- English Grammar

Wishes and hypotheses
Level: intermediate
We use the verb wish or the phrase if only to talk about things which we want but which are not possible:
I wish I could see you next week. If only we could stop for a drink. I wish we had a bigger house. They are always busy. If only they had more time. John was very lazy at school. Now he wishes he had worked harder.
We use wish and if only with past tense forms :
- We use past tense modals would and could to talk about wishes for the future :
I don't like my work. I wish I could get a better job. That's a dreadful noise. I wish it would stop. I always have to get home early. If only my parents would let me stay out later.
- We use past simple and continuous to talk about wishes for the present :
I don't like this place. I wish I lived somewhere more interesting. These seats are very uncomfortable. I wish we were travelling first class. I wish I was taller. John wishes he wasn't so busy. I'm freezing. If only it wasn't so cold.
- After I/he/she/it , we can use were instead of was :
I wish I was/were taller. John wishes he wasn't/weren't so busy. I'm freezing. If only it wasn't/weren't so cold.
- We use the past perfect to talk about wishes for the past :
I wish I had worked harder when I was at school. Mary wishes she had listened to what her mother told her. I wish I hadn’t spent so much money last month.
MultipleChoice_MTY0NzM=
GapFillTyping_MTY0NzQ=
Hypotheses (things we imagine)
Expressions.
When we are talking about hypotheses, we use expressions like:
We use these expressions:
- with present tense forms to talk about the present or future if we think something is likely to be true or to happen:
We should phone them in case they are lost. Those steps are dangerous. Suppose someone has an accident.
- with past tense forms to talk about the present or future to suggest something is not likely to be true or to happen:
Imagine you won the lottery. What would you do with the money? What if he lost his job? What would happen then?
- with the past perfect to talk about things in the past which did not happen :
Suppose you hadn't passed your exams. What would you have done? What if he had lost his job? What would his wife have said?
Modal verbs
We use modals would and could for a hypothesis about the present or future :
We can't all stay in a hotel. It would be very expensive. Drive carefully or you could have an accident.
We use would in the main clause and the past tense in a subordinate clause for a hypothesis about the present or future :
I would always help someone who really needed help. I would always help someone if they really needed it.
We use modals with have to talk about something that did not happen in the past :
I didn't see Mary, or I might have spoken to her. It's a pity Jack wasn't at the party. He would have enjoyed it. Why didn't you ask me? I could have told you the answer.
We use would have in the main clause and the past perfect in a subordinate clause to talk about something that did not happen in the past :
I would have helped anyone who had asked me. I would have helped you if you had asked me.
MultipleChoice_MTY0NzU=
GapFillTyping_MTY0NzY=
Hello Kirk Why do you use the simple past with wish with some verbs are correct with other verbs are incorrect and both meaning are not true examples about future those example are incorrect and I mean is not true I wish you came tomorrow I wish it rained tomorrow
and those example are correct and I mean is not true I wish John wasn't busy tomorrow I wish that we didn't need to work tomorrow
examples about present this example is incorrect and I mean is not true I wish it didn’t rain heavily now
this example is correct and I mean is not true I wish it wasn't raining heavily now I wish that I had a big house now I wish my students studied more ( I don't know about now or repeatedly or regularly )
I think with wish with simple past I use stative verbs only to talk about now and future and Non-stative verbs I use to talk about repeatedly or regularly same meaning simple present
- Log in or register to post comments
The difference between the first two sentences and the second two is that the second two are clearly referring to scheduled events; it's as if we're looking at a diary and can see that John is busy and that we have to work. The past tense refers to an unreal/untrue situation.
The first two sentences are unnatural. You could say 'I wish you were coming tomorrow'; the continuous tense has the same idea as the present continuous does for talking about the future. The second sentence is unnatural because we don't use the present simple to talk about the weather at a specific time like tomorrow; in the same line, we don't use the past simple to refer to an unreal event at a specific time.
The fifth sentence is not correct because it's a simple tense. We use continuous tenses to talk about the weather at a particular time like now.
Hope this helps.
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hello Team Do stative verbs with the simple past mean now and also the future and means simple present habits and facts? I wish I was taller means now I wish John wasn't busy tomorrow means future I wish that he didn't need to work all my life means simple present habits and facts but with Non-stative verbs with simple past can not use for now and future I can use only for mean simple present habits and facts
- 'I wish I was taller.'
- 'I wish John wasn't busy tomorrow.'
- 'I wish that he didn't need to work all my life.'
As you say, 1 refers to the present. It's a wish about your height now.
As you say, 2 refers to the future ('tomorrow').
In 3, the past verb form 'didn't need' refers to the present. It means that he does need to work all my life, but you that you wish this was not true.
Unless I'm forgetting something, it doesn't matter whether the verb after 'I wish' is stative or not. Non-stative verbs have similar meanings to 1-3 above. For example, 'I wish we were travelling first class' is very similar to 3. Or 'I wish my students studied more' also refers to a present situation and talks about a situation that is not true.
Does that answer your question?
Hello, how are you? Can you tell me if I have understood correctly? 1 - I wish my English would get better with more practice → I think it"s impossible 2 - I hope my English will get better with more practice → I think it's possible Thank you in advance and happy new year! Fanny
Hello Pompsinette,
Yes, those sentences are correct. However, the first one does not mean that it is impossible but rather than it is not happening yet. That means a dialogue like this is possible:
A: I wish my English would get better with more practice, but it just doesn't seem to be happening. B: Don't give up! Sometimes you don't see any progress and then suddenly there's a leap forwards!
The LearnEnglish Team
Hi, I have a few questions: 1) When I say I wish it would stop raining, does it mean it won't happen ( it probably won't stop raining) 2) If yes, does 'wish' prefer something likely to happen while 'hope' prefers something unlikely to happen 3) When I say "I wish you a good day" and "I hope you have a good day", is there any difference in the meaning like the probabilities of something will happen? Thanks in advance
Hello wkey12,
1) It means a) that it is raining and b) that you expect it to continue raining. You don't like the situation but you're pretty sure that it will continue.
2) We use 'wish [that]' to speak about something we would like to happen but which we consider unlikely. Your previous sentence about the rain is a good example. It can also be used to speak about a regret, i.e. a wish that something was different in the past: 'I wish I had worked harder in school. Now I could get a better job if I had.'
3) The use of 'wish' in 'I wish you a good day' is different from 2. In this case, 'wish' means 'hope you have'. Except for its use in some set expressions (e.g. 'I wish you a Merry Christmas' or 'Wishing you a happy birthday'), this use of 'wish' as a verb is unusual in most situations nowadays. There is no difference in meaning or probability between the two forms. The difference is that 'wish' is a form we don't use nearly as much as 'I hope'.
Great questions!
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hello can I use past simple for future examples I wish it rained tomorrow I wish you came tomorrow I wish I stayed with you longer is this correct ?
No, the past tense forms here don't express wishes for the future. Instead, they communicate the idea of something that doesn't exist or isn't true or possible:
- 'I wish it were raining' means that it's not raining now but that I want it to rain
- 'I wish you could come tomorrow' means that I would like you to come tomorrow but you cannot
- 'I wish I could stay with you longer' means I'd like to stay longer but I can't
We often use 'hope' to express wishes for the future. So your sentences should be something like:
- 'I hope it rains tomorrow'
- 'I hope you come tomorrow'
- 'I hope I can stay with you longer'
Does that make sense?
Please help me know which sentence is correct: It rains heavily, so I can’t go out. I wish it didn’t rain heavily so that I can go out. Or I wish it didn’t rain heavily so that I could go out.
Hi Rita_79,
If you are talking about rain at this moment (the moment of speaking), it would be better to use a continuous form (e.g. It's raining ). Simple forms ( it rains = present simple; it didn't rain = past simple), mean the idea of raining repeatedly or regularly (e.g. It rains very often in London ).
So, to talk about the rain right now, you can say either of these options.
- It's raining heavily, so I can’t go out.
- I wish it wasn't raining heavily so that I could go out. ("could" is needed, because this is an unreal action, not a real action)
I hope that helps.
LearnEnglish team
Hello respected team, school boards have the power to change this situation. Were they, for example, to mandate that every school employ a nutritionist to oversee cafeteria offerings as well as conduct healthy eating workshops, this could easily change the reality on the ground and going forward. The sentence "Were they, for example, to mandate that every school.." why "were" is in the beginning of the sentences? Where can I read about this? Thank you
Hi Hosseinpour,
This structure is called an inverted second conditional. The meaning is the same as "If they mandated that ..." or "If they were to mandate that ...". You can read more about this on our new C1 grammar page, Inversion and conditionals (linked) .
I hope it helps.
Thank you sir for the help and time. Thank you
Hi, I have a wonder. In this article, you say 'when we talk about wishes for futures, we use wish + would/ could", but in a video of BBC Learning (I attached the link below), they say "we use 'hope' for wishes in the futures'. Can you explain this difference? Thanks! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LJcXRxy-nDU
Hello janele9284,
