “I’ve been in Paris.”
Reported Speech – or also known as indirect speech, is a sentence in which it reports what has been said or spoken by someone. It always used past tenses instead of speech marks.
For changing direct to reported speech, all the verb that has been used would be changed into past tense.
Clara asked, “Why are you studying math?” → Clara asked me why I was studying math.
D. Application
1. Individual Guided Activity
The teacher will be asking students to answer the following questions. A. Identify if the statement is direct or reported speech.
- My teacher said that education is the most important thing in this world.
- “I will pursue my dreams no matter what,” John said.
- “I am so happy that you are one of my friends whom I can trust,” Shiela stated.
- I said, “I am also glad to have met you.”
- The speaker of the the seminar said that she had fun sharing her experiences that could help students.
- “I love you,” he said.
- Sam said that she would be late for her Science class.
- Matt said that he loves to play basketball rather than chess.
- Mrs. Dela Cruz stated, “you will all pass this semester.”
- “I believe I will pass this semester,” Jane said.
2. Group Differentiated Task The teacher will ask the students to find their selves a partner. Then, they will be asked to share their opinion on how to fight or lessen the positive cases of Covid-19. After that, they will create an article or a short summary quoting the opinions of their partner. In addition, their article must use direct and indirect speech in quoting their partner’s point of view.
IV. Evaluation The teacher will ask the students to make the following activities. A. Create 5 direct speech and 5 reported speech.
B. Watch the Ted Talk video entitled “Everything happens for a reason” — and other lies I’ve loved. After that, make a summary of the video while quoting some information or lesson that caught your attention or feelings.
https://youtu.be/DTcJmIbn5nw
VI. Assignment Students will be asked to interview one or more of their family members about the importance of education. Then, they will be asked to make a summary about their interview to their family members.
Share this:
Published by Shane Montalvo
View all posts by Shane Montalvo
One thought on “ Lesson Plan for Grade 8: Direct and Reported Speech ”
- Pingback: Assessment 5.3 – Lesson Plans – Shane Montalvo
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
NCERT Guides.Com
Free NCERT Solutions
- Class 8 NCERT Solutions
Reporting Questions | Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 8
by Manjusha · Published June 24, 2021 · Updated May 5, 2024
When we report a question we normally use the reporting verb asked.
Note that a reported question has the same word order as a sentence. That means in a reported question, the subject goes before the verb.
Study the examples given below.
- The teacher said to the boy, ‘What are you doing there?’
- The teacher asked the boy what he was doing there . (NOT The teacher asked the boy what was he doing there.)
A reported question does not have a question mark.
Report the questions given below.
1. He asked me, ‘Why did you insult my brother?’
2. ‘Where did you go yesterday?’ the man said to his servant.
3. ‘When will your classes start?’ the father said to his daughter.
4. The teacher asked, ‘Why were you absent yesterday?’
5. ‘How far the railway station is from here?’ the old man enquired.
6. ‘Where can I buy that book?’ the boy said.
7. ‘When do you usually reach office?’ I said to him.
8. ‘Where does he keep his money?’ they asked her.
9. ‘Why are you in a hurry, young man?’ said the Sage.
10. ‘When are you leaving for Delhi?’ He asked me.
11. ‘Where were you all the time?’ the father asked the daughter.
12. ‘Why didn’t you consult a doctor?’ she asked me.
1. He asked me why I had insulted his brother.
2. The man asked his servant where he had gone the previous day.
3. The father asked his daughter when her classes would start.
4. The teacher asked me why I had been absent the day before.
5. The old man asked how far the railway station was from there.
6. The boy asked where he could buy that book.
7. I asked him when he usually reached office.
8. They asked her where he kept his money.
9. The Sage asked the young man why he was in a hurry.
10. He asked me when I was leaving for Delhi.
11. The father asked the daughter where she had been all the time.
12. She asked me why I hadn’t consulted a doctor.
- Direct and indirect speech worksheet for classes 7 and 8
- Changing yes/no questions from direct speech to indirect speech
Tags: class 8 reported speech worksheet direct and indirect speech worksheet for class 8 reported speech worksheet for class 8 reporting questions worksheet
- Next story Reporting Yes/No Questions Worksheet For Class 8
- Previous story Participles Worksheet For Class 8 | Combine Using Participles
You may also like...
Ncert class 8 science chapter 5 coal and petroleum | important questions.
September 30, 2021
by Manjusha · Published September 30, 2021
Phrasal Verbs Worksheet For Class 8
June 23, 2021
by Manjusha · Published June 23, 2021 · Last modified May 21, 2024
Noun Clause, Adjective Clause Or Adverb Clause Exercise For Class 8
September 23, 2021
by Manjusha · Published September 23, 2021 · Last modified April 30, 2024
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Biographies
- Career Guidance
- Class 10 NCERT Solutions
- Class 2 Solutions
- Class 3 Solutions
- Class 4 Solutions
- Class 5 Solutions
- Class 6 NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Solutions
- Class 9 NCERT Solutions
- English Grammar
- English Grammar Worksheets
- English Vocabulary Exercises
- General Knowledge
- Inspirational Stories
- Kerala Syllabus English
- KSEEB Solutions
- Personality Development
- Political Science
- Sample Question Papers
- Social Science
- State Boards
- Tamil Nadu Board
- West Bengal Board
- Writing Skills
- Underline the Proper Nouns Worksheet for Class 2
- Reported Speech Exercise for Class 10 TN Board
- List of Plural Nouns for Class 10
- Suffixes Worksheet for Class 10
- Synonyms Worksheet for Class 10 TN Board
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Minutes after Trump shooting, misinformation started flying. Here are the facts
What began as a jubilant rally for Donald Trump, just days before he becomes the official Republican presidential nominee, ended in mere minutes with the former president bloodied and a suspected would-be assassin shot dead by Secret Service.
Trump 2024 flag is raised outside of Trump Tower, Sunday, July 14, 2024, in New York. (AP Photo/Yuki Iwamura)
- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — Within minutes of the gunfire, the attempted assassination of former President Donald Trump spawned a vast sea of claims — some outlandish, others contradictory — reflecting the frightening uncertainties of the moment as well as America’s fevered, polarized political climate.
The cloudburst of speculation and conjecture as Americans turned to the internet for news about the shooting is the latest sign of how social media has emerged as a dominant source of information — and misinformation — for many, and a contributor to the distrust and turbulence now driving American politics.
Mentions of Trump on social media soared up to 17 times the average daily amount in the hours after the shooting, according to PeakMetrics, a cyber firm that tracks online narratives. Many of those mentions were expressions of sympathy for Trump or calls for unity . But many others made unfounded, fantastical claims.
“We saw things like ‘The Chinese were behind it,’ or ‘ Antifa was behind it,’ or ‘the Biden administration did it.’ We also saw a claim that the RNC was behind it,’” said Paul Bartel, senior intelligence analyst at PeakMetrics. “Everyone is just speculating. No one really knows what’s going on. They go online to try to figure it out.”
Here’s a look at the claims that surfaced online following the shooting:
Claims of an inside job or false flag are unsubstantiated
Many of the more specious claims that surfaced immediately after the shooting sought to blame Trump or his Democratic opponent, President Joe Biden, for the attack.
Some voices on the left quickly proclaimed the shooting to be a false flag concocted by Trump, while some Trump supporters suggested the Secret Service intentionally failed to protect Trump on the White House’s orders.
The Secret Service on Sunday pushed back on claims circulating on social media that Trump’s campaign had asked for greater security before Saturday’s rally and was told no.
What to know :
- Timeline of events : How the assassination attempt on former President Donald Trump unfolded.
- RNC: The Republican presidential ticket came together when Trump named JD Vance as his running mate. Follow live updates .
- Biden’s response : The president says it was a “mistake” to say he wanted to put a “bull’s-eye” on Trump .
- Key question : Officials are demanding to know how an armed man was able to get to the top of a building and shoot the former president .
- A “man of conviction” : Victim Corey Comperatore, a former fire chief, used his body to shield his family from gunfire.
- Stay informed. Keep your pulse on the news with breaking news email alerts. Sign up here .
“This is absolutely false,” agency spokesman Anthony Guglielmi wrote Sunday on X. “In fact, we added protective resources & technology & capabilities as part of the increased campaign travel tempo.”
Videos of the shooting were quickly dissected in partisan echo chambers and Trump supporters and detractors looked for evidence to support their beliefs. Videos showing Secret Service agents moving audience members away from Trump before the shooting were offered as evidence that it was an inside job. Images of Trump’s defiantly raised fist were used to make the opposite claim — that the whole event was staged by Trump.
“How did the USSS allow him to stop and pose for a photo opp if there was real danger??” wrote one user, using the abbreviation for the U.S. Secret Service.