We use wish + could/would to talk about situations in the future that we do not believe will come true. In this sense they are true wishes, not expectations or beliefs. In all of the examples on the page, the situation is one in which the desired outcome is a dream or fantasy, not a reality:
I don't like my work. I wish I could get a better job. [...but I can't] That's a dreadful noise. I wish it would stop. [...but it won't] I always have to get home early. If only my parents would let me stay out later. [...but they won't ]
Hope (or other verbs like want, desire, plan, mean, intend, expect etc) suggests that something is a realistic possibility. We have some optimism that it can occur. For example:
I hope I win the lottery! [I have a ticket - there's a chance] I wish I could win the lottery! [I don't believe it will happen - in fact, I may not even have a ticket]
Hi! What verbs would you use in a sentence where another clause is inside a hypothetical clause? For example:
I wish that the class were one of the one that was offered to everyone.
Should the "was" be another "were"? "that were offered to everyone"? "that would be offered to everyone"? Which of these is most right?
Hello bbctol,
The correct sentence would be as follows:
I wish that the class were one of the ones that was offered to everyone.
Inside the relative clause here (that was offered...) there is no hypothetical meaning. It has an adjectival function providing a description of the preceding noun phrase.
Dear teacher, I have a question about the usage of wish in the present and in the future. I think they should be all the wish in the future, due to it's contrary to the fact of this moment, nothing is real now, so can I use all the present wish with wish structure in the future (with "would", "could") ?. For example, I'd use lesson examples:
I don't like this place. I wish I lived somewhere more interesting. ==> Can I say : I don't like this place. I wish I could live somewhere more interesting ? John wishes he wasn't so busy. ==> Can I say : John wishes he wouldn't be so busy. Don't you ever wish you ___ more free time? ==> the answer is "had", but I want another answer, can I say Don't you ever wish you could have more free time ?
Hello lien.t,
Re: 1, you can say both 'I wish I lived' and 'I wish I could live', but there is a slight difference in meaning. 'I wish I could live' focuses on your ability to live in a different place -- perhaps, for example, you have the money to live in a different city, but you need to stay where you are so that you can take care of your elderly parents. 'I wish I lived' doesn't focus on ability; it's less specific.
Re: 2, we don't typically use 'I wish I would + verb' but instead 'I wish I verb-ed' (past form). We do use 'I wish (some other subject) + would + verb'. In this case, 'would' expresses the idea of the person or object not being willing to act as we wish. This is mentioned on our Wishes: 'wish' and 'if only' page.
3 is similar to 2. It's not correct to say 'John wishes he wouldn't be so busy'.
Re: 4, yes, you could also say 'could have'. It's similar to 1.
Does that help make sense of it?
Dear teacher Kirk, yes I can understand now. Thank you so much!
Hello, About the verb "wish", in the present tense form, for something is likely to be true or to happen. In the two sentences below: I wish my English becomes better with practice or I would like my English to become better with practice Is there any difference, or is the meaning the same?
Thanks for your reply.
Hello User_1,
'I wish my English becomes better with practice' is not correct -- we use a past form of some sort after 'wish' to express the idea of unreality, i.e. that things are not how we want them to be. I don't know Italian, but in Spanish and Catalan, for example, a subjunctive form is used to express this idea; in English, we use a past form as a kind of subjunctive form for the same purpose.
So you could say ' I wish my English became better with practice' and that would be correct. This expresses a wish that you don't think can be fulfilled; it means that your English is not improving despite your practice.
Or you use 'I hope' to express a wish for the future: ' I hope my English becomes better with practice'. This expresses a wish that you do think can be fulfilled.
I hope this helps you.
Hello Kirk, I am really sorry for my mistake. I got confused. Thanks for your explanation.
For sure, I prefer the expression "I hope my English becomes better with practice", and I hope this becomes reality.
All the best
No need to apologize! Making mistakes is an essential part of the learning process and I'm glad the explanation was useful.
Which one correct 1. It is raining outside. I wish I slept I wish I was sleeping
Hi MirnaS,
It should be I wish I was sleeping - because the idea is sleeping as a continuous action going on at the moment of speaking.
I hope that helps!
Hello everyone!
I have a question about “wish” when it refers to present and past. Here’s a situation:
Robin: I go to work by car. How do you go to work? Jack: I always go to work on my foot. I wish I went to work by car.
Robin: I don’t smoke. What about you? Jack: I smoke. I wish I didn’t smoke.
Do these wish sentences are correct If we consider them as a state?
Hello khaledA15,
Yes, those sentences are fine. You can also use modal verbs to refer to possibility:
I wish I could go to work by car but it's not possible.
I wish I was able to stop smoking, but it's too difficult.
Thank you so much for this clarification
Please help I am so confused about this kind of sentences: The situation is: I did not pass the exam just now. Can I say: 1) I wish I passed the exam as a present wish. Or 2) I wish I had passed the exam as a past regret. ???
Hello AboodKh9,
After 'wish' we move the tense (time reference) backwards to show that we are talking hypothetically. Thus, a wish or regret about the present uses past:
I wish I was taller! [wishing something about the present]
A wish or regret about the past uses past perfect:
I wish I had passed the exam.
Thank you, and I appreciate your effort. But I want to know exactly about this situation: After I took my exam mark and I failed, I said "I wish I passed" it's correct or not?!
I will be so grateful if you clarify it to me.
Hello AboodKh9,
No, you need to use the past perfect as passing the exam was an act in the past:
Let me wrap it up,please.When we don't know about the result of an event so that we could wish for something different, we use 'hope',whether it's in the past ,present or future.Like: I hope you did well on your test.(hope for a past event) I hope you do/will do well on your test.(hope for a present or future event) Did I get it right,Sir?
Hi Sajatadib,
Yes, that's right!
Hello dear teachers,I've got a question concerning "hope".As it's been said in one of the comments,"hope" is used when the action is possible, but are these sentences correct: I hope you will win the game.( hope for the future) I hope you win the game.( hope for the present or future) Many thanks.
Hello Sajatadib,
We generally use the present simple after 'hope' ('I hope you win the game') and so I would recommend that version, but it's OK to use 'will' ('I hope you will win the game').
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
Hello! Could you please explain the difference between usage wish and past perfect and would + present perfect (modals with have) for actions which didn't happen in the past? like: Suppose you hadn't passed your exams. What would you have done? Suppose you wouldn't have passed your exams. What would you have done?
Hi Kristina Karp,
Traditionally, only the first sentence is correct. So, if you are taking an exam (for example), I would recommend using that structure.
However, in modern English usage, it is becoming fairly common to use "would" as in your second sentence. Here's another example: " If you would have called me , I would have helped you." This is usually heard in speaking, especially in informal situations, but there are many people who consider it incorrect too. In any case, the meaning is the same as the first sentence.
It's a bit complicated but I hope that helps!
Hello there, I wanted to know if we could use wish with simple present tense like "I wish I score good mark" and if yes what does it imply or mean by that. Thanks
Hello NobelZ,
To express a wish that we think is possible but we don't know will happen or not, we actually use 'hope' (+ present simple) instead of 'wish': 'I hope I score a good mark'. We can also use this same structure to express good will or intentions to others, e.g. 'I hope you get a good mark on your exam'.
It's also possible to use 'wish' to express good will, but the structure is different. We can say 'I wish you success on your exam' ('wish' + indirect object 'you' + direct object 'success on your exam').
More often, we use 'wish' to speak about a wish that we regard as not possible. That is the grammar explained on this page. If you wished you could get a good mark on an exam but see it as impossible, the most direct way of saying it is probably 'I wish I could get a good mark'.
Good morning! I wanted to know if 'I wish you to be quiet' and 'I wish that you will be quiet' mean the same. Thanks in advance!
Actually, the second sentence should be "I wish (that) you WOULD be quiet" (use "would" with past forms to say your wishes for the future. See the examples on the page above).
Yes, it means the same things as your first sentence, but the first sentence is more formal in style than the second. :)
Jonathan The LearnEnglish Team
Hi Ahmed Imam,
Both are grammatically correct, but I would choose would here. Would refers to the person's willingness. The sentence is asking the person to try a bit harder to hurry.
Could refers to the person's ability. I wish you could hurry means that, for some reason, the person is unable (not just unwilling) to hurry. So, I think the would option would be the more common situation.
Yes, I agree with your colleague. The two options both make sense, but they have slightly different meanings:
- I wish I had been rich, ... - this third conditional structure shows an imagined past situation. In the sentence, 'being rich' refers specifically to the time when I borrowed the money (i.e., 'If I had been rich at that time , ...'). It sounds like the borrowing did not happen recently.
- I wish I were rich, ... - this second conditional structure shows an imagined (i.e. unreal) present situation, i.e. being rich now. We might use this if the borrowing happened recently.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
What to Know A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
As anyone who has worked in a laboratory or out in the field can tell you, science is about process: that of observing, making inferences about those observations, and then performing tests to see if the truth value of those inferences holds up. The scientific method is designed to be a rigorous procedure for acquiring knowledge about the world around us.