Social media bots helped amplify the false claims on platforms including Facebook, Instagram, X and TikTok, according to an analysis by the Israeli tech firm Cyabra, which found that a full 45% of the accounts using hashtags like #fakeassassination and #stagedshooting were inauthentic.
An image created using artificial intelligence — depicting a smiling Trump moments after the shooting — was also making the rounds, Cyabra found.
Moments like this are ‘cannon fodder’ for extremists
Conspiracy theories quickly emerged online that misidentified the suspected shooter, blamed other people without evidence and espoused hate speech, including virulent antisemitism.
“Moments like this are cannon fodder for extremists online , because typically they will react with great confidence to whatever has happened without any real evidence” said Jacob Ware, a research fellow at the Council on Foreign Relations. “People will fall into spirals and will advance their own ideologies and their own conclusions.”
Before authorities identified the suspect, photos of two different people circulated widely online falsely identifying them as the shooter.
In all the speculation and conjecture, others were trying to exploit the event financially. On X on Sunday morning, an account named Proud Patriots urged Trump supporters to purchase their assassination-attempt themed merchandise.
“First they jail him, now they try to end him,” reads the ad for the commemorative Trump Assassination Attempt Trading Card. “Stand Strong & Show Your Support!”
Republicans cast blame on Biden
After the shooting, some Republicans blamed Biden for the shooting, arguing sustained criticisms of Trump as a threat to democracy have created a toxic environment. They pointed in particular to a comment Biden made to donors on July 8, saying “it’s time to put Trump in the bullseye.”
Ware said that comment from Biden was “violent rhetoric” that is “raising the stakes,” especially when combined with Biden’s existential words about the election. But he said it was important not to make conclusions about the shooter’s motive until we know more information. Biden’s remarks were part of a broader approach to turn scrutiny on Trump, with no explicit call to violence.
Trump’s own incendiary words have been criticized in the past for encouraging violence. His lies about the 2020 election and his call for supporters to “fight like hell” preceded the Jan. 6, 2021, attack on the Capitol, which led to his second impeachment on charges of incitement of insurrection. Trump also mocked the hammer attack that left 80-year-old Paul Pelosi, the husband of the former House speaker, with a fractured skull.
Surveys find that Americans overwhelmingly reject violence as a way to settle political differences, but overheated rhetoric from candidates and social media can motivate a small minority of people to act, said Sean Westwood, a political scientist who directs the Polarization Research Lab at Dartmouth College.
Westwood said he worries that Saturday’s shooting could spur others to consider violence as a tactic.
“There is a real risk that this spirals,” he said. “Even if someone doesn’t personally support violence, if they think the other side does, and they witness an attempted political assassination, there is a real risk that this could lead to escalation.”
The Associated Press receives support from several private foundations to enhance its explanatory coverage of elections and democracy. See more about AP’s democracy initiative here . The AP is solely responsible for all content.

Suspect came within inches of killing Trump, but left few clues as to why
- Medium Text
NEVER KNOWN TO BE POLITICAL

Sign up here.
Reporting by Nathan Layne and Gabriella Borter in Bethel Park, Jasper Ward and Kanishka Singh in Washington; Additional reporting by Aaron Josefczyk in Bethel Park, Brendan O'Brien in Chicago, Tyler Clifford in New York, and Daniel Trotta in Carlsbad, California; Editing by Paul Thomasch, Lisa Shumaker and Lincoln Feast.
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

Thomson Reuters
Gabriella Borter is a reporter on the U.S. National Affairs team, covering cultural and political issues as well as breaking news. She has won two Front Page Awards from the Newswomen’s Club of New York - in 2020 for her beat reporting on healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic, and in 2019 for her spot story on the firing of the police officer who killed Eric Garner. The latter was also a Deadline Club Awards finalist. She holds a B.A. in English from Yale University and joined Reuters in 2017.

Bangladesh top court scraps most job quotas that triggered deadly protests
Streets near the Supreme Court were quiet after the decision and army teams were deployed throughout Dhaka. A military tank was stationed outside the Supreme Court gate, television footage showed.

Online Education Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8 CBSE With Answers

In Online Education When we want to tell somebody else what another person said, we can use either direct speech and reported speech.
When we use direct speech, we use the same words but use quotation marks, For example: Scott said, “I am coming to work. I will be late because there is a lot of traffic now.”
When we use reported speech, we usually change the verbs, specific times, and pronouns. For example: Scott said that he was coming to work. He said that he would be late because there was a lot of traffic at that time.
Online Education Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8 CBSE With Answers Pdf
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English will help you to write better answers in your Class 10 exams. Because the Solutions are solved by subject matter experts. https://ncertmcq.com/reported-speech-exercises-for-class-8/
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 8
Fundamentals: The art of reporting the words of a speaker is called Narration. It is of two types:-
- Direct Speech: We quote the actual words of the speaker in inverted commas: He said to me, “I am playing.”
- Indirect Speech: We quote the words or speech of the speaker in our own words, without inverted commas: He told me that he was playing.
In narration a sentence has two parts:-
- Reporting verb: He said to me,
- Reported speech: “I am playing.”
Reported Speech Class 8
Rules of Changing Pronouns
- The pronoun of First Person is changed according to the subject of Reported speech.
- The pronoun of Second Person is changed according to Object
- The pronoun of Third Person is not changed at all. (The formula to change pronoun is 123/SON.) SON: S – subject, O – object, N – no change
Persons: There are three types of persons:-
- First Person (I, we, my, me, our)
- Second Person (You, your)
- Third Person (He, she, it, his, they, them etc.)
Reported Speech Class 8 Exercise
Part-I (Assertive Sentences in Present or Future)
Rules 1. If Reporting Verb is in Present or Future Tense the tense of Reported speech is not changed. 2. (” “) inverted commas are replaced with the conjunction ‘that’. 3. Say to is replaced with tell, says to with tells and said to with told.
- The boys say, “We have learnt the lesson”. The boys say that they have learnt the lesson.
- Reena will say, “I am going to America”. Reena will say that she is going to America.
- The servant says to me, “The manager will come in the evening”. The servant tells me that the manager will come in the evening.
- He has said to them, “You were playing cricket yesterday.” He has told them that they were playing cricket yesterday.
Reported Speech Class 8 Exercise With Answers
Part-II (Assertive Sentences in Past)
Rules:- 1. ‘said to’ is changed into ‘told’. 2. Use conjunction ‘that’ to connect 3. If Reporting Verb is in Past Tense the tense of the Reported Speech is changed according to the rules given below: –
- Present Indefinite changes to Past Indefinite
- Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous
- Present Perfect changes to Past Perfect
- Present Perfect.Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Indefinite changes to Past Perfect
- Past Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous
- Will/Shall changes to Would/Should
- Can changes to Could
- May changes to Might
In Reported Speech words showing nearness changes into words showing distance:-
- This becomes That
- These becomes Those
- Now becomes Then
- Today becomes That day
- Tonight becomes That night
- Yesterday becomes The previous day
- Last night becomes The previous night
- The next day becomes The following day
- Here becomes There
- Ago becomes Before
Reported Speech For Class 8
- He said, “I am going to college today.” He said that he was going to college that day.
- Sunny said to me, “You will get good marks in this test.” Sunny told me that I would get good marks in that test.
- She said to her mother, “My teacher awarded me yesterday.” She told her mother that her teacher had awarded her the previous day.
- Rajani said to her friends, “You were shopping in the market.” Rajani told her friends that they had been shopping in the market.
- I said, “Ritu, you will learn very fast.” I told Ritu that she would learn very fast.
- “I may go to London next month,” he said. He told that he might go to London the following month.
Note: If Reported Speech has an explanation of Universal Truth, Habitual Fact or Historical Fact its Tense is not changed at all. Examples:-
- He said, “The earth moves round the sun.” He.said that the earth moves round the sun.
- She said to me, “Mohan plays with left hand.” She told me that Mohan plays with left hand.
- The teacher said to the students, “India became independent in 1947.” The teacher told the students that India became independent in 1947.
Reported Speech Exercise Class 8
Part-III (Interrogative Sentences) Rules: 1. In Interrogative sentences said or said to of reporting verb are replaced with asked or enquired. 2. If the interrogative (question) begins with Helping Verb or Modal (is, am, are, do, does, was, were, has, have, had, will, shall, would, can, could, should, may, might, must, etc.) the inverted commas (” “) are replaced with the conjunction if or whether. 3. If the interrogative (question) begins with WH-family (Why, what, which, when, whose, who, whom, how, etc.) the inverted commas (” “) are not replaced with any conjunction at all. 4. If there are no interrogatives (questions) in indirect speech we place helping verb or modal after the subject.