In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done. A theory, on the other hand, is supported by evidence: it's a principle formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data.
Toward that end, science employs a particular vocabulary for describing how ideas are proposed, tested, and supported or disproven. And that's where we see the difference between a hypothesis and a theory .
A hypothesis is an assumption, something proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is usually tentative, an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
When a character which has been lost in a breed, reappears after a great number of generations, the most probable hypothesis is, not that the offspring suddenly takes after an ancestor some hundred generations distant, but that in each successive generation there has been a tendency to reproduce the character in question, which at last, under unknown favourable conditions, gains an ascendancy. Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species , 1859 According to one widely reported hypothesis , cell-phone transmissions were disrupting the bees' navigational abilities. (Few experts took the cell-phone conjecture seriously; as one scientist said to me, "If that were the case, Dave Hackenberg's hives would have been dead a long time ago.") Elizabeth Kolbert, The New Yorker , 6 Aug. 2007
What is a Theory?
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, its likelihood as truth is much higher than that of a hypothesis.
It is evident, on our theory , that coasts merely fringed by reefs cannot have subsided to any perceptible amount; and therefore they must, since the growth of their corals, either have remained stationary or have been upheaved. Now, it is remarkable how generally it can be shown, by the presence of upraised organic remains, that the fringed islands have been elevated: and so far, this is indirect evidence in favour of our theory . Charles Darwin, The Voyage of the Beagle , 1839 An example of a fundamental principle in physics, first proposed by Galileo in 1632 and extended by Einstein in 1905, is the following: All observers traveling at constant velocity relative to one another, should witness identical laws of nature. From this principle, Einstein derived his theory of special relativity. Alan Lightman, Harper's , December 2011
Non-Scientific Use
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch (though theory is more common in this regard):
The theory of the teacher with all these immigrant kids was that if you spoke English loudly enough they would eventually understand. E. L. Doctorow, Loon Lake , 1979 Chicago is famous for asking questions for which there can be no boilerplate answers. Example: given the probability that the federal tax code, nondairy creamer, Dennis Rodman and the art of mime all came from outer space, name something else that has extraterrestrial origins and defend your hypothesis . John McCormick, Newsweek , 5 Apr. 1999 In his mind's eye, Miller saw his case suddenly taking form: Richard Bailey had Helen Brach killed because she was threatening to sue him over the horses she had purchased. It was, he realized, only a theory , but it was one he felt certain he could, in time, prove. Full of urgency, a man with a mission now that he had a hypothesis to guide him, he issued new orders to his troops: Find out everything you can about Richard Bailey and his crowd. Howard Blum, Vanity Fair , January 1995
And sometimes one term is used as a genus, or a means for defining the other:
Laplace's popular version of his astronomy, the Système du monde , was famous for introducing what came to be known as the nebular hypothesis , the theory that the solar system was formed by the condensation, through gradual cooling, of the gaseous atmosphere (the nebulae) surrounding the sun. Louis Menand, The Metaphysical Club , 2001 Researchers use this information to support the gateway drug theory — the hypothesis that using one intoxicating substance leads to future use of another. Jordy Byrd, The Pacific Northwest Inlander , 6 May 2015 Fox, the business and economics columnist for Time magazine, tells the story of the professors who enabled those abuses under the banner of the financial theory known as the efficient market hypothesis . Paul Krugman, The New York Times Book Review , 9 Aug. 2009
Incorrect Interpretations of "Theory"
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general use to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
More Differences Explained
- Epidemic vs. Pandemic
- Diagnosis vs. Prognosis
- Treatment vs. Cure
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes

Commonly Confused
'canceled' or 'cancelled', 'virus' vs. 'bacteria', your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, is it 'jail' or 'prison', 'deduction' vs. 'induction' vs. 'abduction', grammar & usage, words commonly mispronounced, more commonly misspelled words, is 'irregardless' a real word, 8 grammar terms you used to know, but forgot, homophones, homographs, and homonyms, great big list of beautiful and useless words, vol. 3, even more words that sound like insults but aren't, 10 lesser-known reduplications, the words of the week - mar. 8.
Understanding a Hypothesis (Definition, Null, and Examples)

You come home exhausted and plop down on the couch. You don’t know why you are feeling so weary. You think about several possible reasons. Is it because you stayed up late last night? Is it because you skipped breakfast? Or is it because you had to take the stairs due to a power outage? Or is it because of all the above reasons?
What you are doing is hypothesizing about why you are feeling tired.
If you enjoy reading detective stories, you would have already come across a hypothesis. A good whodunit mystery confounds the reader with multiple hypotheses about who committed the crime.