- The teacher said to us, “Have you completed your home work?” The teacher asked us if we had completed our home work.
- He said to me, “Did you finish your work yesterday?” He asked me if I had finished my work the previous day.
- Rocky said, “Meena, do you want to go to Shimla?” Rocky asked Meena if she wanted to go to Shimla.
- I said to him, “Will you return tomorrow?” I asked him if he would return the next day.
- Ravi said to him, “What have you learnt?” Ravi asked him what he had learnt.
- She said, “Which train will go to Jaipur?” She enquired which train would go to Jaipur.
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 8 Pdf With Answers
Interrogative Sentences in present or future:
- She says to them, “Have you taken the money?” She asks them if they have taken the money.
- He will say to me, “What can I do for you?” He will ask me what he can do for me.
Part-IV (Imperative Sentences) Rules: 1. In Imperative sentences said to is replaced with ordered, commanded, advised, suggested, proposed, persuaded, warned, etc. 2. Inverted commas (” “) are replaced with ‘to’. The first form of verb is applied after ‘to’. 3. In Negative sentences ‘said’ to is replaced with ‘forbade’ or ‘do’ is replaced with ‘not’.
- She said to me, “Work hard”. She advised me to work hard.
- I said to my friend, “Please give me your car for two hours.” I requested my friend to give me his car for two hours.
- She said to Meena, “Do not make a noise”. She forbade Meena to make a noise. (or She ordered Meena not to make a noise.)
- The general said to the soldiers, “March forward.” The general commanded the soldiers to march forward.
- Ramesh said to him, “Let me do my home work.” Ramesh requested him to let him do his home work.
- The manager said to the peon, “Let the visitors come in.” The manager ordered the peon to let the visitors come in.
- He said to me, “Let us go on picnic this Sunday”. He proposed/suggested me that we should go on a picnic that Sunday. (or He proposed me to go on a picnic that Sunday.
- He said, “Thank you, doctor.” He thanked the doctor.
- Dinkar said to me, “Beware of such politicians.” Dinkar warned me against such politicians.
Reported Speech Exercise For Class 8
PART-V (Exclamatory Sentences)
Rules: 1. Use conjunction ‘that’ to connect the speech with reporting verb. 2. Change tenses according to the rules learnt in PART-II. 3. ‘Said’ is mostly changed into ‘exclaimed’ (sometimes ‘applauded saying’) 4. Replace ‘what’ or ‘how’ with ‘very’ (sometimes ‘big’ or ‘great’). 5. Replace exclamatory words as follows: AH!, Alas!…. with sorrow; Aha!, Ha!, Hurrah! ….with joy; Oh with surprise; Pooh! ….with contempt; Sorry! with regret, Bravo! with applauded saying.
- The child said, “What a bitter medicine!” The child exclaimed that the medicine was very bitter.
- He said, “How big the train is!” He exclaimed that the train was very big.
- Vikas said, “Alas! I have lost my wallet.” Vikas exclaimed with sorrow that he had lost his wallet.
- Rajani said to her friend, “Pooh! You have cheated me.” Rajani exclaimed with contempt that her friend had cheated her.
- The captain said to the players, “Bravo! You played well today.” The captain applauded his players saying that they had played well that day.
Reported Speech Worksheet For Class 8 Pdf
PART-VI (Optative Sentences)
Rules: 1. Such sentences indicate greeting & wishes (good morning, good noon, good day, would that, etc.), and prayer (may, may God). Therefore ‘said’ is mostly replaced with ‘wished’ or ‘prayed’. 2. In case of good bye, farewell, good night (when parting company) ‘said’ is replaced with ‘bade’. Examples:-
- He said, “Good morning uncle!” He wished his uncle good morning.
- Ranjita said, “Good bye friends!” Ranjita bade her friends good bye.
- My grandmother said to me, “May you live long.” My grandmother prayed me that I might live long.
- Montu said, “Would that I were a minister!” Montu wished that he had been a minister.
Reported Speech Exercises For Class 8 With Answers
Indirect Speech of two or more sentences:
- She said to me, “I am going to the market. Do you want to go?” She told me that she was going to the market and asked if I wanted to go.
- The manager said to the clerk, “You may leave now. Don’t forget to keep these files in the file cabinet.” The manager told the clerk that he might leave then and ordered not to forget to keep those files in the file cabinet.
- The doctor said to the patient, “Why didn’t you come yesterday. You have a high fever.” The doctor asked the patient why he hadn’t come the previous day as he had a high fever was high.
- I said to Rocky, “Don’t abuse others. It is a bad habit. How will you feel if others abuse you?” I advised Rocky not to abuse others because it is a bad habit and asked how he would feel if others abused him.
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 8 CBSE
Reported Speech Class 8 Worksheet Question 1. Fill in the blanks (i) She looks pretty sick. I think she _____________ go to a doctor. (a) should (b) can Answer: (a) should
(ii) You’ve been driving all day. You _____________ be exhausted! (a) should (b) must Answer: (b) must
(iii) You _____________ smoke so much. It’s bad for your health. (a) can’t (b) shouldn’t Answer: (b) shouldn’t
(iv) Hey I’m lost _____________ you help me? (a) can (b) should Answer: (a) can
(v) You have such a beautiful voice. You _____________ sing for us! (a) should (b) can Answer: (a) should
(vi) I know he speaks five languages, but _____________ he speak Arabic? (a) should (b) can Answer: (b) can
(vii) That looks very expensive. It _____________ have cost a fortune! (a) should (b) must Answer: (b) must
(viii) I _____________ believe that you failed your test! (a) can’t (b) shouldn’t Answer: (a) can’t
(ix) I’m on my way. I _____________ be there in about 10 minutes. (a) should (b) can Answer: (a) should
(x) I _____________ afford that. (a) can’t (b) shouldn’t Answer: (a) can’t
Exercise On Reported Speech For Class 8 Question 2. Complete the sentences. (i) Jacob: “I work in an office.” Jacob told me (that) _____________ worked in an office.
(ii) Ryan and Lucas: “We play football.” Ryan and Lucas told me (that) _____________ played football.
(iii) Victoria: “I like my cat.” Victoria told me (that) _____________ liked _____________ cat.
(iv) Henry: “Can you see me?” Henry asked me if _____________ could see
(v) Julian: “I will have to borrow your pencil.” Julian told me (that) _____________ would have to borrow
(vi) Melanie: “My father is Jamaican.” Melanie told me (that) _____________ father is Jamaican.
(vii) Emma and Doris: “Can we use your camera?” Emma and Doris asked me if _____________ could use _____________ camera.
(viii) Leah: “How is your journey?” Leah’ asked me how _____________ journey was.
(ix) Isabella and Ella: “We love our pets.” Isabella and Ella told me (that) _____________ loved _____________ pencil.
(x) Grandmother: “Please bring me a cup of my tea.” Grandmother told me to bring _____________ a cup of _____________ tea. Answer: (i) he (ii) they (iii) she, her (iv) I, him (v) he, my (vi) her (vii) they, my (viii) my (ix) they, their (x) her, her.
Question 3. Change the direct speech into reported speech. Choose the past simple of ‘ask’, ‘say’, or ‘tell: (i) “Don’t do it!” She _____________
(ii) “I’m leaving tomorrow” She _____________
(iii) “Please get me a cup of tea” She _____________
(iv) “She got married last year” She _____________
(v) “Be quick!” She _____________
(vi) “Could you explain number four, please?” She _____________
(vii) “Where do you live?” She _____________
(viii) “We went to the cinema and then to a Chinese restaurant” She _____________
(ix) “I’ll come and help you at twelve” She _____________
(x) “What are you doing tomorrow?” She _____________ Answer: When I used ‘said’ you can also use ‘told me’) (i) She told me to do it. (ii) She said (that) she was learning tomorrow. (the next day). (iii) She asked me to get her a cup of tea. (iv) She said (that) she got married last year. (v) She told me to be quick. (vi) She asked me to explain number four. (vii) She asked me where I lived. (viii) She said (that) they went (had been) to the cinema and then to a Chinese restaurant. (ix) She said (that) she would come and help me at twelve. (x) she asked me what I was doing tomorrow (the day after).
Reported Speech Practice Examples Exercises for Class 8 CBSE
Question 1. Change the direct speech into reported speech. Choose the past simple of ‘ask’, ‘say, or “tell: (i) “Don’t go!”. She _____________
(ii) “Do you work in London?” She _____________
(iii) “Could you tell me where the post office is?” She _____________
(iv) “Come here!” She _____________
(v) “I’ve never been to Wales” She _____________
(vi) “Have you ever seen ‘Lord of the Rings?” She _____________
(vii) “I don’t like mushroom” She _____________
(viii) “Don’t be silly!” She _____________
(ix) “Would you mind waiting a moment please?” She _____________
(x) “How often do you play sport?” She _____________
Question 2. Write here, that day, the day before, the next day, the week before, according to the sentences.