- What is a Hypothesis?
The term hypothesis is often used in a scientific context as a possible explanation for an occurrence.
The word originated from ancient Greek and means “putting under” indicating its early association with experimentation.
A hypothesis is:
- An assumption that serves as a starting point for further research
- A supposition made on the basis of insufficient evidence
- A tentative and logical statement that can be tested for its authenticity
- An idea that seeks to explain why a phenomenon takes place
- A prediction about the outcome of a study according to known facts
- A proposal about the possible relationship between two or more variables
A scientist testing a hypothesis is no different from a detective investigating a crime scene. Famous detectives such as Sherlock Holmes combine the evidence with their powers of prediction to identify the criminal from several potential suspects.
The scientist examines each hypothesis rigorously for any inconsistencies through experiments before it can receive the stamp of approval.
Scientists accept a hypothesis as a theory only after it has been validated several times in different conditions. This includes use of scientific methods and protocols involving observation and analysis of results.
A good hypothesis seeks to establish a causal relationship between two or more variables, primarily between the independent and the dependent variable.
Brushing your teeth at least twice in a day reduces the incidence of dental caries.
The independent variable or cause in the above example is the number of times you brush in a day. The dependent variable or effect is the incidence of dental caries or cavities.
A scientist or researcher tests a hypothesis by changing the independent variable and measuring its effect on the dependent variable.
A relationship between a single independent and dependent variable is known as a simple hypothesis.
The mathematical expression of this relationship is:
- where x is the independent variable and Y is the dependent variable and
- where x is the input and Y is the output or a function of x
So, brushing your teeth at least twice daily is an input and the reduction of dental caries is an output or a function of the action of brushing your teeth.
If there are multiple independent variables or in some cases more than a single dependent variable, the statement is a complex hypothesis.
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and using dental floss reduces the incidence of cavities and periodontitis.
In the above example the two independent variables are brushing teeth and using dental floss. The dependent variables are reduction in cavities and periodontitis or gum infection. In this example the two independent variables are common for the two dependent variables.
The equation of a complex hypothesis can be written as:
Y = f(x 1 +x 2 +x 3 …)
Y 1 = f(z 1 +z 2 +z 3 …)
where z is a different set of independent variables for Y1 as the dependent variable
- Developing a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a frame of reference or a window through which you observe a phenomenon. The phenomenon is the dependent variable. Your job is to determine the independent variables that are causing the event.
Cultivate the habit of looking for patterns in anything that happens. Train your mind to think in terms of stimulus and reaction or cause and effect.
This will enable you to glean insights from the knowledge you gather. You will then be able to write a strong hypothesis that focuses on the variables that matter over the noise.
The six steps to developing a hypothesis are:
- Ask a question
- Preliminary research
- Formulate the hypothesis
- Refine the hypothesis
- Phrase your hypothesis in three ways
- Write a null hypothesis
Ask a Question
The first step is to write a research question.
To write an effective research question be as curious as possible. Start with asking yourself a ton of questions.
Begin with broad and open-ended questions before narrowing it down to more specific ones.
You can use the 5W1H method to get into the mode of writing a research question.
- What took place?
- When did it happen?
- Where did it occur?
- Why did it take place?
- Who did it affect ?
- How did it happen?
The research question needs to be clear, objective , well-defined and measurable.
Do people who take health supplements log in fewer sick days at work in a year than those who don’t?
After you have framed the right question you can make an educated guess to answer it. This answer will be your preliminary hypothesis. Your hypothesis will attempt to answer the research question with observable facts through various experiments.
Preliminary Research
You don’t have to start from scratch. You can draw from preexisting knowledge and well-established theories to discount fallacious premises at the outset.
Resources that you can refer to include case studies, research papers and theses published in academic or scientific journals. A thorough background research will help you to look at the research question from several angles.
Do keep an open mind or a blank slate to avoid falling in the trap of preconceived notions and prejudices. Your initial research should help you focus on the areas where you are most likely to find the answers.
You can come up with a blueprint or outline highlighting the variables that you think are most relevant to your research question.
Think how changing the attributes of a single variable potentially affects others. You may need to operationalize or define how you are going to measure the variables and their effects.
Formulate the Hypothesis
It’s time now to put together your hypothesis into words.
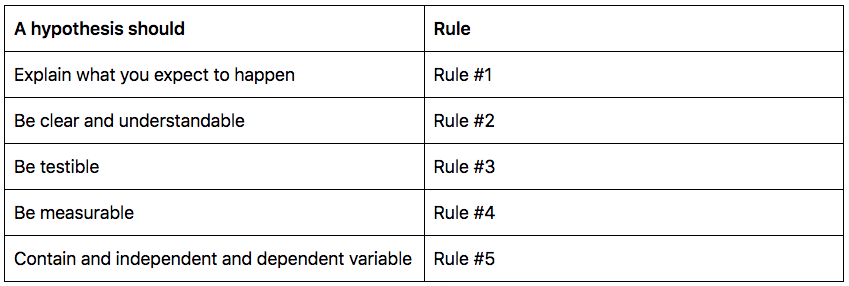
A sound hypothesis states:
- Who or what is being studied?
- The relationship between the variables
- A measurable and reproducible outcome
- The possibility to prove it as true or false
Teenagers in the 14-16 age group who eat a high-protein diet are taller by two inches than the average height for that age group.
The next step is to ensure your statement ticks all the boxes for a strong hypothesis.
Is the hypothesis:
- Precise and quantifiable without any ambiguity
- Lucid and focused on the results described in the research question
Does the hypothesis include:
- An independent and dependent variable
- Variables that can be changed or controlled
- Terms that even a layman can understand
- A well-defined outcome
Phrase your Hypothesis in Three Ways
A hypothesis is often written in an If-then format. This format describes the cause and effect relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable.
Phrase your hypothesis as “If {you make changes to an independent variable} then {you will observe this change in the dependent variable}.”
If employees are given more autonomy to take work-related decisions then their overall performance improves.
Another way to write a hypothesis is by directly stating the outcome between the two variables.
More autonomy in terms of taking work-related decisions helps to improve an employee’s overall performance.
You can also state a hypothesis as a comparison between two groups.
Employees who are offered more autonomy to take work-related decisions show better overall performance than those who work in a micro-managed environment.
Write a Null Hypothesis
The next step is to frame a null hypothesis, especially if your study requires you to analyze the data statistically. A null hypothesis by default takes a converse position to the researcher’s hypothesis.
Your statement is known as the alternative hypothesis while its opposite outcome is referred to as the null hypothesis.
If you expect a change according to a relationship between the variables the null hypothesis denies the possibility of any change or association between the variables. If you expect the conditions to remain constant the null hypothesis states that change will take place.
The null hypothesis is referred to as H 0. Your hypothesis which is the alternative is written as H 1 or H a .
H 1 : A player who is more than two meters tall has a better chance of winning the National Basketball Association Most Valuable Player Award.
H 0 : The height of a player does not affect his prospects of winning the National Basketball Association Most Valuable Player Award.
Hypothesis Examples
Examples of research questions.
- Which loop diuretic drug is more effective for treating heart failure?
- Does attending online learning sessions help students to improve their exam scores?
- Does talking on the phone while driving cause more accidents?
- Does increasing the pressure affect the rate of reaction between gases?
- Is a person more likely to be obese if she or he eats unhealthy foods at least four times in a week?
Examples of a Hypothesis
- The clinical trial of the new drug Furosemide proved that it is better at treating heart failure than other loop diuretic drugs such as Bumetanide.
- The students who attended online learning sessions had better exam scores than those who skipped the sessions.
- Drivers who talk on the phone are likely to have an accident than those who don’t.
- Increasing the pressure affects the concentration of gases and it acts as a catalyst in speeding up the rate of reaction.
- People who eat processed foods frequently are more likely to be obese than people who limit their intake of such foods.
Examples of a Null Hypothesis
- The clinical trial proved that there is no difference between the effectiveness of Furosemide and other loop diuretic drugs, such as Bumetanide, for treating heart failure.
- There is no difference in the exam scores of students who attended online learning sessions and those who did not attend.
- There is no difference in the rate of accidents experienced by drivers who talk on the phone compared with those who don’t talk on the phone while driving.
- The elevation of pressure has no effect on the rate of reaction between gases.
- The food consumed and its frequency of consumption do not affect the probability of a person becoming obese.
What are Null Hypotheses?
The null hypothesis states the opposite outcome to the researcher’s hypothesis.
In most cases, the null hypothesis’s default position is a prediction that no relationship exists between any two or more variables. The null hypothesis denies the possibility of a causal relationship existing between an assumed independent and dependent variable.
The symbol of the null hypothesis is H 0 .
The notion of a null hypothesis fulfills the requirement of the falsifiability of a hypothesis before it can be accepted as valid.
A null hypothesis is often written as a negative statement that posits that the original hypothesis is false. It either claims that the results obtained are due to chance or there is no evidence to prove any change.
Original Hypothesis: Use of nitrogen fertilizers helps plants grow faster as compared to use of phosphorus or potassium fertilizers.
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The fertilizer used has no bearing on the rate of plant growth
What are Alternative Hypotheses?
An alternative hypothesis states the researcher’s supposition of a causal relationship between any two or more variables. Alternative hypotheses are based upon an observable effect and seek to predict how changing an independent variable will affect the dependent variable.
An alternative hypothesis is symbolized as H 1 or H a . It’s often written together with a null hypothesis with the two statements existing as a dual pair of opposite assumptions. Only a single statement among two can be true.
Alternative hypotheses try to determine that the results are obtained due to significant changes related to the variables and not due to chance.
Research Question: Does washing hands thoroughly with soap before eating a meal reduce the rate of recurrence of respiratory ailments?
Alternative Hypothesis (H 1 ): Washing hands with soap before eating reduces the rate of recurrence of respiratory ailments by 30% compared with those who neglect hand hygiene.
Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): Washing hands with soap before eating has no effect on the rate of recurrence of respiratory ailments.
What is Hypothesis Testing?
After you have formulated a hypothesis, you need to choose a research and testing method.
Use a descriptive approach when experiments are difficult to conduct. A descriptive method incorporates case studies and surveys to collect data.
You can employ statistical tools such as a correlational study to measure the relationship between variables.
A correlational study calculates the probability of whether a linkage between two variables can be determined or do the changes occur purely due to chance. Do note that correlation is not equivalent to causality.
This method lets you arrive at a conclusion by generalizing the data obtained without performing any actual experiments. A hypothesis proved using this approach is known as a statistical hypothesis.
The other approach is the experimental method in which causal relationships are established between different variables through demonstrations. A working or empirical hypothesis often makes use of the experimental method to determine the relationships between the variables.
The steps for testing a hypothesis experimentally are:
- Design of experiments
- Collating data
- Analysis of observable facts
- Summarizing the conclusions
- Validating the hypothesis as a theory
How to Write a Good Hypothesis
To find ideas for a hypothesis, you can look through discussion sections in academic and scientific journals or browse online publications. You will come across questions that can be investigated further.
Simple Steps
The steps to write a strong hypothesis are:
- Choose your frame of reference or direction for determining the cause
- Such an approach is known as a directional hypothesis
- If you are unable to determine a starting point or the current theories are ambiguous and contradictory, you can choose a non-directional approach
- This method involves stating the facts and observations randomly and then seeking to find a pattern
- Identify the key variables
- A variable is any attribute that can have measurable values such as temperature, time, or length
- Tentatively label some variables as independent and some as dependent
- State the relationship between the variables using clear and objective language
- Operationalize or define how you will measure the variables for testability
- Write the statement in the If-then format. You can also write it as a declarative sentence
- Avoid jargon and use simple words that can be understood by a layman
- Write a null hypothesis to satisfy the condition of falsifiability
If you watch television for more than three hours a day, then your ability to concentrate diminishes.
How to Write a Scientific Hypothesis
A good scientific hypothesis is:
- Consistent: Use preexisting knowledge as a springboard for further research
- Testable: Include words that are quantifiable or measurable
- Concise: Cut down on verbose phrases and use precise words
- Scalable: Formulate the statement in a universal context based on the variables
- Promising: State unexplained occurrences as loose ends that can be investigated further
Simple steps
- Record your observations and facts about the topic
- Evaluate your statements for possible links to determine the cause and effect
- Document all potential explanations to analyze further
- Write the null hypothesis along with your own hypothesis
- This satisfies the requisite condition for a valid hypothesis. It can either be confirmed or disproved
If you plant cotton in black soil, then the production is boosted by 20% as compared to the output from red soil.
How to write a Psychology Hypothesis
A psychology hypothesis often begins with how the environment or certain parameters within it influence or cause a specific behavior.
To write a sound psychology hypothesis:
- Choose a topic that you are genuinely interested in
- Do not ramble. Keep it short and simple
- Use previous research and your own study to direct your vision
- Ascertain and define the variables
- You can write the hypothesis either as an If-then statement
- Other alternatives are to write the hypothesis as a direct sentence or a comparative supposition
Use the following questions to guide your understanding of the topic.
- Is your hypothesis based on a preexisting theory or your own research?
- Can your hypothesis be tested for falsifiability?
- What are the independent and dependent variables?
People who exercise regularly are less at risk from depression than people who lead a sedentary life.
- What is and How to Write a Good Hypothesis in Research?
- How to Write a Hypothesis in 6 Steps
- Developing Hypothesis and Research Questions
- Forming a Good Hypothesis for Scientific Research
- 6 Hypothesis Examples in Psychology
- Correlational Research | When & How to Use
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis in 6 Simple Steps
- How to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
- How To Develop a Hypothesis (With Elements, Types and Examples)
- Definition of Hypothesis
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

Definition of 'hypothesis'

Video: pronunciation of hypothesis

hypothesis in American English
Hypothesis in british english, examples of 'hypothesis' in a sentence hypothesis, related word partners hypothesis, trends of hypothesis.
View usage over: Since Exist Last 10 years Last 50 years Last 100 years Last 300 years
In other languages hypothesis
- American English : hypothesis / haɪˈpɒθɪsɪs /
- Brazilian Portuguese : hipótese
- Chinese : 假设
- European Spanish : hipótesis
- French : hypothèse
- German : Hypothese
- Italian : ipotesi
- Japanese : 仮説
- Korean : 가설
- European Portuguese : hipótese
- Spanish : hipótesis
- Thai : สมมุติฐาน
Browse alphabetically hypothesis
- hypothermia
- hypothermic
- hypothesis states
- hypothesis suggests
- hypothesis testing
- All ENGLISH words that begin with 'H'

Related terms of hypothesis
- Gaia hypothesis
- null hypothesis
- initial hypothesis
- View more related words
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5
Wordle Helper

Scrabble Tools

- Professional development
- Knowing the subject
- Teaching Knowledge database D-H
Hypotheses are possible ideas about language rules that learners form as they receive information.

Learners test their hypotheses by using language and these ideas change as new information is received.
Example A learner has noticed that English often uses the suffix -ness to form a noun from an adjective and so develops a hypothesis that this is a rule. The teacher gives them more information and the learner adjusts the hypothesis accordingly.
In the classroom Learners often make systematic errors as they test hypotheses. For example, overuse of the past -ed may be due to an incorrect hypothesis about past forms in English. Teachers can find out a lot about learners' current understanding of the new language from noticing the errors learners make.
Further links:
https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/integrating-pronunciation-classroom-activities
https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/theories-reading
https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/article/presenting-new-language
Research and insight
Browse fascinating case studies, research papers, publications and books by researchers and ELT experts from around the world.
See our publications, research and insight

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, what is a hypothesis and how do i write one.
General Education

Think about something strange and unexplainable in your life. Maybe you get a headache right before it rains, or maybe you think your favorite sports team wins when you wear a certain color. If you wanted to see whether these are just coincidences or scientific fact, you would form a hypothesis, then create an experiment to see whether that hypothesis is true or not.
But what is a hypothesis, anyway? If you’re not sure about what a hypothesis is--or how to test for one!--you’re in the right place. This article will teach you everything you need to know about hypotheses, including:
- Defining the term “hypothesis”
- Providing hypothesis examples
- Giving you tips for how to write your own hypothesis
So let’s get started!

What Is a Hypothesis?
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as “an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.” In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess . Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it’s true or not. Keep in mind that in science, a hypothesis should be testable. You have to be able to design an experiment that tests your hypothesis in order for it to be valid.
As you could assume from that statement, it’s easy to make a bad hypothesis. But when you’re holding an experiment, it’s even more important that your guesses be good...after all, you’re spending time (and maybe money!) to figure out more about your observation. That’s why we refer to a hypothesis as an educated guess--good hypotheses are based on existing data and research to make them as sound as possible.
Hypotheses are one part of what’s called the scientific method . Every (good) experiment or study is based in the scientific method. The scientific method gives order and structure to experiments and ensures that interference from scientists or outside influences does not skew the results. It’s important that you understand the concepts of the scientific method before holding your own experiment. Though it may vary among scientists, the scientific method is generally made up of six steps (in order):
- Observation
- Asking questions
- Forming a hypothesis
- Analyze the data
- Communicate your results
You’ll notice that the hypothesis comes pretty early on when conducting an experiment. That’s because experiments work best when they’re trying to answer one specific question. And you can’t conduct an experiment until you know what you’re trying to prove!
Independent and Dependent Variables
After doing your research, you’re ready for another important step in forming your hypothesis: identifying variables. Variables are basically any factor that could influence the outcome of your experiment . Variables have to be measurable and related to the topic being studied.
There are two types of variables: independent variables and dependent variables. I ndependent variables remain constant . For example, age is an independent variable; it will stay the same, and researchers can look at different ages to see if it has an effect on the dependent variable.
Speaking of dependent variables... dependent variables are subject to the influence of the independent variable , meaning that they are not constant. Let’s say you want to test whether a person’s age affects how much sleep they need. In that case, the independent variable is age (like we mentioned above), and the dependent variable is how much sleep a person gets.
Variables will be crucial in writing your hypothesis. You need to be able to identify which variable is which, as both the independent and dependent variables will be written into your hypothesis. For instance, in a study about exercise, the independent variable might be the speed at which the respondents walk for thirty minutes, and the dependent variable would be their heart rate. In your study and in your hypothesis, you’re trying to understand the relationship between the two variables.
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
The best hypotheses start by asking the right questions . For instance, if you’ve observed that the grass is greener when it rains twice a week, you could ask what kind of grass it is, what elevation it’s at, and if the grass across the street responds to rain in the same way. Any of these questions could become the backbone of experiments to test why the grass gets greener when it rains fairly frequently.
As you’re asking more questions about your first observation, make sure you’re also making more observations . If it doesn’t rain for two weeks and the grass still looks green, that’s an important observation that could influence your hypothesis. You'll continue observing all throughout your experiment, but until the hypothesis is finalized, every observation should be noted.
Finally, you should consult secondary research before writing your hypothesis . Secondary research is comprised of results found and published by other people. You can usually find this information online or at your library. Additionally, m ake sure the research you find is credible and related to your topic. If you’re studying the correlation between rain and grass growth, it would help you to research rain patterns over the past twenty years for your county, published by a local agricultural association. You should also research the types of grass common in your area, the type of grass in your lawn, and whether anyone else has conducted experiments about your hypothesis. Also be sure you’re checking the quality of your research . Research done by a middle school student about what minerals can be found in rainwater would be less useful than an article published by a local university.