1. Anita (a week ago): “Tanya and I are going to a concert tomorrow.” You (today): Anita said she and Tanya were going to a concert ________ 2. Jyoti (two days ago): “I’ve only been in England since yesterday.” You (today): Jyoti said he had only been in England since ________ 3. Nitin (a week ago): “I’m meeting my friend at the airport later today.” You (today): Nitin said he was meeting his friend at the airport later ________ 4. Mohan (in the street): “I’ll see you at the coffee bar.” You (at the coffee bar): Mohan said he would see me ________ 5. Pawan (a month ago): “The festival was in the last week.” You (today): Pawan told me the festival had been ________
Advertisement
Supported by
A Fiery Biden, Ignoring Critics, Attacks Trump to Chants of ‘Lock Him Up’
Facing rising frustration in his party, the president brushed it off in an energetic speech in Michigan. Inside the room, at least, the Democratic mood was defiant, with cheers of “Don’t go, Joe.”
- Share full article

By Nicholas Nehamas and Reid J. Epstein
Nicholas Nehamas reported from Detroit, and Reid J. Epstein from Washington.
President Biden on Friday strove to turn the nation’s attention back to former President Donald J. Trump, delivering a fiery and energetic speech in battleground Michigan that painted his Republican rival as a convict, a rapist and a cheater while simultaneously attacking the news media for an insufficient focus on such misdeeds.
Even as Mr. Biden faces mounting pressure from congressional Democrats and major donors , he largely ignored the brewing Democratic revolt over his refusal to drop out of the race, beyond an emphatic statement that “I am running, and we’re going to win.”
The president’s defiance, and the crowd’s enthusiastic response, helped give the Biden event at a Detroit high school gym the flavor of a Trump rally at times. When Mr. Biden referred to his political opponent, there were chants of “Lock him up” — which the president did not discourage. When he criticized news media coverage, big cheers followed, with his supporters turning to boo and point fingers at reporters.
Mr. Biden thundered that his rival was a “convicted criminal” and a “business fraud,” and said that he had “raped” the writer E. Jean Carroll, whom Mr. Trump was found liable of sexually abusing by a civil court.
In all, the 35-minute speech was a version of Mr. Biden that has been absent since he began his re-election campaign — and maybe one not seen since he was on a presidential ticket with Barack Obama. After two weeks of Democratic panic since his distressing debate performance, plummeting donations and polls that show him falling further behind Mr. Trump, Mr. Biden acted as if he was in the presidential race to stay.
“I’m the nominee of the Democratic Party, the only Democrat or Republican who has beaten Donald Trump ever,” said Mr. Biden, whose remarks were greeted by loud chants of “Don’t go, Joe” and “Don’t you quit.”
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. When the Reporting Verb is in Past Tense. When the reporting verb is past tense, the change of reported speech takes place as shown below. Read the following examples. Direct The man said to the boy, " You are not serious about your studies.". Indirect The man told the boy that he was not serious about his studies.
Here are some distinctive points regarding the Direct Speech and Indirect Speech : In the Direct Speech. 1. The Reported Speech is put within Reported (Inverted) Commas. 2. The Reported Speech and the Reporting Verb are separated by a Comma. 3. The first word of the Reported Speech begins with a capital letter.
Class 8 English Grammar Reported Speech (Direct and Indirect) Exercise with Answer. Reported Speech - Reported speech refers to recording the speaker's speech, whether it is done directly by recording the speaker's words or indirectly by recording the speaker's words but changing them. For example. Shyam said, "Taj Mahal was built by ...
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 8 CBSE With Answers. When we want to tell somebody else what another person said, we can use either direct speech and reported speech. When we use direct speech, we use the same words but use quotation marks, For example: Scott said, "I am coming to work. I will be late because there is a lot of traffic now
Reported Speech Practice Exercises for Class 8 CBSE. A. Write the following sentences in indirect speech. The first one has been done for you. 1. He said, "I will meet you outside the post office at three tomorrow afternoon.". He said that he would meet me outside the post office at there the following afternoon.
on October 25, 2023, 5:50 AM. Class 8 English Grammar Chapter 16 Direct and Indirect Speech. When we use the actual words of the speaker, we use Direct Speech but when we report what he said in our own words, we use Indirect Speech. The actual words of the speaker are called Reported Speech and the verb introducing the Reported Speech is called ...