Writing Your Hypothesis
Once you’ve considered all of the factors above, you’re ready to start writing your hypothesis. Hypotheses usually take a certain form when they’re written out in a research report.
When you boil down your hypothesis statement, you are writing down your best guess and not the question at hand . This means that your statement should be written as if it is fact already, even though you are simply testing it.
The reason for this is that, after you have completed your study, you'll either accept or reject your if-then or your null hypothesis. All hypothesis testing examples should be measurable and able to be confirmed or denied. You cannot confirm a question, only a statement!
In fact, you come up with hypothesis examples all the time! For instance, when you guess on the outcome of a basketball game, you don’t say, “Will the Miami Heat beat the Boston Celtics?” but instead, “I think the Miami Heat will beat the Boston Celtics.” You state it as if it is already true, even if it turns out you’re wrong. You do the same thing when writing your hypothesis.
Additionally, keep in mind that hypotheses can range from very specific to very broad. These hypotheses can be specific, but if your hypothesis testing examples involve a broad range of causes and effects, your hypothesis can also be broad.

The Two Types of Hypotheses
Now that you understand what goes into a hypothesis, it’s time to look more closely at the two most common types of hypothesis: the if-then hypothesis and the null hypothesis.
#1: If-Then Hypotheses
First of all, if-then hypotheses typically follow this formula:
If ____ happens, then ____ will happen.
The goal of this type of hypothesis is to test the causal relationship between the independent and dependent variable. It’s fairly simple, and each hypothesis can vary in how detailed it can be. We create if-then hypotheses all the time with our daily predictions. Here are some examples of hypotheses that use an if-then structure from daily life:
- If I get enough sleep, I’ll be able to get more work done tomorrow.
- If the bus is on time, I can make it to my friend’s birthday party.
- If I study every night this week, I’ll get a better grade on my exam.
In each of these situations, you’re making a guess on how an independent variable (sleep, time, or studying) will affect a dependent variable (the amount of work you can do, making it to a party on time, or getting better grades).
You may still be asking, “What is an example of a hypothesis used in scientific research?” Take one of the hypothesis examples from a real-world study on whether using technology before bed affects children’s sleep patterns. The hypothesis read s:
“We hypothesized that increased hours of tablet- and phone-based screen time at bedtime would be inversely correlated with sleep quality and child attention.”
It might not look like it, but this is an if-then statement. The researchers basically said, “If children have more screen usage at bedtime, then their quality of sleep and attention will be worse.” The sleep quality and attention are the dependent variables and the screen usage is the independent variable. (Usually, the independent variable comes after the “if” and the dependent variable comes after the “then,” as it is the independent variable that affects the dependent variable.) This is an excellent example of how flexible hypothesis statements can be, as long as the general idea of “if-then” and the independent and dependent variables are present.
#2: Null Hypotheses
Your if-then hypothesis is not the only one needed to complete a successful experiment, however. You also need a null hypothesis to test it against. In its most basic form, the null hypothesis is the opposite of your if-then hypothesis . When you write your null hypothesis, you are writing a hypothesis that suggests that your guess is not true, and that the independent and dependent variables have no relationship .
One null hypothesis for the cell phone and sleep study from the last section might say:
“If children have more screen usage at bedtime, their quality of sleep and attention will not be worse.”
In this case, this is a null hypothesis because it’s asking the opposite of the original thesis!
Conversely, if your if-then hypothesis suggests that your two variables have no relationship, then your null hypothesis would suggest that there is one. So, pretend that there is a study that is asking the question, “Does the amount of followers on Instagram influence how long people spend on the app?” The independent variable is the amount of followers, and the dependent variable is the time spent. But if you, as the researcher, don’t think there is a relationship between the number of followers and time spent, you might write an if-then hypothesis that reads:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will not spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
In this case, the if-then suggests there isn’t a relationship between the variables. In that case, one of the null hypothesis examples might say:
“If people have many followers on Instagram, they will spend more time on the app than people who have less.”
You then test both the if-then and the null hypothesis to gauge if there is a relationship between the variables, and if so, how much of a relationship.

4 Tips to Write the Best Hypothesis
If you’re going to take the time to hold an experiment, whether in school or by yourself, you’re also going to want to take the time to make sure your hypothesis is a good one. The best hypotheses have four major elements in common: plausibility, defined concepts, observability, and general explanation.
#1: Plausibility
At first glance, this quality of a hypothesis might seem obvious. When your hypothesis is plausible, that means it’s possible given what we know about science and general common sense. However, improbable hypotheses are more common than you might think.
Imagine you’re studying weight gain and television watching habits. If you hypothesize that people who watch more than twenty hours of television a week will gain two hundred pounds or more over the course of a year, this might be improbable (though it’s potentially possible). Consequently, c ommon sense can tell us the results of the study before the study even begins.
Improbable hypotheses generally go against science, as well. Take this hypothesis example:
“If a person smokes one cigarette a day, then they will have lungs just as healthy as the average person’s.”
This hypothesis is obviously untrue, as studies have shown again and again that cigarettes negatively affect lung health. You must be careful that your hypotheses do not reflect your own personal opinion more than they do scientifically-supported findings. This plausibility points to the necessity of research before the hypothesis is written to make sure that your hypothesis has not already been disproven.
#2: Defined Concepts
The more advanced you are in your studies, the more likely that the terms you’re using in your hypothesis are specific to a limited set of knowledge. One of the hypothesis testing examples might include the readability of printed text in newspapers, where you might use words like “kerning” and “x-height.” Unless your readers have a background in graphic design, it’s likely that they won’t know what you mean by these terms. Thus, it’s important to either write what they mean in the hypothesis itself or in the report before the hypothesis.
Here’s what we mean. Which of the following sentences makes more sense to the common person?
If the kerning is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
If the space between letters is greater than average, more words will be read per minute.
For people reading your report that are not experts in typography, simply adding a few more words will be helpful in clarifying exactly what the experiment is all about. It’s always a good idea to make your research and findings as accessible as possible.

Good hypotheses ensure that you can observe the results.
#3: Observability
In order to measure the truth or falsity of your hypothesis, you must be able to see your variables and the way they interact. For instance, if your hypothesis is that the flight patterns of satellites affect the strength of certain television signals, yet you don’t have a telescope to view the satellites or a television to monitor the signal strength, you cannot properly observe your hypothesis and thus cannot continue your study.
Some variables may seem easy to observe, but if you do not have a system of measurement in place, you cannot observe your hypothesis properly. Here’s an example: if you’re experimenting on the effect of healthy food on overall happiness, but you don’t have a way to monitor and measure what “overall happiness” means, your results will not reflect the truth. Monitoring how often someone smiles for a whole day is not reasonably observable, but having the participants state how happy they feel on a scale of one to ten is more observable.
In writing your hypothesis, always keep in mind how you'll execute the experiment.
#4: Generalizability
Perhaps you’d like to study what color your best friend wears the most often by observing and documenting the colors she wears each day of the week. This might be fun information for her and you to know, but beyond you two, there aren’t many people who could benefit from this experiment. When you start an experiment, you should note how generalizable your findings may be if they are confirmed. Generalizability is basically how common a particular phenomenon is to other people’s everyday life.
Let’s say you’re asking a question about the health benefits of eating an apple for one day only, you need to realize that the experiment may be too specific to be helpful. It does not help to explain a phenomenon that many people experience. If you find yourself with too specific of a hypothesis, go back to asking the big question: what is it that you want to know, and what do you think will happen between your two variables?

Hypothesis Testing Examples
We know it can be hard to write a good hypothesis unless you’ve seen some good hypothesis examples. We’ve included four hypothesis examples based on some made-up experiments. Use these as templates or launch pads for coming up with your own hypotheses.
Experiment #1: Students Studying Outside (Writing a Hypothesis)
You are a student at PrepScholar University. When you walk around campus, you notice that, when the temperature is above 60 degrees, more students study in the quad. You want to know when your fellow students are more likely to study outside. With this information, how do you make the best hypothesis possible?
You must remember to make additional observations and do secondary research before writing your hypothesis. In doing so, you notice that no one studies outside when it’s 75 degrees and raining, so this should be included in your experiment. Also, studies done on the topic beforehand suggested that students are more likely to study in temperatures less than 85 degrees. With this in mind, you feel confident that you can identify your variables and write your hypotheses:
If-then: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, significantly fewer students will study outside.”
Null: “If the temperature in Fahrenheit is less than 60 degrees, the same number of students will study outside as when it is more than 60 degrees.”
These hypotheses are plausible, as the temperatures are reasonably within the bounds of what is possible. The number of people in the quad is also easily observable. It is also not a phenomenon specific to only one person or at one time, but instead can explain a phenomenon for a broader group of people.
To complete this experiment, you pick the month of October to observe the quad. Every day (except on the days where it’s raining)from 3 to 4 PM, when most classes have released for the day, you observe how many people are on the quad. You measure how many people come and how many leave. You also write down the temperature on the hour.
After writing down all of your observations and putting them on a graph, you find that the most students study on the quad when it is 70 degrees outside, and that the number of students drops a lot once the temperature reaches 60 degrees or below. In this case, your research report would state that you accept or “failed to reject” your first hypothesis with your findings.
Experiment #2: The Cupcake Store (Forming a Simple Experiment)
Let’s say that you work at a bakery. You specialize in cupcakes, and you make only two colors of frosting: yellow and purple. You want to know what kind of customers are more likely to buy what kind of cupcake, so you set up an experiment. Your independent variable is the customer’s gender, and the dependent variable is the color of the frosting. What is an example of a hypothesis that might answer the question of this study?
Here’s what your hypotheses might look like:
If-then: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will buy more yellow cupcakes than purple cupcakes.”
Null: “If customers’ gender is female, then they will be just as likely to buy purple cupcakes as yellow cupcakes.”
This is a pretty simple experiment! It passes the test of plausibility (there could easily be a difference), defined concepts (there’s nothing complicated about cupcakes!), observability (both color and gender can be easily observed), and general explanation ( this would potentially help you make better business decisions ).

Experiment #3: Backyard Bird Feeders (Integrating Multiple Variables and Rejecting the If-Then Hypothesis)
While watching your backyard bird feeder, you realized that different birds come on the days when you change the types of seeds. You decide that you want to see more cardinals in your backyard, so you decide to see what type of food they like the best and set up an experiment.
However, one morning, you notice that, while some cardinals are present, blue jays are eating out of your backyard feeder filled with millet. You decide that, of all of the other birds, you would like to see the blue jays the least. This means you'll have more than one variable in your hypothesis. Your new hypotheses might look like this:
If-then: “If sunflower seeds are placed in the bird feeders, then more cardinals will come than blue jays. If millet is placed in the bird feeders, then more blue jays will come than cardinals.”
Null: “If either sunflower seeds or millet are placed in the bird, equal numbers of cardinals and blue jays will come.”
Through simple observation, you actually find that cardinals come as often as blue jays when sunflower seeds or millet is in the bird feeder. In this case, you would reject your “if-then” hypothesis and “fail to reject” your null hypothesis . You cannot accept your first hypothesis, because it’s clearly not true. Instead you found that there was actually no relation between your different variables. Consequently, you would need to run more experiments with different variables to see if the new variables impact the results.
Experiment #4: In-Class Survey (Including an Alternative Hypothesis)
You’re about to give a speech in one of your classes about the importance of paying attention. You want to take this opportunity to test a hypothesis you’ve had for a while:
If-then: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will listen better than students who do not.
Null: If students sit in the first two rows of the classroom, then they will not listen better or worse than students who do not.
You give your speech and then ask your teacher if you can hand out a short survey to the class. On the survey, you’ve included questions about some of the topics you talked about. When you get back the results, you’re surprised to see that not only do the students in the first two rows not pay better attention, but they also scored worse than students in other parts of the classroom! Here, both your if-then and your null hypotheses are not representative of your findings. What do you do?
This is when you reject both your if-then and null hypotheses and instead create an alternative hypothesis . This type of hypothesis is used in the rare circumstance that neither of your hypotheses is able to capture your findings . Now you can use what you’ve learned to draft new hypotheses and test again!
Key Takeaways: Hypothesis Writing
The more comfortable you become with writing hypotheses, the better they will become. The structure of hypotheses is flexible and may need to be changed depending on what topic you are studying. The most important thing to remember is the purpose of your hypothesis and the difference between the if-then and the null . From there, in forming your hypothesis, you should constantly be asking questions, making observations, doing secondary research, and considering your variables. After you have written your hypothesis, be sure to edit it so that it is plausible, clearly defined, observable, and helpful in explaining a general phenomenon.
Writing a hypothesis is something that everyone, from elementary school children competing in a science fair to professional scientists in a lab, needs to know how to do. Hypotheses are vital in experiments and in properly executing the scientific method . When done correctly, hypotheses will set up your studies for success and help you to understand the world a little better, one experiment at a time.

What’s Next?
If you’re studying for the science portion of the ACT, there’s definitely a lot you need to know. We’ve got the tools to help, though! Start by checking out our ultimate study guide for the ACT Science subject test. Once you read through that, be sure to download our recommended ACT Science practice tests , since they’re one of the most foolproof ways to improve your score. (And don’t forget to check out our expert guide book , too.)
If you love science and want to major in a scientific field, you should start preparing in high school . Here are the science classes you should take to set yourself up for success.
If you’re trying to think of science experiments you can do for class (or for a science fair!), here’s a list of 37 awesome science experiments you can do at home
Need more help with this topic? Check out Tutorbase!
Our vetted tutor database includes a range of experienced educators who can help you polish an essay for English or explain how derivatives work for Calculus. You can use dozens of filters and search criteria to find the perfect person for your needs.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Definition of hypothesis – Learner’s Dictionary
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
(Definition of hypothesis from the Cambridge Learner's Dictionary © Cambridge University Press)
Translations of hypothesis
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
someone's way of living; the things that a person or particular group of people usually do