Reported speech is used when someone says a sentence, like, "I'm going to the movie tonight". Later, we want to tell a 3rd person what the first person is doing. It works like this: We use a reporting verb i.e 'say' or 'tell'. In the present tense, just put in 'he says. Direct Speech: I like burgers.
clause should be used at the end of the sentence.At. tence full stop should be placed.Indirect SpeechImage: Indirect Speech It is the speech that tells what someone has said but it does. not explain the actual words spoken by the person. It just conveys the basic n. rration of what is being said to the third p.
Whenever you report a speech there's a reporting verb used like "say" or "tell". For example: Direct speech: I love to play football. Reported speech: She said that she loves to play football. (Note 1 : Assume a gender if not mentioned already. Note 2: Using "that" is optional.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
My mother said to me, "Clean your room immediately." My mother ordered me ___________ at that time. The boys said, "Hurray! we have won the match." The boys exclaimed with joy __________. [Intermediate] Learn the concepts of Class 8 English Transformation of Sentences with Videos and Stories. Identify direct and reported speech, understand how ...
The PDFs include reported speech exercises for Class 8 CBSE with answers, tips and tricks to learn grammar faster, sample question papers, etc. The PDFs of Vedantu are downloadable from the comfort of your homes. They are free. The content is regularly updated by Vedantu's subject matter experts.
Reported Speech Class 8 English Grammar Worksheet - Change Sentences into Indirect Speech. Q1.) Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech. (15 marks) 1.) Ram said, "I attend the class every day.". 2.) He said to me, " My name is Ram". 3.) He said to me, " I am listening to the radio.".
Rule 1: Change of Tense. 1. If the reporting verb is in the Present or Future tense (e.g. say, will say) there is no change in the tense of the verb in the Indirect Speech. For Example, Direct: Sabita says ( present ), " I can do ( present) the sum.". Indirect: Sabita says ( present) that she can do ( present) the sum.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise 1. Convert the following sentences from direct to indirect speech. Direct: He said, "I am going to the park.". Direct: "I have completed my homework," said Marie. Direct: "It's raining outside," she said. Direct: "We will visit the church tomorrow," they told us. Direct: "I love waffles ...
Language: English (en) ID: 78911. 01/04/2020. Country code: PL. Country: Poland. School subject: English as a Second Language (ESL) (1061958) Main content: Reported speech (2013113) From worksheet author: This is an activity to revise statements and questions in reported speech.
C. Abstraction. Direct Speech - is a sentence in which the words that someone have been said are written exactly on the sentence. It is usually reproduced in speech marks or also known as quotation marks or inverted commas. For example: The policeman said, "All kids are safe.". Anna said, "I've been in Paris.".
Report the questions given below. 1. He asked me, 'Why did you insult my brother?'. 2. 'Where did you go yesterday?' the man said to his servant. 3. 'When will your classes start?' the father said to his daughter. 4. The teacher asked, 'Why were you absent yesterday?'.
After the shooting, some Republicans blamed Biden for the shooting, arguing sustained criticisms of Trump as a threat to democracy have created a toxic environment. They pointed in particular to a comment Biden made to donors on July 8, saying "it's time to put Trump in the bullseye."
The portrait pieced together so far of the 20-year-old nursing home aide who allegedly tried to assassinate Donald Trump at an election rally reveals frustratingly little about why he would make ...
Cut the Education Department: Project 2025 would make extensive changes to public schooling, cutting longtime low-income and early education federal programs like Head Start, for example, and even ...
President Biden made clear he would not step aside from the presidential race and sought to reassure his top donors and fund-raisers, a day after some House members privately said he should drop out.
Vice President Kamala Harris condemned former President Donald J. Trump as a leader who "incites hate" during an address on Saturday at a convention of Asian American voters in Philadelphia.
Reported Speech Class 8 Exercise With Answers. Part-II (Assertive Sentences in Past) Rules:-. 1. 'said to' is changed into 'told'. 2. Use conjunction 'that' to connect. 3. If Reporting Verb is in Past Tense the tense of the Reported Speech is changed according to the rules given below: -. Present Indefinite changes to Past Indefinite.
Facing rising frustration in his party, the president brushed it off in an energetic speech in Michigan. Inside the room, at least, the Democratic mood was defiant, with cheers of "Don't go ...