Forget doing it or forget to do it? Avoiding common mistakes with verb patterns (2)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- Learner’s Dictionary Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add hypothesis to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of hypothesize verb from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary
hypothesize
Join our community to access the latest language learning and assessment tips from Oxford University Press!
Nearby words
What Is a Hypothesis? (Science)
If...,Then...
Angela Lumsden/Getty Images
- Scientific Method
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject.
In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
In the study of logic, a hypothesis is an if-then proposition, typically written in the form, "If X , then Y ."
In common usage, a hypothesis is simply a proposed explanation or prediction, which may or may not be tested.
Writing a Hypothesis
Most scientific hypotheses are proposed in the if-then format because it's easy to design an experiment to see whether or not a cause and effect relationship exists between the independent variable and the dependent variable . The hypothesis is written as a prediction of the outcome of the experiment.
- Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
Statistically, it's easier to show there is no relationship between two variables than to support their connection. So, scientists often propose the null hypothesis . The null hypothesis assumes changing the independent variable will have no effect on the dependent variable.
In contrast, the alternative hypothesis suggests changing the independent variable will have an effect on the dependent variable. Designing an experiment to test this hypothesis can be trickier because there are many ways to state an alternative hypothesis.
For example, consider a possible relationship between getting a good night's sleep and getting good grades. The null hypothesis might be stated: "The number of hours of sleep students get is unrelated to their grades" or "There is no correlation between hours of sleep and grades."
An experiment to test this hypothesis might involve collecting data, recording average hours of sleep for each student and grades. If a student who gets eight hours of sleep generally does better than students who get four hours of sleep or 10 hours of sleep, the hypothesis might be rejected.
But the alternative hypothesis is harder to propose and test. The most general statement would be: "The amount of sleep students get affects their grades." The hypothesis might also be stated as "If you get more sleep, your grades will improve" or "Students who get nine hours of sleep have better grades than those who get more or less sleep."
In an experiment, you can collect the same data, but the statistical analysis is less likely to give you a high confidence limit.
Usually, a scientist starts out with the null hypothesis. From there, it may be possible to propose and test an alternative hypothesis, to narrow down the relationship between the variables.
Example of a Hypothesis
Examples of a hypothesis include:
- If you drop a rock and a feather, (then) they will fall at the same rate.
- Plants need sunlight in order to live. (if sunlight, then life)
- Eating sugar gives you energy. (if sugar, then energy)
- White, Jay D. Research in Public Administration . Conn., 1998.
- Schick, Theodore, and Lewis Vaughn. How to Think about Weird Things: Critical Thinking for a New Age . McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2002.
- Null Hypothesis Definition and Examples
- Definition of a Hypothesis
- What Are the Elements of a Good Hypothesis?
- Six Steps of the Scientific Method
- What Are Examples of a Hypothesis?
- Understanding Simple vs Controlled Experiments
- Scientific Method Flow Chart
- Scientific Method Vocabulary Terms
- What Is a Testable Hypothesis?
- Null Hypothesis Examples
- What 'Fail to Reject' Means in a Hypothesis Test
- How To Design a Science Fair Experiment
- What Is an Experiment? Definition and Design
- Hypothesis Test for the Difference of Two Population Proportions
- How to Conduct a Hypothesis Test
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples
Published on November 8, 2019 by Rebecca Bevans . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics . It is most often used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses, that arise from theories.
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o ) and (H a or H 1 ).
- Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test .
- Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
- Present the findings in your results and discussion section.
Though the specific details might vary, the procedure you will use when testing a hypothesis will always follow some version of these steps.
Table of contents
Step 1: state your null and alternate hypothesis, step 2: collect data, step 3: perform a statistical test, step 4: decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis, step 5: present your findings, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about hypothesis testing.
After developing your initial research hypothesis (the prediction that you want to investigate), it is important to restate it as a null (H o ) and alternate (H a ) hypothesis so that you can test it mathematically.
The alternate hypothesis is usually your initial hypothesis that predicts a relationship between variables. The null hypothesis is a prediction of no relationship between the variables you are interested in.
- H 0 : Men are, on average, not taller than women. H a : Men are, on average, taller than women.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
For a statistical test to be valid , it is important to perform sampling and collect data in a way that is designed to test your hypothesis. If your data are not representative, then you cannot make statistical inferences about the population you are interested in.
There are a variety of statistical tests available, but they are all based on the comparison of within-group variance (how spread out the data is within a category) versus between-group variance (how different the categories are from one another).
If the between-group variance is large enough that there is little or no overlap between groups, then your statistical test will reflect that by showing a low p -value . This means it is unlikely that the differences between these groups came about by chance.
Alternatively, if there is high within-group variance and low between-group variance, then your statistical test will reflect that with a high p -value. This means it is likely that any difference you measure between groups is due to chance.
Your choice of statistical test will be based on the type of variables and the level of measurement of your collected data .
- an estimate of the difference in average height between the two groups.
- a p -value showing how likely you are to see this difference if the null hypothesis of no difference is true.
Based on the outcome of your statistical test, you will have to decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
In most cases you will use the p -value generated by your statistical test to guide your decision. And in most cases, your predetermined level of significance for rejecting the null hypothesis will be 0.05 – that is, when there is a less than 5% chance that you would see these results if the null hypothesis were true.
In some cases, researchers choose a more conservative level of significance, such as 0.01 (1%). This minimizes the risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis ( Type I error ).
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The results of hypothesis testing will be presented in the results and discussion sections of your research paper , dissertation or thesis .
In the results section you should give a brief summary of the data and a summary of the results of your statistical test (for example, the estimated difference between group means and associated p -value). In the discussion , you can discuss whether your initial hypothesis was supported by your results or not.
In the formal language of hypothesis testing, we talk about rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis. You will probably be asked to do this in your statistics assignments.
However, when presenting research results in academic papers we rarely talk this way. Instead, we go back to our alternate hypothesis (in this case, the hypothesis that men are on average taller than women) and state whether the result of our test did or did not support the alternate hypothesis.
If your null hypothesis was rejected, this result is interpreted as “supported the alternate hypothesis.”
These are superficial differences; you can see that they mean the same thing.
You might notice that we don’t say that we reject or fail to reject the alternate hypothesis . This is because hypothesis testing is not designed to prove or disprove anything. It is only designed to test whether a pattern we measure could have arisen spuriously, or by chance.
If we reject the null hypothesis based on our research (i.e., we find that it is unlikely that the pattern arose by chance), then we can say our test lends support to our hypothesis . But if the pattern does not pass our decision rule, meaning that it could have arisen by chance, then we say the test is inconsistent with our hypothesis .
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess — it should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations and statistical analysis of data).
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bevans, R. (2023, June 22). Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/hypothesis-testing/
Is this article helpful?
Rebecca Bevans
Other students also liked, choosing the right statistical test | types & examples, understanding p values | definition and examples, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
hypothesis: [noun] an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument. an interpretation of a practical situation or condition taken as the ground for action.
Level: intermediate. Wishes. We use the verb wish or the phrase if only to talk about things which we want but which are not possible:. I wish I could see you next week. If only we could stop for a drink. I wish we had a bigger house. They are always busy. If only they had more time. John was very lazy at school. Now he wishes he had worked harder.. We use wish and if only with past tense forms:
1 [countable] an idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct synonym theory to formulate/confirm a hypothesis a hypothesis about the function of dreams There is little evidence to support these hypotheses. Topic Collocations Scientific Research theory. formulate/advance a theory/hypothesis
4 Alternative hypothesis. An alternative hypothesis, abbreviated as H 1 or H A, is used in conjunction with a null hypothesis. It states the opposite of the null hypothesis, so that one and only one must be true. Examples: Plants grow better with bottled water than tap water. Professional psychics win the lottery more than other people. 5 ...
The hypothesis predicts that children will perform better on task A than on task B. The results confirmed his hypothesis on the use of modal verbs. These observations appear to support our working hypothesis. a speculative hypothesis concerning the nature of matter; an interesting hypothesis about the development of language
A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
3 meanings: 1. a suggested explanation for a group of facts or phenomena, either accepted as a basis for further verification.... Click for more definitions.
Hypothesis definition: . See examples of HYPOTHESIS used in a sentence.
hypothesis definition: 1. an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved…. Learn more.
Developing a hypothesis (with example) Step 1. Ask a question. Writing a hypothesis begins with a research question that you want to answer. The question should be focused, specific, and researchable within the constraints of your project. Example: Research question.
HYPOTHESIS definition: a suggested explanation for something that has not yet been proved to be true. Learn more.
A tentative and logical statement that can be tested for its authenticity. An idea that seeks to explain why a phenomenon takes place. A prediction about the outcome of a study according to known facts. A proposal about the possible relationship between two or more variables.
a suggested explanation for a group of facts or phenomena, either accepted as a basis for further verification ( working hypothesis) or accepted as likely to be true. Compare theory (sense 5) 2. an assumption used in an argument without its being endorsed; a supposition. 3. an unproved theory; a conjecture. Collins English Dictionary.
Hypotheses are possible ideas about language rules that learners form as they receive information. Learners test their hypotheses by using language and these ideas change as new information is received. A learner has noticed that English often uses the suffix -ness to form a noun from an adjective and so develops a hypothesis that this is a rule.
Merriam Webster defines a hypothesis as "an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument.". In other words, a hypothesis is an educated guess. Scientists make a reasonable assumption--or a hypothesis--then design an experiment to test whether it's true or not.
The conceptual peg hypothesis provides a theoretical explanation of the difference. I think it's important to note that what I'm proposing here is a hypothesis rather than a conclusion. The scientific method involves proposing a hypothesis then trying to disprove it.
Here are some examples of some hypothetical situations using a wide variety of forms. They would invest in R & D if they had the capital. - Conditional Form. If only we had enough time to take a vacation. - Partial conditional form / set phrase 'if only'. It's time we improved our sales. - Set phrase 'it's time'.
HYPOTHESIS meaning: a suggested explanation for something that has not yet been proved to be true. Learn more.
Definition of hypothesize verb in Oxford Advanced American Dictionary. Meaning, pronunciation, picture, example sentences, grammar, usage notes, synonyms and more.
Hypothesis definition, a proposition, or set of propositions, set forth as an explanation for the occurrence of some specified group of phenomena, either asserted merely as a provisional conjecture to guide investigation (working hypothesis ) or accepted as highly probable in the light of established facts. See more.
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for an observation. The definition depends on the subject. In science, a hypothesis is part of the scientific method. It is a prediction or explanation that is tested by an experiment. Observations and experiments may disprove a scientific hypothesis, but can never entirely prove one.
In planning a course of action, one may consider various alternatives, working out each in detail.Although the word hypothesis is not typically used in this case, the procedure is virtually the same as that of an investigator of crime considering various suspects. Different methods may be used for deciding what the various alternatives may be, but what is fundamental is the consideration of a ...
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world. ... Eliminate grammar errors and improve your writing with our free AI-powered grammar checker. Try for free ... Stating results in a statistics assignment In our comparison of mean height between men and women we found an average difference of 13.7 cm and a p ...